Предисловие
Вашему вниманию предлагается пособие для учебных заведений энергетического профиля. Пособие соответствует требованиям программы по английскому языку для учебных заведений данного профиля и рассчитано на обучаемых, имеющих начальную языковую подготовку.
В число учебных целей пособия входят формирование умений беседовать на профессиональную тематику и развитие умения читать специальную литературу средней трудности и извлекать из нее нужную для практики информацию. Для достижения поставленных целей в пособии предусмотрена регулярная, от урока к уроку, учебная деятельность по созданию словаря активной лексики, включающего наиболее употребительные для данной специальности термины и слова общетехнического значения. Кроме того, предусмотрена учебная деятельность, направленная на формирование основ потенциального словаря. Специальный раздел пособия посвящен повторению и тренировке грамматических явлений и синтаксических структур, типичных для современной научно-технической литературы.
Материалы, составляющие пособие, отобраны из оригинальной и переводной литературы по данной отрасли. Последовательность текстовых материалов пособия имеет логическую направленность, соответствующую логике структуры данной специальности, а именно: от описаний отдельных деталей и элементов оборудования – к описанию действующих устройств разного назначения, построенных из этих деталей.
Пособие состоит из трех частей: 1. Основной курс (EssentialCourse);
2. Повторение и тренировка грамматики (GrammarRevision); 3. Материалыдлячтенияиобсуждения (Material for Reading and Discussing).
Основной курс состоит из 34 уроков, имеющих аналогичную структуру. Цель этой части – формирование у обучаемых навыков устной речи по профессиональной тематике. Этим определяется подбор учебных материалов, их расположение и характер тренировочных заданий. В начале каждого урока предлагается задание на тренировку новых слов в их английском и русском вариантах. Следует отметить, что при переводе этих слов мы, главным образом, придерживались их терминологических значений. Выполняя первое задание, следует добиваться уровня владения словарем, указанного в задании. Показателем того, что искомый уровень достигнут, служит готовность обучаемых свободно, в нормальном речевом темпе воспроизвести каждое слово в его английском и русском вариантах. Только после этого рекомендуется переходить к активизации слов в контексте и к работе над текстом. Заключительные задания, построенные в вопросо-ответной форме, служат для контроля и самоконтроля степени усвоения лексики и структур данного урока. Неспособность обучаемого выполнить эти задания в требуемом речевом темпе указывает на то, что материал урока не усвоен и цель урока не достигнута. А так как это создает препятствия для дальнейшей деятельности, рекомендуем сделать шаг назад и ликвидировать выявленный пробел.
Следует отметить, что в первой части пособия реализована полная, от урока к уроку, преемственность слов и их многократная повторяемость в разных контекстах. Число новых слов в уроках строго дозировано и определено закономерностями памяти человека. Формируемый на этой основе словарный запас используется для достижения учебной цели первой части пособия – развития умений устного общения. Кроме того, он помогает и в создании потенциального словаря, что составляет одну из задач второй части, содержащей материал и задания по словообразованию. Лексический минимум является основой чтения и активного обсуждения материалов третьей части пособия.
Во вторую часть пособия включены упражнения на повторение и тренировку грамматики. Выполнение этих упражнений помогает активизировать знание грамматических форм и синтаксических оборотов, употребительных в специальной литературе. Кроме того, приводятся серии заданий на запоминание разных способов словообразования, что помогает расширению словарного запаса и образованию основ потенциального словаря. Тесты по основным темам грамматики позволяют преподавателю проконтролировать, усвоена ли тема учащимися или необходимы дополнительные пояснения и упражнения для закрепления знаний по грамматике.
Содержание третьей части составляют текстовые материалы для чтения и задания на извлечение информации из них и устное обсуждение. По уровню языковой и понятийной сложности материалы третьей части пособия можно условно разделить на две группы. В первую входят краткие статьи описательного характера, несложные по содержанию и по характеру синтаксических построений. Статьи построены на широко употребительной лексике – популярной отраслевой терминологии и частотных словах общетехнического значения. Преподаватель, по своему усмотрению, может использовать эти статьи уже на ранней ступени обучения. Во вторую группу входят материалы более сложные как по содержанию, так и по языковым характеристикам. К работе с этими статьями целесообразно приступать после выполнения заданий, представленных во второй части пособия.
Кроме чтения и перевода текстовых материалов разной понятийной и языковой сложности, в число задач заключительного раздела входит развитие и углубление навыков устной речи по темам специальности. Для этого предлагаются вопросо-ответные задания, выступления с сообщениями по темам текстов и их последующее обсуждение. Специальные задания направлены на активизацию мыслительной деятельности учащихся.
