Management and Managers
Менеджмент и Менеджеры
Методические указания по английскому языку
для студентов 1,2 курсов инженерно-экономического факультета
Составители И.В. Губанова
Л.К. Чадина
Утверждены на заседании кафедры
Протокол №4 от 24.12.08
Рекомендованы к печати
учебно-методической комиссией
специальности 080502
Протокол № от
Электронная копия находится
в библиотеке главного корпуса
ГУ КузГТУ
КЕМЕРОВО 2008
Настоящая разработка предназначена для студентов 1 и 2 курса инженерно-экономического факультета, изучающих менеджмент.
Целью разработки является ввести на английском языке основы менеджмента. Студенты познакомятся с определением "менеджмент" и "менеджер", функциями и обязанностями менеджеров, а также качествами, которыми современные менеджеры должны обладать.
Данные методические указания состоят из пяти секций. Каждая секция содержит задания на развитие навыков говорения. Для успешного овладения материалом предлагается англо-русский словарь, упражнения на знание интернациональной лексики и на словообразование. Тексты иллюстрированы диаграммами и схемами, что помогает лучшему восприятию.
Большинство текстов подобраны из американских и английских источников.
SECTION 1.
Words to be learned:
| activity
| - деятельность
|
| authority
| - полномочие, власть, влияние
|
| to be responsible for
| - быть ответственным за
|
| to be in charge of
| - oтвечать за, заведовать
|
| to direct
| - руководить, направлять
|
| employee
| - служащий, работающий по найму
|
| executive
| - администратор, руководитель
|
| to carry out
| - выполнять
|
| to involve
| - затрагивать, вовлекать, касаться
|
| level
| - уровень
|
| to manage
| - руководить, заведовать, управлять
|
| to make decisions
| - принимать решения
|
| to mean (meant,meant)
| - иметь в виду, подразумевать, значить
|
| non - profit
| - некоммерческий
|
| personal relationships
| - личные отношения
|
| profit-making
| - коммерческий
|
| promotion
| - продвижение
|
| to refer to
| - отсылать к, ссылаться на
|
| to sell ( sold , sold )
| - продавать
|
| to solve a problem
| - решать проблему
|
| subordinate
| - подчиненный
|
| to supervise
| - смотреть, надзирать, руководить
|
1.2. Read and translate the following international words:
management, manager, tradition, plan, organize, control, coordination, active, group, expert, organization, Industrial Revolution, professional manager, term, strategy, technique, basis, mission, military, definition, director, service, president, vice-president, line, office, administrator, administration, university, hospital, social, agency, system, personnel, personal, finance, marketing, product, production, problem, risk, company, individual, national, culture, argument, scheme, function, functional, project, contrast, structure, company, diagram; resource
Word-building. Translate into Russian.
to manage – management – manager – managerial; to plan – planning;
to control – controlling; to direct – director – directing; to lead – leader – leading; to organize – organizer – organization; to produce – producer – productive – production; person – personal; function – functional; tradition – traditional – traditionally; industry – industrial; responsible – responsibility; success – successful – successfully
1.4. Read the text and say what the idea of management is.
What Is "Management"?
What is "management"? There are a variety of views about this term. Traditionally, the term “management” refers to planning, organizing, leading (directing) and controlling (coordinating) activities and to the group of people, involved in them.
Another common view is that “management” is getting things done through other people.
But to most employees the term “management” probably means the group of people (executives or other) who are responsible for making decisions in the organization.
Read and render in Russian.
It is interesting to know that… .
The verb "manage" comes from the Italian "maneggiare" (that is "to handle" - especially a horse), which in turn derives from the Latin "manus" (that is "hand"). The French word "mesnagement" (later "ménagement") influenced the development in the meaning of the English word "management" in the 17th and 18th centuries.
The Industrial Revolution began in the eighteenth century and transformed the job of a manager from owner-manager to professional, salaried manager. It is interesting to note that many of the management terms and techniques used today have their basis in military authority (for example: "superior", "subordinate", "strategy", "mission").
What is a Manager?
