

Кормораздатчик мобильный электрифицированный: схема и процесс работы устройства...

История развития пистолетов-пулеметов: Предпосылкой для возникновения пистолетов-пулеметов послужила давняя тенденция тяготения винтовок...

Кормораздатчик мобильный электрифицированный: схема и процесс работы устройства...

История развития пистолетов-пулеметов: Предпосылкой для возникновения пистолетов-пулеметов послужила давняя тенденция тяготения винтовок...
Топ:
Устройство и оснащение процедурного кабинета: Решающая роль в обеспечении правильного лечения пациентов отводится процедурной медсестре...
Характеристика АТП и сварочно-жестяницкого участка: Транспорт в настоящее время является одной из важнейших отраслей народного хозяйства...
Выпускная квалификационная работа: Основная часть ВКР, как правило, состоит из двух-трех глав, каждая из которых, в свою очередь...
Интересное:
Национальное богатство страны и его составляющие: для оценки элементов национального богатства используются...
Уполаживание и террасирование склонов: Если глубина оврага более 5 м необходимо устройство берм. Варианты использования оврагов для градостроительных целей...
Искусственное повышение поверхности территории: Варианты искусственного повышения поверхности территории необходимо выбирать на основе анализа следующих характеристик защищаемой территории...
Дисциплины:
|
из
5.00
|
Заказать работу |
Содержание книги
Поиск на нашем сайте
|
|
|
|
In the absence of a law provision regulating similar relations, the law-enforcer eliminates a gap in a law in accordance with general principles and the meaning of the legislation.
Analogy of law and analogy of legislation take place in the Russian civil law-enforcement practice, but are prohibited in the administrative and criminal laws.
Vocabulary
ascertain v выяснять; устанавливать; определять
compliance n выполнение, соблюдение (правовых норм)
embodiment n воплощение, олицетворение; embody v воплощать; содержать
gap n пробел
implementation n выполнение, осуществление
provision n условие, положение (договора, закона)
social benefit n пособие по социальному страхованию
solely [‘səulli] adv исключительно, только
substantiate v обосновывать
welfare payment n выплата пособия
Text B
Application of Law Enforcement
The state has many ways of making sure that citizens obey the law. It makes the public aware of what the law is and tries to encourage social support for law and order. It uses militia to investigate crimes and catch criminals. It authorizes courts to complete the investigation of criminal and civil offences and to pass sentences to punish the guilty and deter others. And it makes efforts to re-educate and reform people who have broken the law.
Ignorance of the law is almost never a defence for breaking it. Governments usually expect citizens to be aware of the laws which affect their lives. Sometimes this seems very harsh, for example, when the law is very technical. However, there are many laws, such as those prohibiting theft, assault and dangerous driving, which simply reflect social and moral attitudes to everyday behaviour. In such cases a person knows he is breaking the law, even if he doesn’t know exactly which law it is.
The state combats crime through the courts, the Prosecutor's Office, investigating authorities, state security bodies, militia and other law-enforcement agencies. They have to perform a series of acts to establish the fact of the crime, discover the offender and determine the penalty to be imposed in virtue of law.
After receiving information that a crime has been committed, the investigator, for instance, commences the preliminary investigation: he inspects the scene of the crime, summons and questions witnesses, detains suspects. The militia, the investigator, the prosecutor and the court may make such demands only within the power vested in them by law.
The challenge of the militia has always been to protect state and personal property, to maintain public law and order, to safeguard the rights and interests of citizens. To fulfil these functions properly the Internal Affairs bodies compose several departments. The Criminal Detection Department is to detect the criminal, that is to locate and arrest him (her). The Criminal Investigation Department collects evidence to prove the guilt or innocence of a suspect. The Economic Crimes Department reveals the economic offences. The mission of the State Inspection of Road Traffic Security is to regulate safety in the roads. The Juvenile Inspection is responsible for prevention of juvenile delinquency.
Vocabulary
challenge n стремление
combat crime v бороться с преступностью
commence v начинать
commit a crime v совершить преступление
Criminal Investigation Department n уголовный розыск
detain a suspect v задержать подозреваемого
dete r v сдерживать; удерживать от совершения чего-либо
discover v находить
impose a penalty v налагать наказание
investigator n следователь
in virtue of law в силу закона
maintain law and order поддерживать правопорядок
militia [mı' lı∫ə] n милиция
obey the law v следовать закону, подчиняться закону
offence n правонарушение, преступление
offender n правонарушитель
perform acts v проводить действия
pose v создавать (проблему); представлять
preliminary n предварительное следствие
the Prosecutor’s Office n прокуратура
