Perhaps the first electric motors were simple electrostatic devices created by the Scottish monk Andrew Gordon in the 1740s. The theoretical principle behind production of mechanical force by the interactions of an electric current and a magnetic field, Ampere’s force law, was discovered later by André-Marie Ampere in 1820. The conversion of electrical energy into mechanical energy by electromagnetic means was demonstrated by the British scientist Michael Faraday in 1821.
Electric motors are used for converting different forms of energy into mechanical energy. Motors operate on three different physical principles: magnetic, electrostatic and piezoelectric. By far the most common is magnetic. In magnetic motors, magnetic fields are formed in both the rotor and the stator.

The basic components of electric motors area frame, a rotor, a stator, windings, a commutator and a coil.
The frame of the motor holds all the parts in place, and provides a means of mounting the motor to machinery. The frame also conducts heat produced within the motor to the surrounding air.Some motors have fins to help get rid of heat even faster.
In an electric motor the moving part is the rotor which turns the shaft to deliver the mechanical power. The rotor usually has conductors laid into it which carry currents that interact with the magnetic field of the stator to generate the forces that turn the shaft. However, some rotors carry permanent magnets, and the stator holds the conductors.

The stator is the stationary part of the motor’s electromagnetic circuit and usually consists of either windings or permanent magnets. The stator core is made up of many thin metal sheets, called laminations. Laminations are used to reduce energy losses that would result if a solid core were used.
The distance between the rotor and stator is called the air gap. The air gap has important effects, and is generally as small as possible, as a large gap has a strong negative effect on the performance of an electric motor. It is the main source of the low power factor at which motors operate. The air gap increases the magnetizing current needed. For this reason air gap should be minimal. Very small gaps may pose mechanical problems in addition to noise and losses.
Windings are wires that are laid in coils, usually wrapped around a laminated soft iron magnetic core so as to form magnetic poles when energized with current.
A commutator is a mechanism used to switch the input of most direct current(DC) machines and certain alternating current(AC) machines consisting of slip ring segments insulated from each other and from the electric motor's shaft.
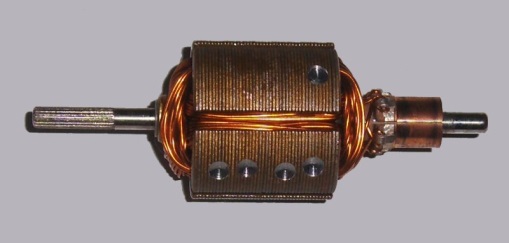 The main part of a motor is a coil or armature. The armature is placed between the poles of a powerful magnet. When a motor is put into operation current starts flowing through the coil (armature) and the armature starts rotating.
The main part of a motor is a coil or armature. The armature is placed between the poles of a powerful magnet. When a motor is put into operation current starts flowing through the coil (armature) and the armature starts rotating.
Each motor is supplied with a nameplate which bears machine ratings: output power, voltage, the rated current, the starting current, the power factor, the efficiency, and the rated torque.These motor ratings should be taken into consideration since they are necessary for the users. The length of motor's service life depends on them, which is normally equal to about 10 years, provided that the operating conditions are normal. Naturally, under abnormal conditions the service life becomes much shorter: motors operate poorly and may have different faults.
An electric motor will try to deliver the required power even at the risk of self-destruction. Therefore, an electric motor must be protected from self-destruction. Motors may be ruined by physical damage to the windings but, usually, the enemy of a motor is excessive heat in the windings. Overheating breaks down the thin varnish like insulation on the windings. When the insulation fails, the motor fails. Overheating is the result of excessive current flow or inadequate ventilation. Accumulation of dust and dirt on and in the motor can reduce ventilation and heat removal.
Electric motors may be powered by direct current or by alternating current which leads to the two main classifications: DC motors and AC motors, the former are increasingly being displaced by the latter.
Electric motors are used practically in every branch of industry, transport, and agriculture.
A lot of farm machines are driven by electric motors. They operate irrigation, pumps, threshing and fanning as well as grain-drying units and otherinstallations connected with field husbandry. Electric motors supply water to the cow house and heat it, cut ensilage, warm hotbeds, actuate milking machines, prepare provender in the feed-processing building, feed it to the cattle, remove barnyard manure.
Three types of motors are used in agriculture: induction, synchronous, and direct current.