A number of different terms are often used instead of the term "manager", including "director", "administrator" and "president". The term "manager" is used more frequently in profit-making organizations, while the others are used more widely in government and non-profit organizations such as universities, hospitals and social work agencies.
So, whom do we call a "manager"?
In its broad meaning the term "managers" applies to the people who are responsible for making and carrying out decisions within a certain system. A personnel manager directly supervises people in an organization. A financial manager is a person who is responsible for finance. A sales manager is responsible for selling of goods. A marketing manager is responsible for promotion of products on the market.
Almost everything a manager does involves decision-making. When a problem exists a manager has to make a decision to solve it. In decision-making there is always some uncertainty and risk.
The amount of responsibility of any individual in a company depends on the position that he or she occupies in its hierarchy. Managers, for example, are responsible for leading the people directly under them, who are called subordinates. To do this successfully, they must use their authority, which is the right to take decisions and give orders.
Managing is a responsible and hard job. There is a lot to be done and there is relatively little time to do it. In all types of organizations managerial efficiency depends on manager's direct personal relationships, hard work on a variety of activities and preference for active tasks. The characteristics of management often vary according to national culture, which can determine how managers are trained, how they lead people and how they approach their jobs.
Levels of Management
Supervisors are managers whose major functions are directing and controlling the work of employees in order to achieve the team goals. They are the only level of management managing non-managers. Thus, most of the supervisor's time is allocated to the functions of directing and controlling. In contrast, top managers spend most of their time on the functions of planning and organizing. The top manager determines the mission and sets the goals for the organization. His or her primary function is long-range planning. Top management is accountable for the overall management of the organization.They engage in more strategic and conceptual matters. Top managers have middle managers working for them and who are
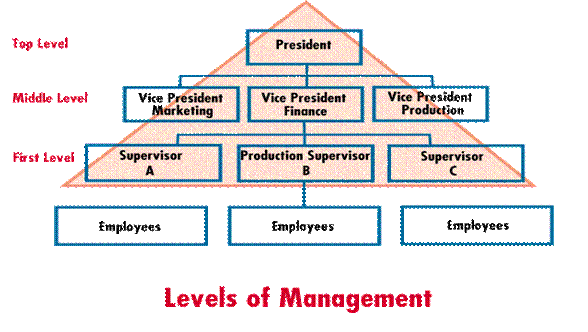
in charge of a major function or department. Middle management is responsible for carrying out the decisions made by top-level management. Middle managers may have first-line managers (or supervisors) working for them and who are responsible to manage the day-to-day activities of a group of workers. Supervisors direct the actual work of the organization at the operating level.
Note that there are different types of managers across the same levels in the organization. At the middle level a functional manager is in charge of a major function, such as a department in the organization, e.g., marketing, sales, engineering, finance, etc. A project manager is in charge of developing a certain project, e.g., development of a new building. A product manager is in charge of a product or service. Similarly, a product line manager is in charge of a group of closely related products. General managers are in charge of numerous functions within an organization or department.
1.8. Read and learn JOB TITLES:
| Chairman of the Board
of Directors
| - председатель совета директоров
|
| General Manager
| - генеральный директор
|
| Managing Director
| - директор-распорядитель
|
| Chief Executive Officer ( CEO )
| - главный исполнительный директор
корпорации (обычно президент)
|
| Deputy Managing Director
| - заместитель директора-
распорядителя
|
| Director
| - директор, член правления
|
| Vice President
| - вице-президент
|
| Accounting Manager
| - главный бухгалтер
|
| Export Manager
| - директор по экспорту
|
| Financial Manager
| - финансовый директор
|
| Functional Manager
| - функциональный руководитель
|
| General Manager
| - директор предприятия,
генеральный управляющий
|
| Goods Expert
| - товаровед
|
| (First) Line Manager
| - руководитель низшего звена
|
| Marketing Manager
| - директор по сбыту (управляющий
по маркетингу)
|
| М iddle М anager
| - руководитель среднего звена
|
| Office Manager
| - руководитель конторы, офис-
менеджер
|
| Personnel Manager
| - начальник отдела кадров
|
| Product Manager
| - руководитель, ответственный за
конструирование, производство и
реализацию изделия
|
| Production Manager
| - директор по производству
|
| Product Line Manager
| - управляющий выпуском
отдельного вида продукции
|
| Project Manager
| - руководитель проекта
|
| Sales Manager
| - коммерческий директор, директор
по сбыту
|
| Top ( Executive ) Manager
| - высший исполнительный
руководитель
|
| Training Manager
| - зав. отделом повышения
квалификации/подготовки кадров
|
| Warehouse Manager
| - зав. складом
|
| Store Manager
| - зав. магазином
|
| Supervisor
| - руководитель низшего звена,
инспектор, руководитель
|
SECTION 2.