prohibit v запрещать
summon v вызывать
state security bodies органы госбезопасности
Reading tasks
Answer these questions.
1 What does implementation of law provisions mean?
2 What is the peculiarity of law enforcement?
3 What are the major requirements to law enforcement acts?
4 Why can’t law enforcement acts be sources of law?
5 How is law enforcement executed?
6 What are the main stages of law enforcement?
7 How do you understand ‘a gap in a law’?
8 What can be done when a gap in a law is discovered?
9 Through what bodies does the state combat crime?
10 What acts must these bodies perform?
11 What does the investigator do after receiving information that a crime has
been committed?
12 What functions does the militia have to perform in the law-enforcement
process?
13 Is ignorance of the law a defence for breaking it? Give reasons for it.
14 What are the ways of making sure that citizens obey the law?
Language focus
Complete the sentences using a gerund or an infinitive in brackets.
A
The Interior Minister hopes 1) _____ (to put / putting) an end to the eternal rivalry of Russian law-enforcement agencies, but these forces are somewhat sceptical to his good will. “It is expedient 2) _____ (to vest / vesting) coordination of the operational activities of law – enforcement agencies in the sphere of 3) _____ (to fight / fighting) organized crime to me by a presidential decree”, the Interior Minister wrote in a classified letter to the Russian President.
B
1 I persuaded my client _____ (to present / presenting) the tape as evidence.
2 They were excited about _____ (to hear / hearting) the President.
3 Supervision on _____ (to observe / observing) the laws is carried out by the
Office of the Prosecutor General.
4 She denied _____ (to steal / stealing) the money.
5 Our neighbour threatened _____ (to call / calling) the police if we didn’t stop
the noise.
6 The customs officer ordered him _____ (to open / opening) the case.
Vocabulary tasks
A Who performs the following actions? Choose the necessary words from the box.
|
1 _____ perform a series of acts to establish the fact of the crime.
2 _____ makes the public aware of what the law is and tries to encourage social
support for law and order.
3 _____ should take part in examinations and searches.
4 _____ authorizes courts to complete the investigation of criminal and civil
offences and to pass sentences to punish the guilty and deter others.
5 _____ makes efforts to re-educate and reform people who have broken the law.
B Finish the sentences using the words in brackets.
1 The Supreme Court examines more serious _____. (crimes, article, case, clause, murder).
2 After receiving the information that a crime has been committed, the investigator commences the preliminary _____. (questioning, seizure, investigation, punishment, sentence).
3 The militia safeguards _____. (a criminal, an offender, the interests of citizens, an assessor).
4 The challenge of the militia has always been to protect _____, to maintain _____. (state and personal property, criminals, offenders, public law and order).
C Complete the following sentences by translating the words and expressions in
brackets.
1 The (следователь) commences the preliminary investigations.
2 The investigator summons and questions (свидетелей).
3 The (уголовный розыск) collects evidence to prove the guilt or innocence of a
suspect.
4 Criminal (процесс) is investigation of criminal cases by investigating bodies.
5 Dangerous antisocial act directed against social and state system is a
(преступление).
6 The courts, the Prosecutor's Office, investigators, state security bodies, the militia are (органы расследования).
D Which law-enforcement body deals with:
1 preliminary investigation?
2 witnesses and suspects?
3 road traffic offences?
4 juvenile delinquency?
E Enumerate:
1 the investigating bodies
2 the functions, performed by the investigating bodies
3 the investigator's duties
4 the acts, performed by the investigator
5 the law-enforcement agencies taking part in investigations of criminal cases
6 the ways the state makes citizens obey the law
7 the departments of the militia
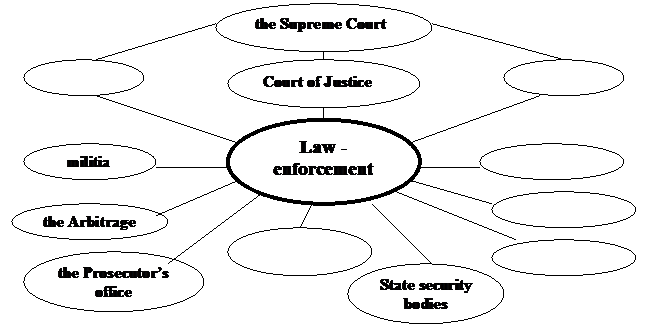
F Complete the diagram. Remove or add the names of law-enforcement bodies if necessary.
Over to you
1 Discuss the problem questions:
a) Why are the agencies combating the crimes so numerous?
b) Should all the combating the crime bodies communicate with each other?
2 Discuss the role of the militia in law enforcement.
CHAPTER VI THE COURTS
|
|
|

Опора деревянной одностоечной и способы укрепление угловых опор: Опоры ВЛ - конструкции, предназначенные для поддерживания проводов на необходимой высоте над землей, водой...

Типы сооружений для обработки осадков: Септиками называются сооружения, в которых одновременно происходят осветление сточной жидкости...

Своеобразие русской архитектуры: Основной материал – дерево – быстрота постройки, но недолговечность и необходимость деления...

Семя – орган полового размножения и расселения растений: наружи у семян имеется плотный покров – кожура...
© cyberpedia.su 2017-2025 - Не является автором материалов. Исключительное право сохранено за автором текста.
Если вы не хотите, чтобы данный материал был у нас на сайте, перейдите по ссылке: Нарушение авторских прав. Мы поможем в написании вашей работы!