EssentialCourse
Основной курс
Unit One [1]
1. a) Cover the right column and read the English words. Translate them into Russian and check your translation.
b) Cover the left column and translate theRussian words back into English.
| addition
| [əˈdɪʃən]
| сложение
|
| subtraction
| [səbˈtrækʃn]
| вычитание
|
| plus
| [plʌs]
| плюс
|
| minus
| [ˈmaɪnəs]
| минус
|
| to add
| [æd]
| складывать, прибавлять
|
| to subtract
| [səbˈtrækt]
| вычитать
|
| to equal
| [ˈiːkwəl]
| равняться
|
| to be equal
|
| быть равным
|
Addition and Subtraction
| 5 + 7 = 12
| – five plus seven equals twelve
|
| 66 + 13 = 79
| – sixty-six plus thirteen is equal to seventy-nine
|
| a + b = c
| – a plus b is equal to c
|
| 15 - 6 = 9
| – fifteen minus six equals nine
|
| 81 - 33 = 48
| – eighty-one minus thirty-three is equal to forty-eight
|
| c - b = a
| – c minus b equals a
|
2. Solve these problems and read them:
| 99 + 77 = ___________
| 8 - 3 = ______________
| 315 + 145 = _________
|
| 61 - 50 = ____________
| 47 - 18 = ____________
| 859 - 600 = __________
|
| 114 + 316 = _________
| 1,203 + 419 = ________
| 4,444 + 7,777 = ______
|
| b + d = _____________
| d - c = ______________
| а - b = ______________
|
Multiplication and Division
| 1 × 1 = 1
| – once one is one
|
| 2 × 2 = 4
| – twice two is four
|
| 3 × 3 = 9
| – three times three equals nine
|
| 4 × 4 = 16
| – four times four is equal to sixteen
|
| 12 × 10 = 120
| – twelve multiplied by ten (by) is equal to one hundred and twenty
|
| a × b = ab
|
|
| 35: 7 = 5
| – thirty-five divided by seven equals five
|
| 1000: 25 = 40
| – one thousand divided by twenty-five is equal to forty
|
| d: b = c
|
|
2. Solve these problems and read them:
| 10 × 7 = _______
| 49: 7 = _______
| 13 × 3 = _______
| 749: 7 = ______
|
| 100 × 100 = ____
| 175: 25 = _____
| 618: 6 = ______
| 3,550 × 5 = ____
|
| 234 × 6 = ______
| 12 × 12 = ______
| 33: 33 = ______
| 10,660: 10 = ___
|
| b × c = ________
| n: m = ________
| 1 × k = ________
| 1 × 1= ________
|
Ohm’s Law
| R =
| V
| Resistance equals voltage divided by current.
|
| I
|
|
|
| I =
| V
| Current equals voltage divided by resistance
|
| R
|
|
|
| V = IR
| Voltage equals current times resistance.
|
| | | | |
|
|
Problem
Suppose that resistance equals one volt and current equals one ampere.
How much is the resistance?
|
Solution
|
| V = 1V
I = 1 amp
R =?
|
Resistors
A resistor is one of the most common elements of any circuit. Resistors are used:
1. to reduce the value of current in the circuit;
2. to produce IR voltage drop and in this way to change the value of the voltage.
When current is passing through a resistor its temperature rises high. The higher the value of current the higher is the temperature of a resistor. Each resistor has a maximum temperature to which it may be heated without a trouble. If the temperature rises higher the resistor gets open and opens the circuit.
Resistors are rated in watts. The watt is the rate at which electric energy is supplied when a current of one ampere is passing at a potential difference of one volt. A resistor is rated as a 1-W resistor if its resistance equals 1,000,000 ohms and its current-carrying capacity equals 1/1,000,000 amp,since
P = E× I = IR ×I = I2R where P - power is given in watts, R - resistance is given in ohms and I - current is given in amperes.
If a resistor has a resistance of only 2 ohms but its current-carrying capacity equals 2,000 amp, it is rated as a 8,000,000-W resistor.
Some resistors have a constant value - these are fixed resistors, the value of other resistors may be varied - these are variable resistors.
5. Complete the sentences using the correct variant:
| 1. A resistor is used
| a) to measure the resistance.
b) to reduce the current.
c) to change the resistance.
d) to produce IR voltage drop.
|
| 2. When current passes through a resistor
| a) its temperature drops.
b) its temperature rises.
|
| 3. Resistors are rated
| a) in ohms.
b) in volts.
c) in watts.
|
| 4. Power is given
| a) in amperes.
b) in watts.
|
| 5. Fixed resistors have
| a) a constant value.
b) a variable value.
|
| 6. The value of a variable resistor
| a) is fixed.
b) is varied.
|
| 7. A two-ohm resistor rated as a 8,000,000-W resistor
| a) has a current-carrying capacity equal to 2,000 amp.
b) has a current-carrying capacity equal to 200 amp.
|
| 8. The higher the value of current,
| a) the lower is the temperature of a resistor.
b) the higher is the temperature of a resistor.
|
6. Complete the sentences using while. Follow the model on page 13.
1. The value of a fixed resistor is constant ….
2. Current-carrying capacity is given in amperes….
3. The lower the value of current, the lower is the temperature of a resistor….
4. An electric source produces energy ….
Capacitors
A capacitor is one of the main elements of a circuit. It is used to store electric energy. A capacitor stores electric energy provided that a voltage source is applied to it.
The main parts of a capacitor are metal plates and insulators. The function of insulators is to isolate the metal plates and in this way to prevent a short.
In the diagram one can see two common types of capacitors in use nowadays: a fixed capacitor and a variable one. The plates of a fixed capacitor cannot be moved; for this reason its capacity does not change. The plates of a variable capacitor move; its capacity changes. The greater the distance between the plates, the less is the capacity of a capacitor. Variable capacitors are commonly used by radiomen; their function is to vary the frequency in the circuit. Fixed capacitors are used in telephone and radio work.
