

Особенности сооружения опор в сложных условиях: Сооружение ВЛ в районах с суровыми климатическими и тяжелыми геологическими условиями...

Кормораздатчик мобильный электрифицированный: схема и процесс работы устройства...

Особенности сооружения опор в сложных условиях: Сооружение ВЛ в районах с суровыми климатическими и тяжелыми геологическими условиями...

Кормораздатчик мобильный электрифицированный: схема и процесс работы устройства...
Топ:
Генеалогическое древо Султанов Османской империи: Османские правители, вначале, будучи еще бейлербеями Анатолии, женились на дочерях византийских императоров...
Оценка эффективности инструментов коммуникационной политики: Внешние коммуникации - обмен информацией между организацией и её внешней средой...
История развития методов оптимизации: теорема Куна-Таккера, метод Лагранжа, роль выпуклости в оптимизации...
Интересное:
Лечение прогрессирующих форм рака: Одним из наиболее важных достижений экспериментальной химиотерапии опухолей, начатой в 60-х и реализованной в 70-х годах, является...
Мероприятия для защиты от морозного пучения грунтов: Инженерная защита от морозного (криогенного) пучения грунтов необходима для легких малоэтажных зданий и других сооружений...
Как мы говорим и как мы слушаем: общение можно сравнить с огромным зонтиком, под которым скрыто все...
Дисциплины:
|
из
5.00
|
Заказать работу |
Содержание книги
Поиск на нашем сайте
|
|
|
|
1 one
2 two
3 three
4 four
5 five
6 six
7 seven
8 eight
9 nine
10 ten
11 eleven
12 twelve
13 thirteen
14 fourteen
15 fifteen
16 sixteen
17 seventeen
18 eighteen
19 nineteen
И далее
20 twenty 100 a (one) hundred
21 twenty-one 101 a (one) hundred and one
22 twenty-two 200 two hundred
30 thirty 300 three hundred
40 forty 1,000 a (one) thousand
50 fifty 1,001 a (one) thousand and one
60 sixty 1,250 one thousand two hundred 70 seventy and fifty
80 eighty 2,000 two thousand
90 ninety 2,235 two thousand two hundred and thirty-five
23,000 twenty three thousand
100,000 a (one) hundred thousand
427,520 four hundred and twenty seven thousand five hundred and twenty
1,000,000 a (one) million
1,000,000,000 a (one) milliard (в Англии)
a (one) billion (в США)
Обратите внимание, что:
1) числительные обозначающие десятки, образуются от соответствующих числительных первого десятка прибавлением суффикса – ty. При этом числительные two, three, four и five видоизменяются: tw enty, th irty, fo rty, fif ty;
2) между десятками и следующими за ними единицами ставится дефис (чёрточка);
3) числительные, обозначающие десятки, имеют ударение на первом слоге: forty [′f:ti], fifty [′fifti], sixty [′siksti].
Обратите внимание, что:
1) перед числительным hundred, thousand, million ставится неопределённый артикль a или числительное one;
2) числительные hundred, thousand и million не принимают окончания
– s, когда перед ними стоит другое числительное;
3) в составных числительных в пределах каждых трёх разрядов перед десятками (а если их нет, то перед единицами) ставится союз and.
4) при обозначении количественных числительных цифрами каждые три разряда (справа налево) отделяются запятой.
Примечания: 1. Русское существительное в единственном числе после составных числительных, оканчивающихся на один (одна, одно) следует переводить на английский язык существительным во множественном числе: двадцать один день twenty one days, триста пятьдесят одна книга three hundred and fifty-one books.
2. Родительный падеж русских существительных после количественных числительных не следует переводить существительным с предлогом of (частая ошибка учащихся): двести солдат two hundred soldiers, три тысячи людей three thousand people (а не: two hundred of soldiers, three thousand of people).
Порядковые числительные (Ordinal numerals).
1. Все порядковые числительные (за исключением первых трёх) образуются от соответствующих количественных числительных путём прибавления суффикса – th.
2. Перед порядковым числительным стоит индивидуализирующий артикль (независимо от того, есть после него существительное или нет):
Ый-12-й 13-й-19-й
1st the first 13 th the thirteen th
2 nd the second 14 th the fourteen th
3 rd the third 15 th the fifteen th
4 th the four th 16 th the sixteen th
5 th the fif th 17 th the seventeen th
6 th the six th 18 th the eighteen th
