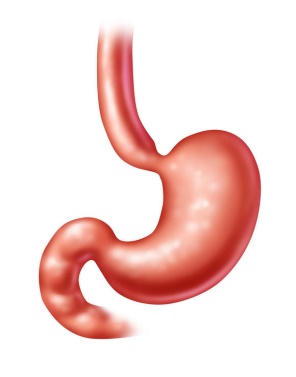
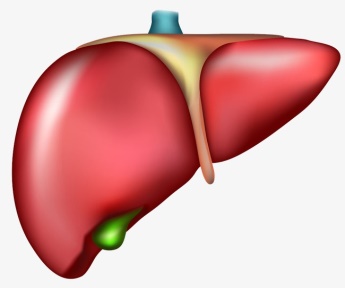

8. Do ‘GI Tract Quiz’
 GI Tract Quiz (Yes\No)
GI Tract Quiz (Yes\No)

1. Gastrointestinal is an adjective meaning ‘pertaining to the stomach and intestines’.
o Yes
o No
2. GI tract is a small fibrous tube.
o Yes
o No
3. The release of hormones and enzymes takes place in the intestines.
o Yes
o No
4. The movement of organ walls is called peristalsis.
o Yes
o No
5. The intestines divide into small intestine and large intestine.
o Yes
o No
6. Food begins its journey through the digestive system in the stomach.
o Yes
o No
7. Esophagus passes through the posterior mediastinum in the pelvis.
o Yes
o No
8. The acid called eithergastric acid or gastric juice, produced in the stomach.
o Yes
o No
9. Accessory organs are the particular organs that are not directly part of the gastrointestinal tract, but rather attached to this system.
o Yes
o No
10. The gallbladder is used both to store and to recycle excess bile from the small intestine.
o Yes
o No
11. Spleen is known as the 'graveyard of red blood cells'.
o Yes
o No
12. The pancreas is a major organ functioning as an accessory digestive gland in the digestive system.
o Yes
o No

