Прошедшее длительное время (Past Progressive Tense) образуется при помощи вспомогательного глагола to be в форме прошедшего времени (was, were) и причастия настоящего времени смыслового глагола (Present Participle):
I was work ing. Я работал.
They were work ing. Они работали.
Таблица форм Past Progressive Tense на примере глагола to work «работать»
| Утверждение
| Вопрос
| Отрицание
|
| I was working.
Я работал.
| WasI working?
Я работал?
| I was not working.
Я не работал.
|
| He (she, it) was working.
Он (она, оно) работал.
| Was he (she, it) working?
Он (она, оно) работал?
| He (she, it) was notworking. Он (она, оно) не работал.
|
| We were working.
Мы работали.
| Were we working?
Мы работали?
| We were notworking.
Мы не работали.
|
| You were working.
Ты работал.
| Were you working?
Ты работал?
| You were notworking.
Ты не работал.
|
| They were working.
Они работали.
| Were they working?
Они работали?
| They were notworking.
Они не работали.
|
| Сравните употребление
Past Indefiniteи Past Continuous
Обратите внимание на обстоятельства времени, характерные для Past Continuous:
at … o’clock yesterday
when mother came home
from 5 till 6 yesterday
the whole evening
Обратите также внимание на следующие два предложения:
We playedchess inthe evening (вечером)
Past Indefinite
We were playingchess the wholeevening (весь вечер)
Past Continuous
|
Exercise 1.
Open brackets using verbs in Past Indefinite or Past Continuous.
1. I (to play) computer yesterday. 2. I (to play) computer games at 5 o’clock yesterday. 3. He (to play) computer games from 2 till 3 yesterday. 4. We (to play) computer games the whole evening yesterday. 5. What Nick (to do) when you came to his place? 6. What you (to do) when I rang you up? 7. I (not to sleep) at 9 o’clock yesterday. 8. What he (to do) yesterday? He (to read) a book. 9. What he (to do) the whole evening yesterday? – He (to read) a book. 10. She (to sleep_ when you came home? 11. My brother (not top play) tennis yesterday. He (to play) tennis the day before yesterday. 12. My sister (not to play) the piano at 4 o’clock yesterday. She (to play) the piano the whole evening. 13. When I came into the kitchen, mother (to cook). 14. She (to cook) the whole day yesterday. 15. We (to wash) the floor in our flat yesterday. 16. We (to wash) the floor in our flat from 3 till 4 yesterday. 17. You (to do) your homework yesterday? 18. You (to do) your homework from 8 till 10 yesterday? 19. Why she (to sleep) at 7 o’clock yesterday? 20. He (to sit) at the table the whole evening yesterday
Exercise 2. Open brackets using verbs in Past Indefinite or Past Continuous.
1. I (to go) to the cinema yesterday. 2. I (to go) to the cinema at 4 o’clock yesterday. 2. I (to go) to the cinema at 4 o’clock yesterday. 3. I (to go) to the cinema when you met me. 4. I (to do) my homework the whole evening yesterday. 5. I (to do) my homework when mother came home. 6. I (to do) my homework yesterday. 7. I (to do) my homework from 5 till 8 yesterday. I (to do) my homework at 6 o’clock yesterday. 9. I (not to play) the piano yesterday. I (to write) a letter to my friend. 10. I (not to play) the piano at 4 o’clock yesterday. I (to read) a book. 11. He (not to sleep) when father came home. He (to do) his homework. 12. When we were in the country last summer, I (to go) to the wood one day. In the wood I (to find) a little fox cub. I (to bring) it home. I (to decide) to tame the club. Every day I (to feed) it and (to take) care of it. I (to tame) it the whole summer. Now the fox cub is quite tame. It lives in my house. 13. When I (to go) to school the day before yesterday, I met Mike and Pete. They (to talk) and (to laugh). They told me a funny story. Soon I (to laugh), too. I still (to laugh) when we came to school. After school I (to tell) this story at home. My father and mother (to like) it very much.
| Обратите внимание на cледующие предложения:
When mother came home, I was reading.
came – однократно действие (пришла)
Past Indefinite
was reading – действие в процессе (читал)
Past Continuous
When mother was reading, I came home.
was reading – действие в процессе (читала)
Past Continuous
came – однократное действие (пришёл)
Past Indefinite
|
Exercise3. Open brackets using verbs in Past Indefinite or Past Continuous.