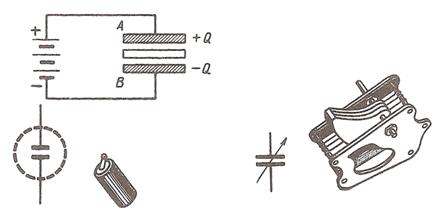
Fig. 8 Fig. 9
Fixed capacitors have insulators produced of paper, ceramics and other materials; variable capacitors have air insulators. Paper capacitors are commonly used in radio and electronics; their advantage is their high capacity: it may be higher than 1,000 picofarad.
Besides, electrolyte capacitors are highly in use. They also have a very high capacity: it varies from 0.5 to 2,000 microfarad. Their disadvantage is that they change their capacity when the temperature changes. They can operate without a change only at temperatures not lower than -40° C.
Common troubles in capacitors are an open and a short. A capacitor stops operating and does not store energy in case it has a trouble. A capacitor with a trouble should be substituted by a new one.
4. Complete these sentences using the correct variant:
| 1. A capacitor is used
| a) to supply voltage.
b) to increase the voltage output.
c) to store energy.
|
| 2. The main parts of a capacitor are
| a) insulators only.
b) metal plates only.
c) metal plates and insulators between them.
|
| 3. The function of insulators is
| a) to store energy.
b) to isolate the metal plates.
c) to prevent a short between the metal plates.
|
| 4. The capacity of a capacitor depends on
| a) the size of the plates.
b) the distance between the plates.
c) the material of the insulators.
|
| 5. The capacity of a fixed capacitor
| a) is constant.
b) is varied.
|
| 6. The plates of a variable capacitor
| a) can be moved.
b) cannot be moved.
|
| 7. In order to charge a capacitor a voltage source is applied
| a) to the metal plates.
b) to the insulators.
|
| 8. The greater the distance between the plates,
| a) the greater is the capacity of a capacitor.
b) the less is the capacity.
|
| 10. Electrolyte capacitors have
| a) a very low capacity.
b) a very high capacity.
|
| 11. In case a capacitor has a trouble
| a) it operates.
b) it stops operating.
|
5. Complete these sentences using while. Follow the model on page 13:
1. The plates of a fixed capacitor cannot be moved to vary the capacity....
2. The capacity of a variable capacitor is varied ….
3. Electrolyte capacitors change their capacity when the temperature changes ….
4. The less the distance between the plates, the greater is the capacity ….
5.When a capacitor has no trouble it stores energy ….
Conductors and Insulators
Conductors are materials having a low resistance so that current easily passes through them. The lower the resistance of the material, the more current can pass through it.
The most common conductors are metals. Silver and copper are the best of them. The advantage of copper is that it is much cheaper than silver. Thus copper is widely used to produce wire conductors. One of the common functions of wire conductors is to connect a voltage source to a load resistance. Since copper wire conductors have a very low resistance a minimum voltage drop is produced in them. Thus, all of the applied voltage can produce current in the load resistance.
It should be taken into consideration that most materials change the value of resistance when their temperature changes.
Metals increase their resistance when the temperature increases while carbon decreases its resistance when the temperature increases. Thus metals have a positive temperature coefficient of resistance while carbon has a negative temperature coefficient. The smaller is the temperature coefficient or the less the change of resistance with the change of temperature, the more perfect is the resistance material.
Materials having a very high resistance are called insulators. Current passes through insulators with great difficulty.
The most common insulators are air, paper, rubber, plastics.
Any insulator can conduct current when a high enough voltage is applied to it. Currents of great value must be applied to insulators in order to make them conduct.The higher the resistance of an insulator, the greater the applied voltage must be.
When an insulator is connected to a voltage source, it stores electric charge and a potential is produced on the insulator. Thus, insulators have the two main functions:
1. to isolate conducting wires and thus to prevent a short between them and
2. to store electric charge when a voltage source is applied.
6. Find answers to these questions in the text above:
1. What materials are called conductors?
2. What is the advantage of copper compared with silver?
3. What is the most common function of wire conductors?
4. Why is a minimum voltage drop produced in copper conductors?
5. What is the relation between the value of resistance and the temperature in carbon?
6. What materials are called insulators?
7. What are the most common insulators?
8. What are the two main functions of insulators?
7. Complete the sentences using the correct variant:
| 1. Insulators are materials having
| a) low resistance.
b) high resistance.
|
| 2. Current passes through conductors
| a) easily.
b) with great difficulty.
|
| 3. Copper and silver are
| a) common conductors.
b) common insulators.
|
| 4. Air, paper and plastics are
| a) common insulators.
b) common conductors.
|
| 5. In case a high voltage is applied to an insulator
| a) it does not conduct current.
b) it conducts current.
|
| 6. Insulators are used
| a) to store electric charge.
b) to reduce voltage.
c) to prevent a short between conducting wires.
|
| 7. Metals increase their resistance
| a) when the temperature decreases.
b) when the temperature increases.
|
| 8. Carbon decreases its resistance
| a) when the temperature increases.
b) when the temperature decreases.
|
| 9. Metals have
| a) a positive temperature coefficient of resistance.
b) a negative temperature coefficient of resistance.
|
8. Complete the sentences using while. Follow the model on page 13.
1. Conductors have a low resistance….
2. Current passes through insulators with great difficulty ….
3. Metals are common conductors ….
4. To make insulators conduct, currents of great value must be applied….
3. Carbon decreases its resistance when the temperature increases ….
6. Metals have a positive temperature coefficient of resistance ….
9. Pair work. Put these questions to your groupmate, and ask him/her toanswer them:
1.What is the difference between conductors and insulators?
