1.__________ (also known as fusion) is a physical process that results in the phase transition of a substance from a solid to a liquid. This occurs when the internal energy of the solid increases, typically by the application of heat or pressure, which increases the substance's temperature to the melting point. At the melting point, the ordering of ions or molecules in the solid breaks down to a less ordered state, and the solid melts to become a liquid. An object that has melted completely is molten (although this word is typically used for substances that melt only at a high temperature, such as molten iron or molten lava).
Substances in the molten state generally have reduced viscosity as the temperature increases. An exception to this principle is the element sulfur, whose viscosity increases to a point due to polymerization and then decreases with higher temperatures in its molten state.
Some organic compounds melt through mesophases, states of partial order between solid and liquid.
2. __________ is the change of the physical state of matter from gas phase into liquid phase, and is the reverse of evaporation. The word most often refers to the water cycle. It can also be defined as the change in the state of water vapour to liquid water when in contact with a liquid or solid surface or cloud condensation nuclei within the atmosphere. When the transition happens from the gaseous phase into the solid phase directly, the change is called deposition.
3. __________, or the solidification of a gas by cooling, is the opposite of sublimation, which vaporizes solids without first liquifying them. In chemistry, this process is used widely to create materials in industry, especially to apply a thin coating to materials used for cutting or shaping. Much research is ongoing in the field of chemical vapor deposition, especially in the area of materials used to cover polymers, and finding materials that are less harmful to the environment.
4. __________ of an element or compound is a phase transition from the liquid phase to vapor. There are two types of this process: evaporation and boiling. Evaporation is a surface phenomenon, whereas boiling is a bulk phenomenon.
Evaporation is a phase transition from the liquid phase to vapor (a state of substance below critical temperature) that occurs at temperatures below the boiling temperature at a given pressure. Evaporation occurs on the surface. Evaporation only occurs when the partial pressure of vapor of a substance is less than the equilibrium vapor pressure.
Boiling is also a phase transition from the liquid phase to gas phase, but boiling is the formation of vapor as bubbles of vapor below the surface of the liquid. Boiling occurs when the equilibrium vapor pressure of the substance is greater than or equal to the environmental pressure. The temperature at which boiling occurs is the boiling temperature, or boiling point. The boiling point varies with the pressure of the environment.
5. __________ is the process by which an atom or a molecule acquires a negative or positive charge by gaining or losing electrons to form ions, often in conjunction with other chemical changes. This process can result from the loss of an electron after collision s with subatomic particles, collisions with other atoms, molecules and ions, or through the interaction with light. Heterolytic bond cleavage and heterolytic substitution reactions can result in the formation of ion pairs.
This process can occur through radioactive decay by the internal conversion process, in which an excited nucleus transfers its energy to one of the inner-shell electrons causing it to be ejected.
6. __________ is the process of ions removal. The term is generally used with respect to removal of ions from water. It is commonly achieved by passing the water through successive ion exchange columns. In one column, ions are exchanged for H+ ions. In another column, anions are exchanged for OH- ions. Following a reaction of H+ with OH- ions, no ions remain in solution.
7. __________, or solidification, is a phase transition in which a liquid turns into a solid when its temperature is lowered below its freezing point. Most liquids freeze by crystallization, formation of crystalline solid from the uniform liquid. This is a first-order thermodynamic phase transition, which means that, as long as solid and liquid coexist, the temperature of the whole system remains very nearly equal to the melting point due to slow removal of heat when in contact with air, which is a poor heat conductor. Because of the latent heat of fusion, the freezing is greatly slown down and the temperature will not drop anymore once the freezing starts but will continue dropping once it finishes. Crystallization consists of two major events, nucleation and crystal growth. Nucleation is the step wherein the molecules start to gather into clusters, on the nanometer scale, arranging in a defined and periodic manner that defines the crystal structure. The crystal growth is the subsequent growth of the nuclei that succeed in achieving the critical cluster size.
8. __________ is the transition of a substance directly from the solid to the gas phase without passing through the intermediate liquid phase. This is an endothermic phase transition that occurs at temperatures and pressures below a substance's triple point in its phase diagram. The reverse process is deposition, in which a substance passes directly from a gas to a solid phase.
At normal pressures, most chemical compounds and elements possess three different states at different temperatures. In these cases, the transition from the solid to the gaseous state requires an intermediate liquid state. The pressure referred to is the partial pressure of the substance, not the total (e.g. atmospheric) pressure of the entire system. So, all solids that possess an appreciable vapor pressure at a certain temperature usually can sublimate in air (e.g. water ice just below 0 °C). For some substances, such as carbon and arsenic, sublimation is much easier than evaporation from the melt, because the pressure of their triple point is very high, and it is difficult to obtain them as liquids.
4. Find English equivalents of the following terms:
внутренняя конверсия, возбужденное ядро, вязкость, газообразное состояние, давление насыщенных паров, испарение, кипение, кристаллическое твёрдое тело, невалентный электрон, облачные ядра конденсации, образование центров кристаллизации, однородная жидкость, отвердевание, парциальное давление, последующий, превращение в жидкость (разжижение), расплавленный, раствор, расщепление связи, реакция замещения, с поглощением тепла, столкновение, точка плавления, тройная точка, упорядоченное состояние, фазовый переход, фазовый переход первого рода.
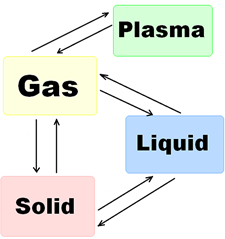
5. Insert the terms from Text B into the phase transition scheme:
6. Comprehension check. Read these statements about Text B and decide if the they are true (T) or false (F) supporting your answers with necessary information from the text:
1. Evaporation occurs below the surface of the liquid.
2. There are two types of melting: evaporation and boiling.
3. Boiling occurs when the equilibrium vapor pressure of the substance is less than the environmental pressure.
4. The boiling point varies with the pressure of the environment.
5. All solids that possess an appreciable vapor pressure at a certain temperature usually can sublimate in air.
6. Deposition is the transition of a substance directly from the solid to the gas phase.
7. The reverse process to sublimation is deposition, in which a substance passes directly from a gas to a liquid phase.
8. Fusion is also called melting.
9. Substances in the molten state generally have reduced viscosity as the temperature decreases.
10. Solidification, or freezing, is a phase transition in which a liquid turns into a solid when its temperature goes down to its freezing point.
11. Air is a good heat conductor.
12. Ionization is the process of ions removal.
13. Deionization can occur through radioactive decay by the internal conversion process.
14. Heterolytic bond cleavage and heterolytic substitution reactions can result in the formation of ion pairs.
15. Deposition is also known as solidification of a gas by cooling.
16. A lot of research is ongoing in the field of chemical vapor deposition, especially in the area of materials used to cover polymers.
17. Evaporation is the change of the physical state of matter from the gas phase into the liquid phase.