2.1. Words to be learned:
| to achieve
| - достигать
|
| to advertize
| - рекламировать
|
| to accomplish
| - совершать, выполнять, достигать
|
| challenge
| - проблема, задача, вызов
|
| efficiently
| - эффективно
|
| facility
| - оборудование, обеспечение, тех. средства
|
| goal
| - цель, задача, заданный уровень
|
| to include
| - включать, содержать в себе
|
| internal environment
| - внутренняя среда, внутренние условия
|
| interrelated
| - взаимосвязанный
|
| objective
| - задача, генеральная линия, цель
|
| to perform
| - выполнять
|
| to set
| - устанавливать
|
| staff
| - штат
|
| to supply
| - снабжать, поставлять
|
2.2. Read the words in (A) and find synonyms in (B).
A. personnel, goal, to perform, problem, to include, position, directing
B. to accomplish, leading, challenge, staff, objective, to contain, job
What Do Managers Do?
Managers create and maintain an internal environment, commonly called the organization, so that others can work efficiently in it. A manager's job consists of planning, organizing, directing, and controlling the resources of the organization. These resources include people, jobs or positions, technology, facilities and equipment, materials and supplies, information, and money. Managers work in a dynamic environment and must anticipate and adapt to challenges. The functions of a manager (planning, organizing, directing, and controlling) are goal-directed, interrelated and interdependent.
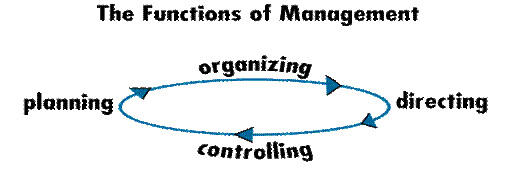
Planning involves identifying goals, objectives, methods, resources, responsibilities and dates of completion of tasks. It prepares the organization for the future. Examples of planning are strategic planning, project planning, promotions planning, advertising and staffing planning. When the plan is ready, the manager can follow it.
Organizing: To achieve the goals a manager often needs to organize new departments, office systems or re-organize businesses according to the plan, recruit, select and train employees. Assigning work and granting authority to employees are two important elements of organizing. A manager in a large organization often works with the company's human resources department to accomplish this goal.
Directing/Leading: Managers must also lead. They set direction for the organization, groups of people or individuals and influence people to follow that direction to achieve organizational goals. Directing/Leading involves motivating, communicating, guiding, and encouraging employees.
Controlling includes constant monitoring and adjustment of systems, processes and structures and taking any corrective actions if necessary.
All managers at all levels of every organization perform these functions, but the amount of time a manager spends on each one depends on both the level of management and the specific organization.
The extent to which managers perform the functions of management - planning, organizing, directing, and controlling - varies by level in the management hierarchy. The term supervisor could be applied at all management levels of the organization to those who direct the work of others. But in common usage, however, the title tends to be used only in the first level of the management hierarchy. If an organization is divided into top, middle, and lower managerial levels, the term generally applies to the lower level.
2.4. Choose the right answer:
1. The planning function is closely linked with the __________ function. Give your reasons.
| a) organizing
| b) controlling
| c) motivating
|
| d) leading
| e) staffing
| f) all of the above
|
| g) none of the above
|
|
|
2. All but one of the following are the elements of the planning process. Find an extra word.
| a) resources
| b) actions
| c) implementation
|
| d) objectives
|
|
|
3. Choose all the right words. Planning implies that managers should be:
| a) leaders
| b) capable organizers
| c) reactive
|
| d) proactive (инициативный)
|
|
4. The term supervisor can be applied at
| a) top level
| b) first level
|
| c) middle level
| d) all of the above
|
5. Controlling is performed at all managerial levels and includes
| a) constant monitoring
| b) adjustment of systems
|
| c) taking corrective actions
| d) all of above
|
Read the text and find out:
a) Which skills are important at each managerial level?
b) What are the most common managers' personal characteristics?