2.How does current pass through insulators?
3.What materials are commonly used to produce insulators?
4.What materials are commonly used to produce conductors?
5.In what case do insulators conduct current?
6. How does resistance change when the temperature decreases?
Unit Twelve [12]
1. a) Cover the right column and read the English words. Translate them into Russian and check your translation.
b) Cover the left column and translate theRussian words back into English.
| core
|
| сердечник
|
| winding
| [ˈwaɪndɪŋ]
| обмотка
|
| turn
|
| виток
|
| to step up
|
| повышать
|
| to step down
|
| понижать
|
| frequency
| [ˈfriːkwənsɪ]
| частота
|
| due to
| [ˈdjuːtə]
| благодаря, из-за
|
2. Put down the Russian for:
| iron core
| _____________
| primary winding
| _____________
|
| closed core
| _____________
| secondary winding
| _____________
|
| input voltage
| _____________
| step-up transformer
| _____________
|
| output voltage
| _____________
| step-down transformer
| _____________
|
Transformers
A transformer is used to transfer energy. Due to the transformer electric power may be transferred at a high voltage and reduced at the point where it must be used to any value. Besides, a transformer is used to change the voltage and current value in a circuit.
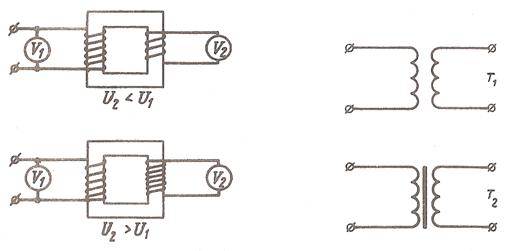
Fig. 10 Fig. 11
A two-winding transformer consists of a closed core and two coils (windings). The primary winding is connected to the voltage source. It receives energy. The secondary winding is connected to the load resistance and supplies energy to the load.
The value of voltage across the secondary terminal depends on the number of turns in it. In case it is equal to the number of turns in the primary winding the voltage in the secondary winding is the same as in the primary.
In case the secondary has more turns than the primary the output voltage is greater than the input voltage. The voltage in the secondary is greater than the voltage in the primary by as many times as the number of turns in the secondary is greater than the number of turns in the primary. A transformer of this type increases or steps up the voltage and is called a step-up transformer. In case the secondary has fewer turns than the primary the output voltage is lower than the input. Such a transformer decreases or steps down the voltage, it is called a step-down transformer.
Compare T1 and T2 in the diagram. T1 has an iron core. For this reason it is used for low-frequency currents. T2 has an air core and is used for high frequencies.
Common troubles in transformers are an open in the winding, a short between the primary and the secondary, and a short between turns. In case a transformer has a trouble it stops operating or operates badly. A transformer with a trouble should be substituted.
3. Complete the sentences using the correct variant:
| 1. A transformer is used
| a) to store charge.
b) to prevent the change of energy.
c) to transfer energy.
d) to change the voltage and current value in a circuit.
|
| 2. Electric power is transferred at a high voltage and reduced to any value
| a) due to resistors.
b) due to capacitors.
c) due to transformers.
|
| 3. A transformer consists of
| a) cores only.
b) the primary and the secondary windings.
c) a core and the primary and the secondary windings.
|
| 4. The function of the primary is
| a) to prevent the change of voltage.
b) to supply energy.
c) to receive energy.
|
| 5. The function of the secondary is
| a) to receive energy.
b) to supply energy.
c) to transfer energy.
d) to decrease the value of charge.
|
| 7. A step-down transformer is used
| a) to step down the secondary voltage.
b) to step down the primary voltage.
|
| 8. A transformer with an iron core
| a) is used for high-frequency currents.
b) is used for low-frequency currents.
|
| 9. A transformer with an air core is used
| a) for high-frequency currents and for low-frequency currents.
b) for high-frequency currents only.
|
| 10. In a step-up transformer
| a) the number of turns of the secondary winding is greater than the number of turns of the primary.
b) the number of turns of the primary winding is greater than the number of turns of the secondary.
|
| 11. A transformer should be substituted
| a) in case it has an open in the winding.
b) in case it has a short between the primary and the secondary.
c) in case it has a short between turns.
|
4. Complete these sentences using while. Follow the model on page 13.
1. The secondary winding of a transformer is connected to the load resistance ….
2.The primary winding receives energy ….
3. A step-down transformer decreases the primary voltage ….
4.An air core transformer is used for high -frequency currents ….
5.In a step-up transformer the number of turns of the secondary winding ….
is greater than the number of turns of the primary winding ….
Current Transformers
Current transformers are used for operating ammeters, wattmeters, and other measuring devices. They produce in the meters a current lower than the measured current but proportional to it.
Current transformers also insulate the instrument from the circuit which is being measured. This is necessary for high voltage circuits.