9. Read the text and check your answers:

Gastrointestinal tract
The gastrointestinal tract (digestive tract, digestional tract, GI tract, GIT, gut, or alimentary canal) is an organ system which takes in food, digests it to extract and absorb energy and nutrients, and expels the remaining wastes. Gastrointestinal is an adjective meaning of or pertaining to the stomach and intestines. The GI tract is a large, muscular tube consisting of mouth, esophagus, stomach and intestines where the movement of muscles, along with the release of hormones and enzymes, allows for the digestion of food. A tract also has a collection of related anatomic structures or a series of accessory organs (the tongue, salivary glands, pancreas, liver and gallbladder). The whole human GI tract is about nine meters (30 feet) long. The large, hollow organs of the GI tract contain a layer of muscle that enables their walls to move. The movement of organ walls, called peristalsis, propels food and liquid through the GI tract and mixes the contents within each organ.
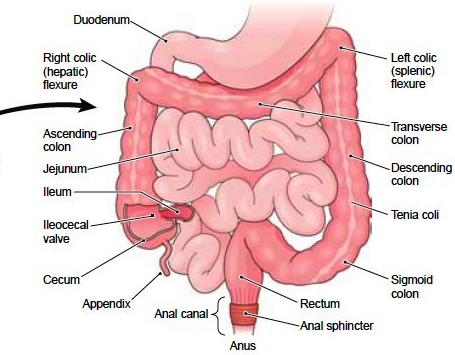
The tract is divided into upper and lower tracts, and the intestines small and large parts.The upper gastrointestinal tract consists of the buccal cavity, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, and duodenum.The lower gastrointestinal tract includes most of the small intestine and all of the large intestine. In human anatomy the intestine (bowel, or gut. Greek: éntera) is the segment of the gastrointestinal tract extending from the pyloric sphincter of the stomach to the anus. In humans, the small intestine is further subdivided into the duodenum, jejunum and ileum while the large intestine also called the colon, consists of cecum (first portion of the colon) and appendix, ascending colon (ascending in the back wall of the abdomen), right colic flexure (flexed portion of the ascending and transverse colon apparent to the liver), transverse colon (passing below the diaphragm), left colic flexure (flexed portion of the transverse and descending colon apparent to the spleen), descending colon (descending down the left side of the abdomen), sigmoid colon (a loop of the colon closest to the rectum), rectum and anus
Food begins its journey through the digestive system in the mouth, also known as the oral cavity. Inside the mouth there are many accessory organs aiding in the digestion of food—the tongue (organ of taste), teeth, and salivary glands (3 sets) producing saliva. Teeth chop food into small pieces, which are moistened by saliva before the tongue and other muscles push the food into the pharynx.
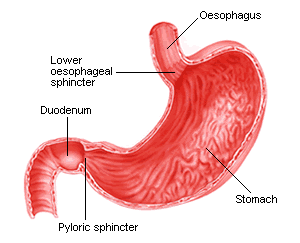
The next hollow organ, after the mouth, is the esophagus. This organ is a tube that is made of muscular tissue measuring approximately 25 cm in length in an adult person. The entire tube is lined with mucosa. It passes through the posterior mediastinum in the thorax and enters the stomach through a hole in the thoracic diaphragm at the level of the tenth thoracic vertebra (T10). It connects the pharynx to the stomach, and is responsible for delivering food to the stomach.
The stomach is a major organ of the GI tract. It is a consistently J-shaped muscular sac joined to the esophagus at its upper end and to the duodenum at its lower end, located on the left side of the abdominal cavity, just inferior to the diaphragm. The acid called either gastric acid or gastric juice, produced in the stomach, plays a vital role in the digestive process. In an average person, the stomach is about the size of two fists placed next to each other. The stomach is a distensible organ and can normally expand to hold about one liter of food.
The small intestine measures around 6.7 meters in length in the adult body constituting the part of the lower gastrointestinal tract. It is located just inferior to the stomach and takes up most of the space in the abdominal cavity. The entire small intestine is coiled like a hose and the inside surface is full of many ridges and folds. The main functional segments of the small intestine are the duodenum, the jejunum, and the ileum.
The large intestine is a long, thick tube about 2.5 meters long. It is located just inferior to the stomach and wraps around the superior and lateral border of the small intestine. The large intestine absorbs water and contains many symbiotic bacteria that aid in the breaking down of wastes to extract some small amounts of nutrients. Feces in the large intestine exit the body through the anal canal.
Accessory organs are the particular organs that are not directly part of the gastrointestinal tract, but rather attached to this system. Food does not move through these organs. Instead, these organs usually secrets certain substances into the stomach to assist with the process of digesting and absorbing food molecules. 
The liver is found to the right of the stomach, just inferior to the diaphragm and superior to the small intestine. It is the second largest organ in the body having a shape that is similar to a cone, with a dark brown/red color. The liver weighs approximately three pounds. It is made up of two fundamental lobes. Each of these lobes is divided into a total of eight segments, and then the segments are once again into around a thousand lobules (small lobes). The lobules are connected to tubes that are called either small ducts or hepatic ducts. They deliver bile to the duodenum. Bile is produced by liver cells inside the liver. Liver delivers bile both to the small intestine, and to the gallbladder. The gallbladder is a small, pear-shaped organ located just posterior to the liver. The gallbladder is used both to store and to recycle excess bile from the small intestine so that it can be reused for the digestion of subsequent meals.