The induction motor is the motor most commonly used in agriculture. The speed of rotation of an induction motor is fairly constant, but it does vary somewhat with loading. As the motor is loaded, it slows down slightly.

The synchronous motor runs at a constant speed regardless of the load on the motor. Synchronous motors usually have an armature. The most common farm application of a synchronous motor is in an electric clock or timer.
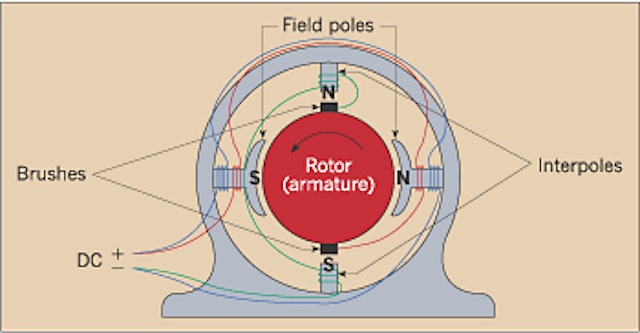 Direct-current motors are used in electric vehicles and for applications where variable speed is required. An application would be a variable-speed motor operating an auger to meter high-protein supplement into a cattle feeding system. Although the motor requires direct current, the supply is usually alternating current. A solid-state rectifier in the motor controller changes AC to DC. One type of direct-current motor can also operate on alternating current. This type is called a universal motor. Its most common application is in such power tools as an electric drill. It is also referred to as a series-wound DC motor. The stator or field winding is wired in series with the armature winding. The speed of these motors is not constant; the more they are loaded, the slower they turn. A big advantage, however, is that they develop very high torque at low speeds. Torque is observed every time an electric drill is forced through tough material.
Direct-current motors are used in electric vehicles and for applications where variable speed is required. An application would be a variable-speed motor operating an auger to meter high-protein supplement into a cattle feeding system. Although the motor requires direct current, the supply is usually alternating current. A solid-state rectifier in the motor controller changes AC to DC. One type of direct-current motor can also operate on alternating current. This type is called a universal motor. Its most common application is in such power tools as an electric drill. It is also referred to as a series-wound DC motor. The stator or field winding is wired in series with the armature winding. The speed of these motors is not constant; the more they are loaded, the slower they turn. A big advantage, however, is that they develop very high torque at low speeds. Torque is observed every time an electric drill is forced through tough material.
A small electric motor requires no special foundation and may be placed on the floor, on a truck, or may be fastened to the wall or ceiling. It is easily started and requires less care than the gasoline engine. The cleanliness of the electric motor and the absence of offensive fumes make it more desirable for use in the house, the dairy and the barn.
 (A) Exercise 1. Choose the correct answer.
(A) Exercise 1. Choose the correct answer.
1. When were the first electric motors created?
a) The first electric motors were created in the 1820s.
b) The first electric motors were createdin the 1740s.
2.Was the conversion of electrical energy into mechanical energy by electromagnetic means demonstrated by M. Faraday or by André-Marie Ampere?
a) It was demonstrated by André-Marie Ampere.
b) It was demonstrated by Michael Faraday.
3.Are electric motors used for converting different forms of energy into mechanical or electrical energy?
a) Electric motors convert different forms of energy into mechanical energy.
b) Electric motors convert different forms of energy into electrical energy.
4.What are the basic components of electric motors?
a) The basic components of electric motors area frame, windings, and a coil.
b) The basic components of electric motors area frame, a rotor, a stator, windings, a commutator and a coil.
5.In an electric motor the moving part is the rotor, isn’t it?
a) Yes, it is. In an electric motor the moving part is the rotor.
b) No, it isn’t. In an electric motor the moving part is the stator.
6.Is a commutatoror a frame used to switch the input of most DC machines?
a) A frame is a mechanism used to switch the input of most DC machines.
b) A commutator is a mechanism used to switch the input of most DC machines.
8. What may ruin motors?
a) Motors may be ruined by physical damage to the windings and by excessive heat in the windings.
b) Motors may be ruined by physical damage to the windings.
9. Are any of farm machines driven by electric motors?
a) Yes, they are. A lot of farm machines are driven by electric motors.
b) No, they aren’t.A lot of farm machines are driven by the gasoline engine.
10.What types of motors are used in agriculture?
a) Two types of motors are used in agriculture: induction and direct current.
b) Three types of motors are used in agriculture: induction, synchronous, and direct current.
(A) Exercise 2. Read the text once again and divide it into parts. Give each a title. Use the titles as plan.
(A) Exercise 3. Using the plan retell the text in Russian/Belarusian.
(B) Exercise 4. Read the statements and tick(✓) Yes if the statement is true and No if it is false.
1. The theoretical principle behind production of mechanical force by the interactions of an electric current and a magnetic field is known as Ohm’s law.
2. In magnetic motors, magnetic fields are formed in both the rotor and the stator.
3. Some motors have fins to provide a means of mounting the motor to machinery.
4. Each motor is supplied with a nameplate which bears machine ratings.
5. Concentration of dust and dirt on and in the motor can increase ventilation and heat removal.
6. A small electric motor doesn’t require special foundation.
7. A universal motor can operate on either alternating current or direct current.