Types of Current
Current is a flow of electricity through a circuit. Let us consider two main types of current: direct and alternating. A direct current (d.c.) flows through a conducting circuit in one direction only. It flows provided a direct voltage source is applied to the circuit.
An alternating current (a.c.) is a current that changes its direction of flow through a circuit. It flows provided an alternating voltage source is applied to the circuit. Alternating current flows in cycles. The number of cycles per second is called the frequency of the current. In a 60-cycle alternating current circuit the current flows in one direction 60 times and in the other direction 60 times per second.
It is easy to transform a.c. power from one voltage to another by a transformer. Transformers are also used to step down the voltage at the receiving point of the line to the low values that are necessary for use.
When necessary a.c. can be changed into d.c. but this is seldom necessary.
4. Complete the sentences using the correct variant:
| 1. D.c. is a current that
| a) changes its direction of flow.
b) flows in one direction.
|
| 2. A.c. flows provided
| a) a direct voltage source is applied.
b) an alternating voltage source is applied.
|
| 3. In an alternating current circuit
| a) current flows in one direction 60 times per second.
b) current flows in one direction 60 times and in the other direction 60 times per second.
|
| 4. A.c.
| a) can be changed into d.c.
b) cannot be changed into d.c.
|
5. Complete these sentences using while. Follow the model on page 13.
1. An alternating current changes its direction of flow ….
2. A direct current flows provided a direct voltage source is applied ….
6. Answer the following questions:
1. What is current?
2. What types of current do you know?
3. When does a direct current flow?
4. What type of current is called an alternating current?
5. What type of current is called a direct current?
6. What is called the frequency of current?
7. What device is used to transform a.c. power from one voltage to another?
8. Is it often necessary to change a.c. into d.c.?
Frequency
The number of cycles per second is the frequency of an alternating current. There are two frequencies: the standard for Europe is 50 cycles per second while the standard for the USA is 60 cycles per second. A standard frequency has a great advantage since different systems can be interconnected.
Coupling
When circuits are indirect-inductively coupled energy is transferred from one circuit to another using electromagnetic field of the inductance through which a varying current is flowing. The coupling device is a transformer. It is not in series with the elements of the circuit, therefore the coupling is indirect. The transformer consists of two windings: the primary and the secondary. The primary circuit is connected to the voltage source, the secondary - to the load circuit.
The coupling may be tight and loose. In case the coils of the coupling element are close together, the coupling is tight. In case the coils are separated the coupling is loose. In the loose coupling the mutual inductance is small compared with the self-inductance.
4. Complete the sentences using the correct variant:
| 1. The circuit connected to the voltage source is called
| a) the secondary circuit.
b) the primary circuit.
|
| 2. The circuit receiving its energy through a coupling is
| a) the primary circuit.
b) the secondary circuit.
|
| 3. The function of a coupling element is
| a) to separate the circuits.
b) to transfer energy.
c) to prevent a short between the circuits.
|
| 4. When the coupling is tight
| a) the coils are separated.
b) the coils are close together.
|
| 5. When the coils are close together
| a) the coupling is loose.
b) the coupling is tight.
|
| 6. The circuits are indirectly coupled when
| a) the coupling element is common to both circuits and is in series with their other elements.
b) the coupling element is not common to the circuits and is not in series with their other elements.
|
5. Complete these sentences using while. Follow the model on page 13.
1. The circuit receiving energy is the secondary circuit ….
2. The coupling is loose when the coils are separated ….
3. When the coupling element is not common to the circuits and not in series with their elements, the circuits are indirectly coupled ….
6. Answer the following questions:
1. What type of circuit is called the primary?
2. What type of circuit is called the secondary?
3.What is the function of a coupling element?
4.What type of coupling is called loose?
5.What type of coupling is called tight?
6.In what case are the circuits directly coupled?
7.In what case are the circuits indirectly coupled?
8.What is the difference between a tight and loose coupling?
9.In what case should a coupling element be substituted?
Electron Tubes
Let us consider electron tubes. Among the electron tubes in usenowadays there are a diode, a triode, a tetrode and a pentode. The mainparts of electron tubes are electrodes. Electrodes are placed into a glass or metal bulb.
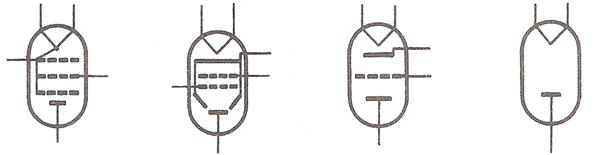
Fig. 14
A diode contains the cathode and the plate. When a diode operates the cathode emits electrons, the plate collects them.
A triode contains the cathode, the plate and the control grid. When the tube operates the cathode emits electrons, the plate collects them and the grid controls the flow of electrons. Therefore, the grid is called a control grid.
A tetrode contains the cathode, the plate, the control grid and the screen grid.
When a tube operates it may oscillate. The function of the screen grid is to eliminate oscillations. Therefore it is called a screen grid.
A pentode contains two electrodes and three grids: the control grid, the screen grid and the suppressor grid. When a pentode operates the suppressor grid eliminates the secondary emission.
Common troubles in tubes are an open heater and low emission. These troubles result from constant use or from some other reason. In case a tube has a trouble it stops operating or operates badly. A tube with a trouble should be replaced by another one.