The spleen breaks down both red and white blood cells that ‘are spent’. This is why it is sometimes known as the 'graveyard of red blood cells'. A product of this ‘digestion’ is the pigment bilirubin, which is sent to the liver and secreted in the bile.
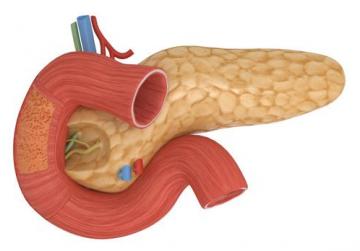
The pancreas is a major organ functioning as an accessory digestive gland in the digestive system. It is both an endocrine gland and an exocrine gland. The pancreas lies below and at the back of the stomach. The endocrine part secretes insulin when the blood sugar becomes high; insulin moves glucose from the blood into the muscles and other tissues for use as energy. The pancreas produces and releases important digestive enzymes in the pancreatic juice that it delivers to the duodenum.
The GI tract has several vital functions to perform both digesting of food and containing the body’s first defensive mechanism against potentially harmful substances, playing an important role in the immune system.
10. Complete words with missing letters:
Int_st_ne, stoma_h, duod_num, l_ver, b_le, g_llbla_der, dia_hra_m, eso_hag_s, med_ast_num, mo_th, enz_me, p_ar_nx, t_ng_e, d_ges_ion.
11. Compose 6pairs of antonyms from the word list given below:
Microscopic anatomy, upper tract, to digest, large intestine, to release, accessory organ, gross anatomy, major organ, lower tract, to ascend, small intestine, to descend
12. Make a word combination, match the words:
large system
gastricgland
gastrointestinal anatomy
transverse tract
alimentary colon
salivary intestine
digestive canal
human juice
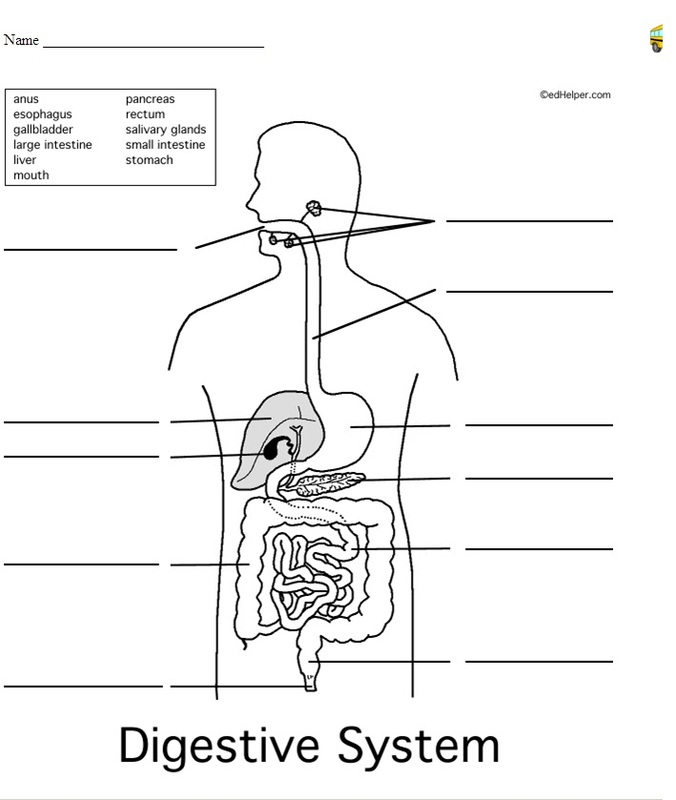
13. Fill in the digestive system diagram with the words in the box:
14. Make word combinations from the verbs and nouns given below:
Verbs: release, absorb, digest, expel, play, divide into,
Nouns: role, segments, energy, food, wastes, enzymes
15. Fill in gaps with prepositions:
in, of, in, into, with, to, into, through, of, in, to
1.Digestive system is a system taking __ food. 2. Both major organs and accessory organs pertaining __ GI tract take part __ food digestion. 3. The small intestine is a muscular tube consisting __ duodenum, jejunum and ilium. 4. The GI tract is divided ____ upper and lower tracts. 5. There are several accessory organs which aid __ food digestion. 6. Esophagus is a tube made __ muscular tissue. 7. The entire tube is lined ____ mucosa. 8. Food does not move _______accessory organs. 9. Liver and pancreas secret certain substances _____ the small intestine. 10. The lobules are connected __ hepatic ducts.
16. Match two parts of the sentence:
1) The GI tract is a large, muscular tube
2) The intestine is the segment of the gastrointestinal tract
3) The small intestine measures around 6.7 meters in length in the adult body
4) The lobules are connected to tubes
5) The gallbladder is a small, pear-shaped organ
6) The pancreas is a major organ functioning
a) as an accessory digestive gland in the digestive system.
b) that are called either small ducts or hepatic ducts.
c) constituting the part of the lower gastrointestinal tract.
d) consisting of mouth, esophagus, stomach and intestines.
e) extending from the pyloric sphincter of the stomach to the anus.
f) located just posterior to the liver.
17. Complete the information with the words\word combinations given below according to the text ‘Gastrointestinal tract’.
esophagus, intestines, pharynx, energy and nutrients, salivary glands, lobules, diaphragm, accessory organs, exocrine gland, body system, stomach, lobes
The GI tract is a ___________ taking in food, digesting it to extract and absorbing___________. It is a large, muscular tube consisting of mouth, ________, __________and intestines. A tract also has a series of______________. The tract itself is divided into upper and lower tracts, and the__________ small and large parts. Inside the mouth there are many accessory organs - the tongue, teeth, and ____________. Esophagus connects the ________to the stomach. The stomach is a major organ of the GI tract located on the left side of the abdominal cavity, just inferior to the ________. Liver is the second largest organ in the body made up of two fundamental______. Each of these lobes is divided into a total of eight segments subdividing into many_______. Pancreas is both an endocrine gland and an ______________.
18. Fill in the chart:
| Gastrointestinal
| tract
|
| Major organs
| Accessory organs
|
|
|
|

Speaking
19. Group work. Discuss the question in the group and fill in the map ’ GI’.
Note:You may add more boxes to fill in your ideas
· What is the most interesting information for you in the text? Why? Give your reasons
· What information have you met for the first time?
· What facts did you know before?
· Think of how you can use this information in your future work in the field of medicine and in everyday life. Give your ideas.












 GI Tract Quiz (Yes\No)
GI Tract Quiz (Yes\No)