1. When I (to come) home, my little sister (to sleep). 2. When Nick (to come) home, his brother (to play) with his toys. 3. When mother (to come) home, I (to do) my homework. 4. When father (to come) home, Pete (to sleep). 5. When mother (to come) home, the children (to play) on the carpet. 6. When I (to get) up, my mother and father (to drink) tea. 7. When I (to come) to my friend’s place, he (to watch) TV. 8. When I (to see) my friend’s, they (to play) football. 9. When I (to open) the door, the cat (to sit) on the table. 10. When Kate (to open) the door, the children (to dance) round the fir-tree. 11. When Tom (to cross) the street, he (to fall). 12. When I (to go) to school, I (to meet) my friend. 13. When we (to go) to the cinema, we (to meet) grandmother. 14. When grandmother (to go) home, she (to see) many children in the yard. 15. When Henry (to walk) about in the forest, he (to find) a bear cub. 16. When we (to walk) about in the forest, we 9to see) a hare. 17. When I (to wash) the floor, I (to find) my old toy under the sofa. 18. When granny (to read) a book on the sofa, she (to fall) asleep. 19. When I (to play) in the yard, I suddenly (to see) my old friend. 20. When Nick (to run) about in the yard, he (to fall).
Exercise 4. Open brackets using verbs in Past Indefinite or Past Continuous.
1. When I (to ring) up my friend, he (to sleep). 2. When grandfather (to watch) TV, he (to fall) asleep. 3. When my friend (to come) to see me, I (to do) my homework. 4. When I (to go) to the stadium, I (to meet) Kate and Ann. 5. When Nick (to ring) me up yesterday, I (to help) mother. 6. When the children (to walk) through the wood, they (to see) a fox. 7. When I (to come) home, my sister (to wash) the floor. 8. When Mike (to play) in the yard, he (to find) a ball. 9. When I (to draw) yesterday, I (to break) two pencils. 10. When I (to meet) Tom, he (to go) to the shop. 11. When I (to look) out of the window, the children (to play) hide-and-seek. 12. I (to go) to the theatre yesterday. 13. At 7 o’clock yesterday I (to go) to the theatre. 14. What you (to do) at 5 o’clock yesterday? – I (to play) the piano. 15. When I (to come) to school, the children (to stand) near the classroom. 16. We (to play) in the yard the whole evening yesterday. 17. When I (to prepare) breakfast in the morning, I (to cut) my finger. 18. Last year I (to go) to the United States. 19. You (to go) to Great Britain last year? – No, I (to go) to France. 20. What you (to do) yesterday? – I (to translate) a very long article.
| Обратите внимание на cледующие предложения:
Father was reading at 7 o’clock yesterday.
действие в процессе - Past Continuous
Father came home at 7 o’clock yesterday. однократное действие - Past Indefinite
|
Exercise 5. Open the brackets using the verbs in Past Indefinite or Past Continuous.
1. He (to get) up at 7 o’clock yesterday. 2. Father (to come) home at 6 o’clock yesterday. 3. I (to read) a book at 6 o’clock yesterday. 4. She (to fall) asleep at 11 o’clock yesterday. 5. Mother (to drink) tea at 11 o’clock yesterday. 6. Father (to watch) TV at 10 o’clock yesterday. 7. I (to go) to bed at 9 o’clock yesterday. 8. I (to finish) my homework at 9 o’clock. 9. I (to play) he piano at 5 o’clock yesterday. 10. He (to begin) to do his homework at 4 o’clock yesterday. 11. She (to wash) the floor at 4 o’clock yesterday. 12. I (to meet) Nick at 3 o’clock yesterday. 13. When I (to come) home, Kate (to play) the piano. 14. When I (to meet) John, he (to go) to the railway station. 15. When I (to go) to the museum, I (to see) a big crowd of people in the street. 16. They (to play) in the yard in the evening yesterday. 17. They (to play) in the yard the whole evening yesterday. 18. I (to clean) my teeth at 8 o’clock in the morning yesterday. 19. We (to go) to the wood in summer. 20. When the teacher (to open) the door of the classroom, the pupils (tom sit) at their desks.