 (B) Exercise 5. Put the questions into the correct order according to the text. Answer the questions.
(B) Exercise 5. Put the questions into the correct order according to the text. Answer the questions.
1. What is the function of the frame of the motor?
2.What is the stator core made up of? What are they used for?
3.What principles are used for motors to operate?Which one is the most common?
4. What turns the shaft to deliver the mechanical power?
5.Why should motor ratings be taken into consideration?
6.Who created the first electric motors? What were they like?
7. What type of current is used to power electric motors?
8.How is the distance between the rotor and stator called? How large is it?
9.What do the basic components of electric motors include?
10.What are electric motors used for?
11. What are the advantages of electric motors?
12.Where is the armature placed?
13. How are electric motors used in agriculture?
14.When does the motor fail?
15.Which of three types of motors are used in agriculture?
16. What mechanism is used to switch the input of most DC machines?
(B) Exercise 6. Make up a summary of the text in English.

(C) Exercise 7. What is your opinion about the information given in the text? How can it be used in your profession?
(C) Exercise 8. Remind strategies of making a project. Make your own project on the basis of the theme “Electric motors”.
(C) Exercise 9. Prepare a presentation of your project and tell the group about your work.
TEXT D
 The transformer is static electrical equipment which transforms electrical energy to the magnetic energy and again to the electrical energy. The operating frequency and nominal power are approximately equal on primary and secondary transformer side because the transformer is very efficient equipment, while the voltage and current values are usually different. Essentially, the main task of the transformer is to convert high voltage (HV) and low current from the primary side to the low voltage (LV) and high current on the secondary side and vice versa. Also, a transformer with its operation principle provides galvanic isolation in the electrical system.
The transformer is static electrical equipment which transforms electrical energy to the magnetic energy and again to the electrical energy. The operating frequency and nominal power are approximately equal on primary and secondary transformer side because the transformer is very efficient equipment, while the voltage and current values are usually different. Essentially, the main task of the transformer is to convert high voltage (HV) and low current from the primary side to the low voltage (LV) and high current on the secondary side and vice versa. Also, a transformer with its operation principle provides galvanic isolation in the electrical system.
A transformer transfers electrical energy from one circuit to another through inductively coupled conductors the transformer's coils. A varying electric current in the first or primary winding creates a varying magnetic flux in the transformer's core and thus a varying magnetic field through the secondary winding. This varying magnetic field induces a varying electromotive force (e. m. f.) or "voltage" in the secondary winding. This effect is called mutual induction.
With those features, the transformer is the most important part of the electrical system and provides economical and reliable transmission and distribution of electrical energy.
The working principle of transformer is very simple. It depends upon Faraday's law of electromagnetic induction. Actually, mutual induction between two or more winding is responsible for transformation action in an electrical transformer.
 In the broadest terms, there are two types of transformers. There are voltage transformers, which are typically what people are talking about when they simply say ‘transformer’, and there are current transformers, often times called instrument transformers. Voltage transformers alter the voltage input to the device and output a voltage that is proportional to the input voltage. Current transformers do the same for amperage.
In the broadest terms, there are two types of transformers. There are voltage transformers, which are typically what people are talking about when they simply say ‘transformer’, and there are current transformers, often times called instrument transformers. Voltage transformers alter the voltage input to the device and output a voltage that is proportional to the input voltage. Current transformers do the same for amperage.
There is an incredible range of transformers where the size of these devices is concerned. Some transformers are small enough to fit in a pocket and some are larger and heavier than most cars. These devices, no matter what size they happen to be, function on largely the same principles.
Transformers can be categorized in different ways, depending upon their purpose, use, construction etc. The main types of transformers are as follows:
1. Step-up transformers
2. Step-down transformers
3. Isolation transformers