5. Complete the sentences using the correct variant:
| 1. A pentode contains
| a) the cathode, the plate, two screen grids and the suppressor grid.
b) the cathode, the plate, the control grids, the screen grid and the suppressor grid.
|
| 2. A tetrode contains
| a) the cathode, the plate, the suppressor grid and the screen grid.
b) the cathode, the plate, the screen grid and the control grid.
|
| 3. A triode contains
| a) the cathode, the plate and the screen grid.
b) the cathode, the plate and the control grid.
|
| 4. The function of the cathode is
| a) to collect electrons.
b) to eliminate the secondary emission.
c) to emit electrons.
|
| 5. The function of the plate is
| a) to eliminate oscillations.
b) to emit electrons.
c) to collect electrons.
|
| 6. The function of the control grid is
| a) to emit electrons.
b) to control the electron flow.
c) to eliminate secondary emission.
|
| 7. The function of the screen grid is
| a) to collect electrons.
b) to reduce the capacity.
c) to eliminate oscillations.
|
| 8. The function of the suppressor grid is
| a) to control the electron flow.
b) to eliminate secondary emission.
c) to eliminate oscillations.
|
| 9. Constant use of a tube results in
| a) high emission.
b) low emission.
c) an open heater.
|
6. Answer the following questions:
1. What types of electron tubes are used nowadays?
2. How many electrodes does a diode (a triode, a tetrode, a pentode) contain?
3. What is the function of the cathode (the plate, the control grid, the screen grid, the suppressor grid)?
4. What does the constant use of a tube result in?
5. What does low emission result from?
6. When must a tube be replaced?
Pentode
When in an operating tube the screen-grid voltage is high, secondary emission does not return to the plate and passes to the screen grid. This results in a counter flow of electrons. To eliminate this counter flow, a third grid was placed between the plate and the screen grid and connected to the cathode. This grid is called a suppressor grid. Since the suppressor grid has a negative potential it returns the secondary emission back to the plate and thus eliminates it in the tube. The tube containing electrodes - the cathode, the plate, the control grid, the screen grid and the suppressor grid - is called a pentode. The cathode emits electrons, the plate collects them, the control grid controls the flow of electrons, the screen grid helps the plate to collect electrons and reduces the capacity between the control grid and the plate, the suppressor grid eliminates the secondary emission.
Unit Eighteen [18]
1. a) Cover the right column and read the English words. Translate them into Russian and check your translation.
b) Cover the left column and translate theRussian words back into English.
| half
| [hɑːf]
| половина
|
| to rectify
| [ˈrektɪfaɪ]
| выпрямлять
|
| to amplify
| [ˈæmplɪfaɪ]
| усиливать
|
| toconvert
| [kənˈvəːt]
| преобразовывать, обращать
|
| bymeansof
|
| посредством, с помощью
|
| that is why
|
| вот почему
|
| to put into operation
|
| приводить в действие, запускать
|
| half
|
| половина
|
2. Read the words and put down their Russian equivalents:
| pulse
| [pʌls]
| _____________
| electron
| [ɪˈlektrɔn]
| ____________
|
| cycle
| [ˈsaɪkl]
| _____________
| radio
| [ˈreɪdɪou]
| ____________
|
3. Distribute the words below into the three columns:
[juːs] use, [juːz] use, rectifier, rectification, amplifier, amplify, convert, user,
converter, application, apply, pulse, pulsation, operate, operator
4. Translate these word combinations into Russian:
| a. half-wave
| ________________________________
|
| half-cycle
| ________________________________
|
| half-wave rectifier
| ________________________________
|
| positive half-cycles
| ________________________________
|
| electron tube application
| ________________________________
|
| negative half-cycles
| ________________________________
|
| by means of a filter
| ________________________________
|
|
|
|
| b.by means of the suppressor grid
| ________________________________
|
| tubes used as rectifiers
| ________________________________
|
| tubes used as oscillators
| ________________________________
|
Use of Electron Tubes
Let us consider some cases of electron tube application. Tubes are common elements of radio and electronic devices. Tubes are used
as rectifiers - to convert a.c. into d.c.,
as oscillators - to produce oscillating waves and
as amplifiers - to amplify the input voltage and current.
Half-Wave Rectifier
Alternating current is converted into direct current by means of a rectifier.
A half-wave rectifier consists of a diode in series with a resistance. In order to put a rectifier into operation, a source of a.c. should be applied to it. When an a.c. source is applied the diode begins to conduct. The rectifier passes currents during positive half-cycles of the applied voltage. That is why it is called a half-wave rectifier. When the device operates d.c. flows in the same direction. It is a pulsating current. Since pulsations should be eliminated, a filter is applied. Pulsations are eliminated by means of this filter.