Skills
In order to perform the functions of management and to assume
multiple roles, managers must be skilled. Robert Katz identified three managerial skills that are essential to successful management: technical, human, and conceptual. Technical skill involves process or technique knowledge and proficiency. Managers use the processes, techniques and tools of a specific area. Human skill involves the ability to cooperate and interact effectively with people. Conceptual skill involves the formulation of ideas. Managers understand abstract relationships, develop ideas, and solve problems creatively. Thus, technical skill deals with things, human skill concerns people, and conceptual skill concerns ideas.
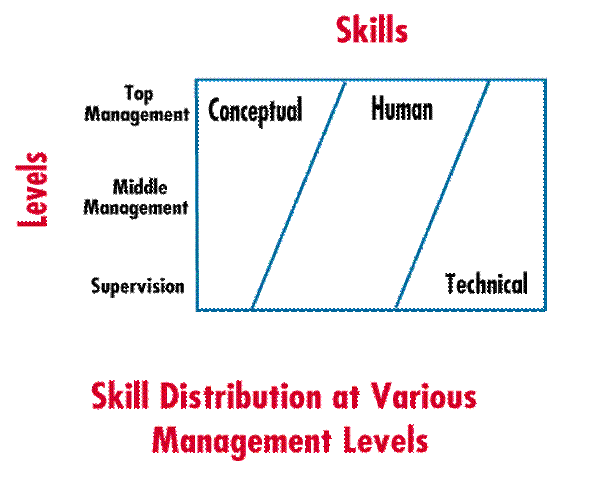
A manager's level in the organization determines the relative importance of possessing technical, human, and conceptual skills. Top level managers need conceptual skills in order to view the organization as a whole. Conceptual skills are used in planning and dealing with ideas and abstractions. Supervisors need technical skills to manage their area of specialty. All levels of management need human skills in order to interact and communicate with other people successfully.
The following are some skills and personal characteristics that are important for managers:
Leadership - ability to influence others to perform tasks
Self-objectivity - ability to evaluate yourself realistically
Analytic thinking - ability to interpret and explain information
Behavioral flexibility - ability to modify personal behavior to react objectively rather than subjectively to accomplish organizational goals
Oral communication - ability to express ideas clearly in words Written communication - ability to express clearly ideas in writing
Personal impact - ability to create a good impression and instill confidence
Resistance to stress - ability to perform under stressful condition
Tolerance for uncertainty - ability to perform in ambiguous situations.
Roles Performed by Managers
A manager wears many hats. Not only is a manager a team leader, but he or she is also a planner, organizer, cheerleader, coach, problem solver, and decision maker - all rolled into one. In addition, managers' schedules are usually jam-packed. Whether they're busy with employee meetings, unexpected problems, or strategy sessions, managers often find little spare time on their calendars. (And that doesn't even include responding to e-mail!)
In his classic book, The Nature of Managerial Work, Henry Mintzberg describes a set of ten roles that a manager fills. These roles fall into three categories:
Interpersonal: This role involves human interaction.
Informational: This role involves the sharing and analyzing of information.
Decisional: This role involves decision making.
SECTION 3.
Management Style
Managing people is very important to be left to chance. Your employees are one of your valuable resources; you must make certain you are not wasting your human resources. But most managers define their jobs in terms of the tasks to be done rather than the methods to be used. They see their role as making things, rather than motivating and aiding those who make them. Thus, their management styles are usually just extensions of their personal styles.
Your management style should reinforce your corporate culture and company mission.
For most companies, especially smaller companies building a sense ofteamwork is essential. Help your employees feel they are an important part of the organization and that their contribution matters.
Communicationis a vital ingredient in team building; if employees know what's going on in the company, they feel a part of a business.
Recognize achievement both privately and publicly. Regardless of your management style, remember that everyone, whether mailroom clerk or company president, wants to feel important.
