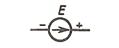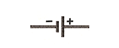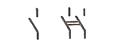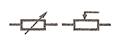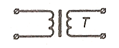| air gap
| ______________________________________________
|
| brush sparks
| ______________________________________________
|
| slow speed
| ______________________________________________
|
| excessive speed
| ______________________________________________
|
| safety devices
| ______________________________________________
|
5. Answer these questions:
1. What do motors’ faults result from?
2. Are there any faults that can be ignored?
3. What makes motors’ service life shorter?
4. What does voltage supply stop result in?
5. What processes show the (dis)advantages of devices?
6. Are the words: spark, short, slow, brush, fault, load, test nouns? Are they verbs? Translate the sentences into Russian:
1. New motors are given a no-load and under a load tests.
2. When the motor is tested it should produce no abnormal noise.
3. In case this noise appears the motor must be disconnected.
4. This generator must be checked; one should give it a test.
3. The motor’s brushes seem to be sparking. Can you see the sparks?
6. The windings of the coil are shorted. I have detected a short in the windings.
7. The armature rotates slowly; let’s check it up!
8. The speed of rotation is too excessive; it must be slowed down.
9. In case the rotor brushes against the stator, the motor operates slowly. The faulty brushes should be replaced.
Faults of Motors and Ways of Their Repair
Motors may have different faults. A faulty motor does not start, or, when it is started, it operates at an excessive speed.
Its brushes may spark and its windings and the commutator may be overheated and burnt. Besides, a motor may produce an abnormal noise, etc. All these and other faults should be detected and repaired.
In case the motor does not start it may have different faults (see the table):
Table
| Possible causes of faults
| Ways of repair
|
| 1. Fuses are faulty.
| 1. Replace the fuses.
|
| 2. Motor is overloaded.
| 2. Reduce motor load.
|
| 3. Circuit in armature winding has an open.
| 3. Repair the armature winding.
|
| In case the motor, when started, stops:
|
| 1. Rheostat is shorted.
| 1. Check the rheostat and repair it.
|
| 2. Rheostat switches from one position to another.
| 2. Slow down operation of rheostat handle.
|
| Brushes may spark in case:
|
| 1. Motor is overloaded.
| 1. Reduce the load and remove overload.
|
| 2. Brushes are in poor condition.
| 2. Replace the brushes.
|
| 3. Pressure is low.
| 3. Adjust the pressure.
|
| 4. Pressure is excessive.
| 4. Adjust the pressure.
|
| In case the armature winding is overheated:
|
| 1. Motor is overloaded.
| 1. Remove the overload.
|
| 2. Ventilation fails to operate properly.
| 2. Check for slowing down the speed of the motor.
|
| In case of abnormal motor speed:
|
| 1. Motor is overloaded.
| 1. Reduce the load.
|
| 2. Rotor circuit has poor contact.
| 2. Repair the shorting mechanism.
|
| In case rotor brushes against stator:
|
| Rotor brushes against stator.
| Adjust air gap.
|
7. Complete the sentences using the correct variant:
| 1. A motor with a fault
| a) operates normally.
b) operates poorly.
|
| 2. Motor brushes spark in case
| a) they are in normal conditions.
b) they are in poor conditions.
|
| 3. Burnt commutator should be
| a) replaced.
b) repaired.
|
| 4. Brushes may spade in case
| a) pressure is low.
b) pressure is excessive.
|
| 5. Air gap is adjusted in case
| a) the rotor brushes against the stator.
b) the stator brushes against the rotor.
|
8. Answer these questions:
1. When does a motor operate poorly?
2. What should be done in case the motor is overloaded?
3. What should be done in case the fuses are faulty?
4. What should be done in case the rheostat is shorted?
5. What should be done in case the brushes spark?
6. What should be done in case the pressure is low?
7. What should be done in case the ventilation does not operate?
8. What should be done in case the rotor brushes against stator?
Say a few words about your electrical engineering laboratory. Are there any faulty devices in it? Have a talk with your groupmate about the faults and the ways to repair them.
You know that all electrical devices and installations are constructed of a certain number of components. To these components belong electric power sources, wires, cables, buses, switches, fuses, resistors, rheostats, capacitors, transformers, motors and others.
Let us have a talk about these components. Speak with your groupmates about their types, their use, operation, possible faults and ways of their repair. Use the table below:
| Circuit components
| Symbols
|
| Electric energy source
| 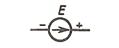
|
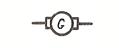
| D.c. generator
| 
|
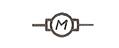
| D.c. motor
| 
|
| Chemical power source (primary or storage cell)
| 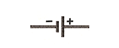
|
| Electric lamp
| 
|
| Electric connection, removable and permanent
| 
|
| Switches, single- and double-pole switches
| 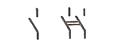
|
| Fuse
| 
|
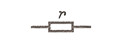
| Load, resistor
| 
|
| Safety earthing system
| 
|
| Rheostat, or variable resistor
| 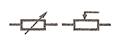
|
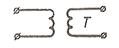
| Transformer, air-core T
| 
|
| Iron-core T
| 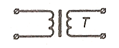
|
| Capacitor, fixed C, variable C
| 
|
11. Draw schemes of circuits and devices constructed from these components. Have a talk with your groupmates about them:
1. Connect four resistors, two voltage sources and a switch in series. Speak about the construction and the operation of the circuit.
2. Connect several resistors and cells in series-parallel. Suppose that one of the resistors gets open; what does it result in? Suppose that a whole set gets open. What does it result in?
3. Measure the value of current (voltage, power, resistance) in the circuit. Use proper meters. Speak about the way you connect the meters to the circuit.
4. Take the proper components and construct an earthing protection system. Draw its scheme. Speak about its operation.
5. Draw a scheme of a thermal relay. What components are necessary for it?
6. Draw a scheme of an overhead transmission line. Speak about its operation. What are its possible faults?
7. Draw a scheme of a substation. Speak about its operation and about its possible faults. What are the ways of their repair?
Unit Thirty [30]
1. a) Cover the right column and read the English words. Translate them into Russian and check your translation.
b) Cover the left column and translate theRussian words back into English.
| toachieve
| [əˈtʃiːv]
| достигать
|
| tobelong (to)
|
| принадлежать, относиться (к)
|
| to feed
|
| снабжать, питать
|
| todetermine
| [dɪˈtəːmɪn]
| определять
|
| torelate
|
| относиться (к), быть связанным (с)
|
| predominant
| [prɪˈdɔmɪnənt]
| преобладающий
|
| graph
| [ɡrɑːf]
| кривая, график
|
| national
|
| народное хозяйство
|