5. Complete the sentences using the correct variant:
| 1. Electron tubes are used
| a) as amplifiers only.
b) as oscillators only.
c) as rectifiers, amplifiers and oscillators.
|
| 2. A.c. is converted into d.c.
| a) by means of a rectifier.
b) by means of an amplifier.
|
| 4. In order to put a rectifier into operation
| a) d.c. is applied.
b) a.c. is applied.
|
| 5. A half-wave rectifier passes currents
| a) during positive and negative half-cycles.
b) during positive half-cycles of the applied voltage.
|
| 6. Rectified current is
| a) direct oscillating current.
b) direct pulsating current.
|
| 7. Pulsations are eliminated
| a) by means of a choke coil.
b) by means of a filter.
|
6. Answer the following questions:
1. How are electron tubes used?
2. What type of device is called a rectifier?
3. By what means is alternating current rectified into direct current?
4. What elements does a half-wave rectifier consist of?
5. What current should be applied to put a half-wave rectifier into operation?
6. When does a half-wave rectifier pass current?
7. By what means are pulsations eliminated?
Full-wave Rectifier
In a full-wave rectifier two diodes are used. They are connected to a common load resistance. The secondary of the transformers has a centre tap to which the load is connected. Current flows through the tubes from their plates to their cathodes. When the upper end of the high-voltage winding is positive, current flows through die upper tube.
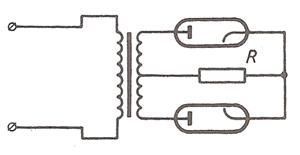 During the opposite half cycle the lower end of die high voltage winding becomes positive. The plate of the lower tube becomes positive and the plate of the upper tube - negative. Thus now the lower tube conducts current. Current flows through the filament winding to its centre tap, then through the load to the centre tap of the high-voltage winding and to the tube plate which is positive.
During the opposite half cycle the lower end of die high voltage winding becomes positive. The plate of the lower tube becomes positive and the plate of the upper tube - negative. Thus now the lower tube conducts current. Current flows through the filament winding to its centre tap, then through the load to the centre tap of the high-voltage winding and to the tube plate which is positive.
4. Complete the sentences using the correct variant:
| 1. A full-wave rectifier contains
| a) one diode.
b) two diodes.
|
| 2. The load is connected to
| a) the centre tap of the primary.
b) the centre tap of the secondary.
|
| 3. Current flows through the tubes
| a) from the plates to the cathodes.
b) from the cathodes to the plates.
|
| 4. When the upper end of the high-voltage winding is positive
| a) current flows through the upper tube.
b) current flows through the lower tube.
|
| 5. During the negative half-cycle
| a) the plate of the lower tube becomes positive.
b) the plate of the lower tube becomes negative.
|
| 6. During the positive half-cycle
| a) the lower tube conducts current.
b) the upper tube conducts current.
|
5. Complete the sentences using while. Follow the model on page 13.
1. A half -wave rectifier contains one diode ….
2. When the upper end of the high-voltage winding is positive, current flows through the upper tube ….
3. During the negative half-cycle the lower tube conducts current ….
Push-pull Amplifier
An amplifier is used to produce the output voltage greater than the input voltage. A push-pull amplifier includes two tubes. Their control grids are connected to the opposite ends of the input transformer secondary winding. The centre of this winding is connected to the tube cathodes. When maximum grid voltage is produced in one tube, minimum grid voltage is produced in the other tube. Thus, the sum of the plate currents remains constant.
The plate currents are fed into the opposite ends of the output transformer or a choke coil. It has its centre connected through the plate current supply to the cathodes. Thus direct current plate components are eliminated but alternating current components add in the circuit.
3. Complete these sentences, using the correct variant:
| 1. An amplifier is used
| a) to separate a.c. from d.c.
b) to change the value of the input voltage.
|
| 2. The input voltage is increased
| a) by means of a rectifier.
b) by means of an amplifier.
|
| 3. A push-pull amplifier includes
| a) only one tube.
b) two tubes.
|
| 4. When maximum grid voltage is produced in one tube
| a) maximum grid voltage is produced in the other tube.
b) minimum grid voltage is produced in the other tube.
|
| 5. The sum of the plate currents
| a) changes.
b) remains constant.
|
| 6. D.c. components
| a) are eliminated.
b) add in the circuit.
|
| 7. A.c. components
| a) add in the circuit.
b) are eliminated.
|
4. Complete the sentences using while. Follow the model on page 13:
1. An amplifier is used to increase the value of the input voltage ….
2. When maximum grid voltage is produced in one tube ….
3. Direct current plate components are eliminated ….
5. Answer the following questions:
1. What is an amplifier used for?
2. By what means is a greater output voltage produced?
3. What are the main parts of a push-pull amplifier?
4. In what way are the tubes and the transformer connected?
5. Why does die sum of the plate currents remain constant?
6. Where are the plate currents fed?
7. What type of current is amplified by a push-pull amplifier?
8. What is the difference between a rectifier and an amplifier?
Amplifier Stages in Series
Amplifiers in use nowadays contain several stages. Sometimes their number is very great. Let us consider an amplifier including three stages. Its circuit uses three triodes connected in series. The circuit has a resistance as the plate load. A common plate voltage supply and a common grid bias are employed. The grid of each tube is insulated from the direct current component of the plate voltage by means of a capacitor. When the amplifier operates the voltage operation of the load of one tube is applied to the grid of the next tube. The voltage variation is transferred to the grid of the following tube through a capacitor.
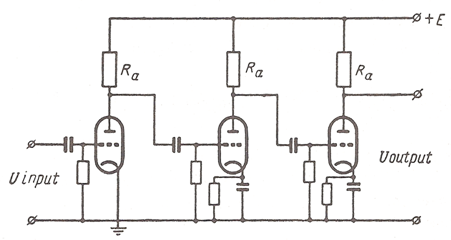
Fig. 17
A change of voltage on the first grid circuit results in an amplified plate current in the third stage.