The step-up transformers can be used in electronic and electrical devices where the voltage boosting is required. But nowadays in the modern electronic device, power electronic circuits are more frequently used because of weight and dimension.
 The step-down transformer converts the high voltage (HV) and low current from the primary side to the low voltage (LV) and high current value on the secondary side. This transformer type has a wide application in electronic devices and electrical systems. When it comes to the operation voltage, the step-up transformer application can be roughly divided in two groups: LV (voltages up to 1 kV) and HV application (voltages above 1 kV).
The step-down transformer converts the high voltage (HV) and low current from the primary side to the low voltage (LV) and high current value on the secondary side. This transformer type has a wide application in electronic devices and electrical systems. When it comes to the operation voltage, the step-up transformer application can be roughly divided in two groups: LV (voltages up to 1 kV) and HV application (voltages above 1 kV).
The step-down transformer is used to provide this low voltage value which is suitable for electronics supplying. It transforms home voltage (230/120 V) from primary to a low voltage on the secondary side which is used for the electronic supplying. If electronic devices are designed to have higher nominal power, transformers with high operating frequency are used (kHz-s). The transformers with higher nominal power value and 50/60 Hz nominal frequency would be too large and heavy. Also, the daily used battery chargers use the step-down transformer in its design.
An isolation transformer is a transformer used to transfer electrical power from a source of alternating current (AC) power to some equipment or device while isolating the powered device from the power source, usually for safety reasons. Isolation transformers provide galvanic isolation and are used to protect against electric shock, to suppress electrical noise in sensitive devices, or to transfer power between two circuits which must not be connected. A transformer sold for isolation is often built with special insulation between primary and secondary, and is specified to withstand a high voltage between windings.
Transformers play an important role in power transmission because they allow power to be converted to and from higher voltages. This is important because higher voltages suffer less power loss during transmission. This is because higher voltages allow for lower current to deliver the same amount of power as power is the product of the two. Thus, as the voltage steps up, the current steps down. It is the current flowing through the components that result in both the losses and the subsequent heating. These losses, appearing in the form of heat, are equal to the current squared times the electrical resistance through which the current flows.
 Transformers are among the most basic electrical components in use. These devices contain few parts, but they perform a vital role in many different electrical applications. From the large plugs on most electronic charging devices for cellular phones and tablet computers to the huge transformers mounted to power poles and located at substations, these devices are so common precisely because they are so useful.
Transformers are among the most basic electrical components in use. These devices contain few parts, but they perform a vital role in many different electrical applications. From the large plugs on most electronic charging devices for cellular phones and tablet computers to the huge transformers mounted to power poles and located at substations, these devices are so common precisely because they are so useful.
Transformers play many different roles in electronics. They are used in amplification devices, on power poles to step voltage down for household use and in computers to provide many different voltages to the motherboard through separate connections to the motherboard.
ASSIGNMENTS
(A, B, C)1. Look at the title of the text. Say what readers’ category it is for.
(A, B, C)2. Read the text and find out whether the title fully represents the content.
(A, B, C)3. Have you read any articles on the basis of this theme? Were they fascinating or scientifically vital to you?

(A, B, C) 4. Read the first paragraph of the text and say what questions are discussed in it.
(A, B, C)5. Divide the text into several parts. Explain your choice.
(A, B, C)6. Scan the text. Focus on the general ideas of each part to say how they are connected and why.
(A, B, C)7. Think of the alternative way to entitle each part.
(A, B, C)8. Find and mark the key-words connected with the main information in each abstract of the text.
| Whatabstract …
- dealswith … (классификациитрансформаторов)
- includes the information about …. (повышающийтрансформатор)
- touchesupon … (понижающий трансформатор)
- presents … (принципработытрансформатора)
- contains the information about … (разделяющийтрансформатор)
|