7 th the seven th 19 th the nineteen th
8 th the eigh th
9 th the nin th
10 th the ten th
11 th the eleven th
12 th the twelf th
Обратите внимание, что:
1) первые три порядковых числительных образуются не по правилу;
2) при прибавлении суффикса –th в числительных five и twelve буквы ve меняются на – f;
3) к числительному eight прибавляется только буква h;
4) в числительном nine опускается буква e.
Й-90-й 100-й и далее
20th the twentieth 100 th the hundredth
21 st the twenty-first 101 st the hundred and first
22 nd the twenty-second 102 nd the hundred and second
30 th the thirtieth 200 th the two hundredth
40 the fortieth 201 st the two hundred and first
50 th the fiftieth 300 th three hundredth
60 th the sixtieth 400 th the four hundredth
70 th the seventieth 1,000 th the thousandth
80 th the eightieth 1,001 st the thousandth
90 th the ninetieth 1,002 nd the thousand and second
Обратите внимание, что при прибавлении суффикса th конечная буква y меняется на ie: twenty –twent ieth, thirty - thirti eth и т.д.
Обратите внимание, что при образовании составных порядковых числительных последний разряд выражается порядковым числительным, а предшествующие разряды количественными числительными (как и в русском языке): the twenty- first двадцать первый, the hundred and twenty- second сто двадцать второй, the two thousand three hundred and forty- eighth две тысячи триста сорок восьмой.
Примечания: 1. Количественные числительные (а не порядковые) употребляются при обозначении номеров домов, комнат, трамваев, автобусов и т.д. (в русском языке в таких случаях возможно употребление как порядковых, так и количественных числительных). Существительные в этих случаях употребляются без артикля и часто пишутся с прописной буквы:
The lecture will take place in Classroom 15 (читается: class-room fifteen). Лекция состоится в пятнадцатой аудитории (в аудитории № 15).
He lives in Gorki Street House 20, Flat 10 (читается: house twenty flat ten).
Он живёт на улице Горького в доме № 20, в квартире № 10.
Хронологические даты. Годы в английском языке, в отличие от русского, обозначаются количественными числительными следующим образом:
1990 – nineteen hundred 1900 г. – тысяча девятисотый год
1904 – nineteen four (в 1904 г. – тысяча девятьсот четвёртый год
официальном языке:
nineteen hundred and four)
1945 – nineteen forty-five 1945 г. – тысяча девятьсот сорок пятый год
(nineteen hundred and forty-five)
1961 – nineteen sixty one 1961 г. – тысяча девятьсот шестьдесят первый год
(nineteen hundred and sixty one)
Слово year после обозначения года не употребляется, но иногда употребляется перед ним – in the year nineteen fifteen.
Даты обозначаются порядковыми числительными:
15 th May 1960 the fifteen of May, nineteen sixty (или: May the fifteenth,
May 15 th, 1960 nineteen sixty)
May 15, 1960
Дробные числительные (Fractional numerals)/
Простые дроби Десятичные дроби
(Common Fractions (Decimal Fractions)
1 - a (one) half 0,1 – nought point one или: point one
2
1 - a (one) third 0,001 – nought point nought one
3 или: point nought one
1 - a (one) quarter
4 или: a (one) fourth 2.35 – two point three five
1 - a (one) fifth 32.305 – three two (или: thirty-two) point
5 three nought five
2 - two fifths
1
1 2 - one and a half
1
2 3 – two and a (one) third
Обратите внимание, что в простых дробях:
1) числитель выражается количественным числительным, а знаменатель – порядковым (как и в русском языке);
2) когда числитель больше единицы, знаменатель принимает окончание – s.
Обратите внимание, что в десятичных дробях:
1) целое число отделяется от дроби точкой (а не запятой, как в русском языке);
2) каждая цифра читается отдельно. Точка, отделяющая целое число от дроби, читается point, 0 читается nought ( в Америке 0 читается zero). Еслицелое число равно нулю, то оно часто не читается.
Exercise 1.Write down in written form:
2, 12, 20, 28, 3, 13, 30, 35, 4, 14, 40, 49, 5, 15, 50, 56, 6, 16, 60, 67, 7, 17, 70, 8, 18, 80, 89, 9, 19, 90, 100, 107, 126, 200, 349, 607, 839, 1, 000, 5,007, 6,456, 8,967, 67, 237, 100,000,000.
Exercise 2.Translate into English:
1) 200 книг; 2) 5,000 студент; 3) 21 ящик; 4) 141 книг; 5) 2,000,000 книг; 6) 3,000 денег; 7) 41 день; 8) 500 детей; 9) 31 мальчиков; 10) 600 домов.