Rewardinitiative with both monetary and nonmonetary awards. Acknowledge jobs well done. Solicit (просить) suggestions, and be responsive (откликающийся) to concerns.
Here are the five most important elements of your management style:
| 1. Clear Policies
| 4. Employee Recognition
|
| 2. Communication
3. Fairness
| 5. Employee’s Ability to Affect
Change
|
Managers often delegate authority. By definition, managers cannot do everything themselves (although some try and fail).They have to rely on other people. This means that employees at lower levels in the company hierarchy can use their initiative that is make decisions without asking their manager.
Symptoms of poor delegators:
- Working longer hours than your workers.
- Taking work home almost every day.
- Having no time for a social life and educational or professional
activities.
What Managers Have to Do about People? When it comes to dealing with people, managers:
- organize and allocate work
- get the right people to the work
- ensure that these people know what to do, and are capable of doing it
- develop skills and capabilities (competence)
- reward people, using both financial and non-financial methods
- involve people and communicate with them
- handle people issues and problems as they arise.
SECTION 4.
Leadership and Management
|
| "Managers are people who do things right, while leaders are people who do the right thing."
Warren Bennis, Ph.D.
"On Becoming a Leader"
|
The English word "leader" means "a person who guides or directs others". Good leaders are made not born. If you have the desire and willpower, you can become an effective leader. Good leaders develop through a never ending process of self-study, education, training, and experience. This text will help you through that process.
To inspire your workers into higher levels of teamwork, there are certain things you must be, know, and, do. These do not come naturally, but are acquired through continual work and study. Good leaders are continually working and studying to improve their leadership skills; they are NOT resting on their laurels.The basis of good leadership is honorable character and selfless service to your organization. In your employees' eyes, your leadership is everything you do that effects the organization's objectives and their well being.
What makes a person want to follow a leader? People want to be guided by those they respect and who have a clear sense of direction. To gain respect, they must be ethical. A sense of direction is achieved by conveying a strong vision of the future.
Principles of Leadership.
To help you be, know, and do follow these eleven principles of leadership:
Know yourself and seek self-improvement - In order to know yourself, you have to understand your be, know, and do, attributes. This can be accomplished through self-study, formal classes, reflection (размышление, обдумывание).
Be technically proficient - As a leader, you must know your job and have a solid familiarity with your employees' tasks.
Seek responsibility and take responsibility for your actions - Search for ways to guide your organization to new heights. And when things go wrong, they always do sooner or later do not blame others. Analyze the situation, take corrective action, and move on to the next challenge.
Make sound and timely decisions - Use good problem solving, decision making, and planning tools.
Set the example - Be a good role model for your employees. They must not only hear what they are expected to do, but also see.
Keep your workers informed - Know how to communicate with not only them, but also seniors and other key people.
Develop a sense of responsibility in your workers - Help to develop good character traits that will help them carry out their professional responsibilities.
Ensure that tasks are understood, supervised, and accomplished - Communication is the key to this responsibility.
Train as a team - Although many so called leaders call their organization, department, section, etc. a team; they are not really teams... they are just a group of people doing their jobs.
Know your people and look out for their well-being - Know human nature and the importance of sincerely caring for your workers.
Use the full capabilities of your organization - by developing a team spirit, you will be able to employ your organization, department, section, etc. to its fullest capabilities.
Leadership and management are not identical. What is the difference between leading and managing? Managers manage things, but lead people.
Personality types
| A Characteristics
The entrepreneur
| B Characteristics
The team worker
|
| You are the adventurous type. You enjoy new challenges and taking risks. You could find success in stock market dealing rooms or anywhere you can put your flashes of genius to good use.
| You work well with others but dislike having responsibility for people, preferring implement other people’s plans rather than your own. You would probably do well in the armed forces or the Civil Service.
|
| C Characteristics
The backroom worker
| D Characteristics
The leader
|
| You are a little shy, and find it difficult to mix with new people. You would do well in any behind-the-scenes job where you don’t have to come face to face with strangers every day, such as researchers or librarians.
| You are confident in your abilities and you prefer to be in charge rather than to take orders. You enjoy having lots of people around you and would do well in a managerial post or any job which involves selling.
|
SECTION 5.