Exercise 6. Open the brackets using the verbs in Past Indefinite or Past Continuous.
1. I (to feed) my cat with fish yesterday. 2. What you (to do) at 4 o’clock yesterday? – I (to feed) my cat. 3. What your brother (to do) yesterday? – He (to play) computer games. 4. I (to begin) repairing my camera at 6 o’clock yesterday. 5. At 5 o’clock yesterday Helen (to cook) soup. 6. We (to play) badminton from 9 till 11 yesterday. 7. Kate (not to go) for a walk yesterday. She (to write) a composition the whole day yesterday. 8. When your father (to come) home yesterday? – He (to come) home at 7 o’clock. 9. When my father (to come) yesterday, my mother (to make) supper. 10. We (not to go) on a tramp last summer. 11. What you (to do) when your sister (to come) home yesterday? 12. You (to have) supper at 9 o’clock yesterday? 14. Nick (to go) to bed at 10 o’clock yesterday. 15. Nick (to sleep) at 11 o’clock yesterday. 16. When we (to play) in the yard yesterday, it suddenly (to start) raining heavily. 17. When I (to see) Mike, he (to cross) the street. 18. He (to begin) repairing his bicycle in the morning yesterday. 19. He (to repair) his bicycle the whole day yesterday. 20. He (to finish) repairing his bicycle in the evening yesterday.
Exercise 7. Open the brackets using the verbs in Past Indefinite or Past Continuous.
They (to translate) a difficult text yesterday. 2. I (to open) the window at 6 o’clock yesterday. 3. You (to go) to the cinema yesterday? 4. I (not to see) Mike last week. 5. When I (to open) the door, my friends (to sit) around the table. 6. When you (to begin) doing your homework yesterday? 7. We (to discuss) the latest news from 3 till 4 yesterday. 8. When the old man (to read) the newspaper, he (to fall) asleep. 9. Lena (to sweep) the floor on Sunday. 10. Lena (to sweep) the floor from 11 till 12 on Sunday. 11. They (to go) to the wood last Sunday? 12. When they (to sail) down the river, they (to see) a little island. 13. We (to work) the whole morning yesterday. 15. She (to finish) cooking at 4 o’clock yesterday. 16. At half past four yesterday we (to have) dinner. 17. You (to watch) TV yesterday? Yes, we (to watch) TV the whole evening yesterday. 18. When you (to go) to bed yesterday? 19. I (to go) to bed at 10 o’clock yesterday. 20. At half past ten yesterday I (to sleep).
Week 6.
Text 6. “Areas of management”
Grammar: Future Continuous
Text 6.
AREAS OF MANAGEMENT
An organizational structure can also be divided more or less horizontally into areas of management. The most common areas are finance, operations, marketing, human resources, and administration. Depending on its purpose and mission, an organization may include other areas as well — research and development, for example, or risk management.
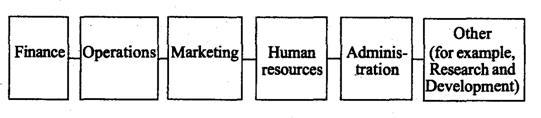
A financial manager is primarily responsible for the organization's financial resources. Accounting and investment are specialized areas within financial management. Because financing affects the operation of the entire firm, many of the presidents of the largest companies are people who got their "basic training" as financial managers.
An operations manager creates and manages the systems that convert resources into goods and services. Traditionally, operations management is equated with the production of goods. However, in recent years many of the techniques and procedures of operations management have been applied to the production of services and to a variety of nonbusiness activities. Like financial management, operations management has produced a good percentage of today's company presidents.
A marketing manager is responsible for the exchange of products between the organization and its customers or clients. Specific areas within marketing are marketing research, advertising, promotion, sales, and distribution.
A human resources manager is in charge of the organization's human resources programs. He or she engages in human resources planning, design systems for hiring, training, and appraising the performance of employees, and ensures that the organization follows government regulations concerning employment practices.
An administrative manager (also called a general manager) is not associated with any specific functional area but provides overall administrative leadership. A hospital administrator is a good example of an administrative manager. He or she does not specialize in operations, finance, marketing, or human resources management but instead coordinates the activities of specialized managers in all these areas.
Будущее длительное время