Exercise 3.Write down on English the following dates:
15 февраля 1959 год, 21 апреля 1959 год, 3 май 1960 год, 12 июнь 1960 год, 15 июль 1961 год, 14 август 1962 год, 17 сентябрь 1962 год, 25 октябрь 1962 год.
Glossary 3.
Week 9.
Text 9. “Definition of Management. Main Resources of Management”
Grammar: Pronouns
Text 9.
Definition of Management
Management is based on scientific theories and today we can say that it is a developing science.
But knowledge of theories and principles doesn't provide practical results. It is necessary to know how to apply this knowledge. Practical application of knowledge in the management area requires certain abilities or skills. Here is an example: Depending on its size, an organization may employ a number of specialized managers who are responsible for particular areas of management. A very large organization may employ many managers, each responsible for activities of one management area. In contrast, the owner of a sole proprietorship may be the only manager in the organization. He or she is responsible for all levels and areas of management. What is important to an organization is not the number of managers it employs but the ability of these managers to achieve the organization's goals, and this ability requires a great skill. In other words, management is the process of coordinating the resources of an organization to achieve the primary organizational goals.
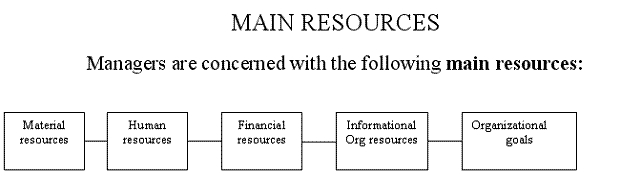
1 2 3 4
1. Material resources are physical materials and the equipment used by an organization to make a product. For example, cars are made on assembly lines. These assembly lines and the buildings that house them are material resources.
2. The most important resources of any organization are its human resources — people. Some firms believe that their employees are their most important assets. To keep employees content, a variety of incentives are used, including higher-man- average pay, flexible working hours, recreational facilities, lengthy paid vacations, cafeterias offering inexpensive meals, etc.
3. Financial resources are the funds the organization uses to meet its obligations to various creditors. A grocery store obtains money from customers and uses a portion of that money to pay the wholesalers from which it buys food. A large bank, borrows and lends money. A college obtains money in the form of tuition, income from its endowments, and federal grants. It uses the money to pay utility bills, insurance premiums, and professors' salaries. Each of these transactions involves financial resources.
4. Finally, many organizations increasingly find they cannot ignore information. External environment — including the economy, consumer markets, technology, politics, and cultural forces — are all changing so rapidly that an organization that does not adapt will probably not survive. And, to adapt to change, the organization must know what is changing and how it is changing. Companies are finding it increasingly important to gather information about their competitors in today's business environment.
It is important to realize that these are only-general categories of resources. Within each category are hundreds or thousands of more specific resources, from which management must choose those that can best accomplish its goals. Managers must coordinate this complex group of specific resources to produce goods and services.
|
|
|

Механическое удерживание земляных масс: Механическое удерживание земляных масс на склоне обеспечивают контрфорсными сооружениями различных конструкций...

Архитектура электронного правительства: Единая архитектура – это методологический подход при создании системы управления государства, который строится...

Папиллярные узоры пальцев рук - маркер спортивных способностей: дерматоглифические признаки формируются на 3-5 месяце беременности, не изменяются в течение жизни...

Состав сооружений: решетки и песколовки: Решетки – это первое устройство в схеме очистных сооружений. Они представляют...
© cyberpedia.su 2017-2025 - Не является автором материалов. Исключительное право сохранено за автором текста.
Если вы не хотите, чтобы данный материал был у нас на сайте, перейдите по ссылке: Нарушение авторских прав. Мы поможем в написании вашей работы!