5.1. Here are a few tips to follow if your goal is to be a good manager. Read them and discuss in groups.
Qualities of a Good Manager
If you are a manager you should stick to the following rules in your everyday activities:
1. be competent
2. be able to deal with people, to talk to them about their jobs,
problems, and their future
3. be adaptable to the situation
4. be able to persuade people that his way is right. It is necessary to
make people accept his decisions and follow his leadership
5. be firm with his people. That’s how they will come to respect him
6. be mentally competent be physically fit. In the age of pressures only
the fittest can survive.
How to Manage Managers
Law on Enterprise enacted (принятый) by the Government help create a relationship when a factory manager and his work collective become partners. Management and employees must be equally interested in the fruits of their labour.
In a result-oriented management the key thing is not to issue instructions but get results. That is why a manager's pay should be linked to the performance of the enterprise where he works. If a factory produces more, a manager's pay should increase. If the production plan is not met, then a manager must be penalized along with the workers he supervises. About 40 or 50 per cent of a manager's monthly pay should depend on the end result of the enterprise. If the result is poor and a manager doesn't get the full pay for a few months running he must leave his office. New people should come instead. It'll be a natural selection of a managerial staff when people with better knowledge and truly original thinking will come to management.
Moscow News
5.9. Answer the questions:
1. What relationship should be built between the management
and the staff?
2. How should the work of a manager be assessed?
3. Should a manager fill in the vacancy on a competitive basis?
4. What did the government do to improve the system of
management?
5. Do you know any enterprise where managers and workers are
equal partners?
6. Are the problems of management still acute (острый) nowadays?
7. Can managerial problems be solved only with the help of laws
enacted by the government?
8. What are your ways of solving managerial problems?
Time Management
Time is constant. No matter what position a person has in a company, he cannot stop time, he cannot slow it down, and he cannot speed it up. Time must be managed well if a person wants to be creative. Time is wasted when it is used for things that are less important. A person with a clear set of objectives and priorities can identify important activities and plan the best way to use the time.
Section 6.
The Big Rocks of Time
In First Things First, Stephen Covey tells a great story:
One day an expert in time management was speaking to a group of business students. As he stood in front of the group he said, "Okay, time for a quiz" He then pulled out a one-gallon (4-4.5л), wide-mouthed mason jar (керамический сосуд) and set it on the table. He took about a dozen fist-sized (величиной с кулак) rocks and placed them into the jar. When the jar was filled to the top, he asked, "Is this jar full?" Everyone in the class said, "Yes." Then he said, "Really?"
Then he put some gravel into the jar and shook it. The gravel fell down into the space between the big rocks. Then he asked the group once more, "Is the jar full?" By this time the class was on (понять) to him. "Probably not," one of them answered. "Good!" he replied. Then he put some sand into the jar until it filled the spaces left between the rocks and the gravel. Once more he asked the question, "Is this jar full?" No!" the class shouted. Once again he said, "Good." Then he took some water and began to pour it in until the jar was filled to the brim.
Then he looked at the class and asked, "What is the point of this illustration?" One student raised his hand and said, "The point is, no matter how full your schedule is, if you try really hard you can always fit some more things in it!" "No," the speaker replied, "that's not the point." "The truth this illustration teaches us is that if you don't put the big rocks in first, you'll never get them in at all. What are the 'big rocks' in your life? Your children, your loved ones, your education, your dreams, teaching others, doing things that you love, your health, your mate. Remember to put these BIG ROCKS in first or you'll never get them in at all.
So, tonight, or in the morning ask yourself this question: What are the 'big rocks' in my life? Then, put those in your jar first.
Food for Thought.
1. Who do you manage and how?
2. Who managers you and why?
3. What are the things that must be managed, and if mismanaged, inevitably create problems in your life? Tick the ones you think apply and complete the list with your own ideas.
| a. Time
| d. Career
| g. …..
|
| b. Money
| e. Studies
| h. ….
|
| c. Energy
| f. Human relationships
| i. ….
|
6.3. Read the text and say what surprised you more? Do you know any Russian businessman or businesswoman who used his/her own management secrets to make a fortune (нажить состояние)?