3. Complete these sentences, using the correct variant:
| 1. Amplifiers in use nowadays
| a) include only one stage.
b) include several stages.
|
| 2. A three-stage amplifier uses
| a) three triodes connected in parallel.
b) three triodes connected in series.
|
| 3. The grid of each tube is insulated
| a) by means of a coil.
b) by means of a capacitor.
|
| 4. The voltage variation is transferred
| a) through a tube.
b) through a capacitor.
|
| 5. The circuit uses
| a) a different grid bias.
b) a common grid bias.
|
4. Answer the following questions:
1. How many stages do amplifiers include?
2. What are the main parts of a three-stage amplifier?
3. By what means are the grids of the tubes insulated?
4. What type of grid bias is employed?
5. In what way is the voltage variation transferred?
Unit Twenty-Two [22]
1. a) Cover the right column and read the English words. Translate them into Russian and check your translation.
b) Cover the left column and translate theRussian words back into English.
| spring
|
| пружина
|
| cross-section
|
| поперечное сечение
|
| to close
| [klouz]
| замыкать, закрывать
|
| close to
| [ˈkloustə]
| близко к (от)
|
| to move
|
| двигаться), приводить в движение
|
| to switch on
|
| включать
|
| to switch off
|
| выключать
|
| various
| [ˈvɛərɪəs]
| различный, разнообразный
|
Electromagnetic Relay
Electromagnetic devices called relays are widely used in various branches of industry.
The main parts of a relay are an electromagnet, a spring and an armature. When a current starts flowing in the electromagnet winding, the armature moves and the spring closes the contacts. The primary circuit of a relay is its electromagnet circuit and the secondary circuit is the one closed by the contacts.
When there is no current in the relay’s primary circuit, the spring pulls the armature and the contacts open.
Fig. 18 shows how a relay is used to control the work of an electric motor. The relay is placed close to the motor which is connected to its secondary circuit. The armature closes the contacts of the secondary circuit, and the motor starts operating; it will stop when the relay opens.
Without a relay, conductors with a large cross-section would have to be brought to the motor. This would be very uneconomical. The current in a relay is tens and even thousands of times smaller than that used to power the motor. Therefore, the connecting wires can have small cross-sections.

Fig. 18
In many systems the relay primary circuit operates automatically. Every evening and morning street lights are switched on and off from the main control panel by means of a great number of relays.
5. Complete the sentences using the correct variant:
| 1. The main parts of a relay are
| a) an electromagnet, a capacitor, and a spring.
b) an electromagnet, an armature, and a spring.
|
| 2. When current starts flowing
| a) the spring opens the contacts.
b) the spring closes the contacts.
|
| 3. The spring pulls the armature
| a) when there is current in the primary circuit.
b) when there is no current in the primary circuit.
|
| 4. The wires connecting the panel with the relay
| a) have a large cross-section.
b) have a small cross-section.
|
| 5. Street lights are switched on and off
| a) by means of relays.
b) by means of electric motors.
|
6. Complete these sentences using while. Follow the model on page 13:
1. The primary circuit of a relay is its electromagnetic circuit ….
2. When there is no current in the relay’s primary circuit the contacts open ….
3. Without a relay conductors with a large cross-section should be used ….
4. Every evening street lights are switched on ….
7. Answer the following questions:
1. What are the main parts of a relay?
2. How is a relay put into operation?
3. When does the spring pull the armature?
4. What wires connect the panel with the relay?
5. By what means are street lights switched on and off?
8. Pair work. a) Match the questions and the answers, b) Ask the questions and let your groupmate answer them.
| 1. In what position does die switch have high (low) resistance?
2. What are die functions of the switch?
3. In what position is the switch open? Closed?
4. In what way is the switch connected to the circuit?
| a) Switches are used to open and close the circuits.
b) Closed is the on-position; open is the off-position.
c) The switch is connected in series with the load.
d) In the on-position the closed switch has a very low resistance, which results in maximum current in the load with zero voltage loss across the switch. When the switch is off it has a very high resistance and no current flows through the circuit.
|
Unit Twenty-Three [23]
1. a) Cover the right column and read the English words. Translate them into Russian and check your translation.
b) Cover the left column and translate the Russian words back into English.
| fuse
| [fjuːz]
| плавкий предохранитель
|
| link
| [lɪŋk]
| звено, связь
|
| fault
| [fɔːlt]
| дефект, неисправность
|
| faulty
|
| неисправный
|
| equipment
| [ɪˈkwɪpmənt]
| оборудование
|
| installation
| [ˌɪnstəˈleɪʃn]
|
|
|
|








 During the opposite half cycle the lower end of die high voltage winding becomes positive. The plate of the lower tube becomes positive and the plate of the upper tube - negative. Thus now the lower tube conducts current. Current flows through the filament winding to its centre tap, then through the load to the centre tap of the high-voltage winding and to the tube plate which is positive.
During the opposite half cycle the lower end of die high voltage winding becomes positive. The plate of the lower tube becomes positive and the plate of the upper tube - negative. Thus now the lower tube conducts current. Current flows through the filament winding to its centre tap, then through the load to the centre tap of the high-voltage winding and to the tube plate which is positive.