Management and Managers
Менеджмент и Менеджеры
Методические указания по английскому языку
для студентов 1,2 курсов инженерно-экономического факультета
Составители И.В. Губанова
Л.К. Чадина
Утверждены на заседании кафедры
Протокол №4 от 24.12.08
Рекомендованы к печати
учебно-методической комиссией
специальности 080502
Протокол № от
Электронная копия находится
в библиотеке главного корпуса
ГУ КузГТУ
КЕМЕРОВО 2008
Настоящая разработка предназначена для студентов 1 и 2 курса инженерно-экономического факультета, изучающих менеджмент.
Целью разработки является ввести на английском языке основы менеджмента. Студенты познакомятся с определением "менеджмент" и "менеджер", функциями и обязанностями менеджеров, а также качествами, которыми современные менеджеры должны обладать.
Данные методические указания состоят из пяти секций. Каждая секция содержит задания на развитие навыков говорения. Для успешного овладения материалом предлагается англо-русский словарь, упражнения на знание интернациональной лексики и на словообразование. Тексты иллюстрированы диаграммами и схемами, что помогает лучшему восприятию.
Большинство текстов подобраны из американских и английских источников.
SECTION 1.
Words to be learned:
| activity
| - деятельность
|
| authority
| - полномочие, власть, влияние
|
| to be responsible for
| - быть ответственным за
|
| to be in charge of
| - oтвечать за, заведовать
|
| to direct
| - руководить, направлять
|
| employee
| - служащий, работающий по найму
|
| executive
| - администратор, руководитель
|
| to carry out
| - выполнять
|
| to involve
| - затрагивать, вовлекать, касаться
|
| level
| - уровень
|
| to manage
| - руководить, заведовать, управлять
|
| to make decisions
| - принимать решения
|
| to mean (meant,meant)
| - иметь в виду, подразумевать, значить
|
| non - profit
| - некоммерческий
|
| personal relationships
| - личные отношения
|
| profit-making
| - коммерческий
|
| promotion
| - продвижение
|
| to refer to
| - отсылать к, ссылаться на
|
| to sell ( sold , sold )
| - продавать
|
| to solve a problem
| - решать проблему
|
| subordinate
| - подчиненный
|
| to supervise
| - смотреть, надзирать, руководить
|
1.2. Read and translate the following international words:
management, manager, tradition, plan, organize, control, coordination, active, group, expert, organization, Industrial Revolution, professional manager, term, strategy, technique, basis, mission, military, definition, director, service, president, vice-president, line, office, administrator, administration, university, hospital, social, agency, system, personnel, personal, finance, marketing, product, production, problem, risk, company, individual, national, culture, argument, scheme, function, functional, project, contrast, structure, company, diagram; resource
Word-building. Translate into Russian.
to manage – management – manager – managerial; to plan – planning;
to control – controlling; to direct – director – directing; to lead – leader – leading; to organize – organizer – organization; to produce – producer – productive – production; person – personal; function – functional; tradition – traditional – traditionally; industry – industrial; responsible – responsibility; success – successful – successfully
1.4. Read the text and say what the idea of management is.
What Is "Management"?
What is "management"? There are a variety of views about this term. Traditionally, the term “management” refers to planning, organizing, leading (directing) and controlling (coordinating) activities and to the group of people, involved in them.
Another common view is that “management” is getting things done through other people.
But to most employees the term “management” probably means the group of people (executives or other) who are responsible for making decisions in the organization.
Read and render in Russian.
It is interesting to know that… .
The verb "manage" comes from the Italian "maneggiare" (that is "to handle" - especially a horse), which in turn derives from the Latin "manus" (that is "hand"). The French word "mesnagement" (later "ménagement") influenced the development in the meaning of the English word "management" in the 17th and 18th centuries.
The Industrial Revolution began in the eighteenth century and transformed the job of a manager from owner-manager to professional, salaried manager. It is interesting to note that many of the management terms and techniques used today have their basis in military authority (for example: "superior", "subordinate", "strategy", "mission").