You may startwith:
The first abstract …
The second abstract …
The third abstract …
The fourth abstract …
The fifth abstract …
(A, B, C)9. Extend the following statements.
LEVEL A – 1 sentence
LEVEL B – 2-3 sentences
LEVEL C – 3-4 sentences.
1. The transformer is static electrical equipment.
2. The transformer is the most important part of the electrical system.
(A, B, C) 10. State what you have learned from the text about:
| 1) classification of transformers
| 4) step down transformers
|
| 2) the working principle of transformers
| 5) isolation transformers
|
| 3) step up transformers
| 6) the importance of transformers
|
(A, B, C) 11. Make up a plan of the text in a form of:
| a) (A) key-words
|
|
|
|
| b) (B) key-sentences
|
|
|
|
| c) (C) questions
|
(A, B, C) 12. Express your opinion about the text. You may start with the phrases given below.
| LEVEL A – 1-2 sentence
LEVEL B – 2-3 sentences
LEVEL C – 4-6 sentences.
ü I found the text interesting (useful, informative) …
ü I think (believe, should say, consider) …
ü In my opinion …
ü To my mind …
ü It seems to me …
ü From my point of view …
|
(A, B, C)13.Promote theses to the text.
LEVEL A – 1-3 sentence
LEVEL B – 4-5 sentences
LEVEL C – 6-8 sentences.





 The main part of a motor is a coil or armature. The armature is placed between the poles of a powerful magnet. When a motor is put into operation current starts flowing through the coil (armature) and the armature starts rotating.
The main part of a motor is a coil or armature. The armature is placed between the poles of a powerful magnet. When a motor is put into operation current starts flowing through the coil (armature) and the armature starts rotating.

 Direct-current motors are used in electric vehicles and for applications where variable speed is required. An application would be a variable-speed motor operating an auger to meter high-protein supplement into a cattle feeding system. Although the motor requires direct current, the supply is usually alternating current. A solid-state rectifier in the motor controller changes AC to DC. One type of direct-current motor can also operate on alternating current. This type is called a universal motor. Its most common application is in such power tools as an electric drill. It is also referred to as a series-wound DC motor. The stator or field winding is wired in series with the armature winding. The speed of these motors is not constant; the more they are loaded, the slower they turn. A big advantage, however, is that they develop very high torque at low speeds. Torque is observed every time an electric drill is forced through tough material.
Direct-current motors are used in electric vehicles and for applications where variable speed is required. An application would be a variable-speed motor operating an auger to meter high-protein supplement into a cattle feeding system. Although the motor requires direct current, the supply is usually alternating current. A solid-state rectifier in the motor controller changes AC to DC. One type of direct-current motor can also operate on alternating current. This type is called a universal motor. Its most common application is in such power tools as an electric drill. It is also referred to as a series-wound DC motor. The stator or field winding is wired in series with the armature winding. The speed of these motors is not constant; the more they are loaded, the slower they turn. A big advantage, however, is that they develop very high torque at low speeds. Torque is observed every time an electric drill is forced through tough material. (A) Exercise 1. Choose the correct answer.
(A) Exercise 1. Choose the correct answer.
 (B) Exercise 5. Put the questions into the correct order according to the text. Answer the questions.
(B) Exercise 5. Put the questions into the correct order according to the text. Answer the questions.
 The transformer is static electrical equipment which transforms electrical energy to the magnetic energy and again to the electrical energy. The operating frequency and nominal power are approximately equal on primary and secondary transformer side because the transformer is very efficient equipment, while the voltage and current values are usually different. Essentially, the main task of the transformer is to convert high voltage (HV) and low current from the primary side to the low voltage (LV) and high current on the secondary side and vice versa. Also, a transformer with its operation principle provides galvanic isolation in the electrical system.
The transformer is static electrical equipment which transforms electrical energy to the magnetic energy and again to the electrical energy. The operating frequency and nominal power are approximately equal on primary and secondary transformer side because the transformer is very efficient equipment, while the voltage and current values are usually different. Essentially, the main task of the transformer is to convert high voltage (HV) and low current from the primary side to the low voltage (LV) and high current on the secondary side and vice versa. Also, a transformer with its operation principle provides galvanic isolation in the electrical system. In the broadest terms, there are two types of transformers. There are voltage transformers, which are typically what people are talking about when they simply say ‘transformer’, and there are current transformers, often times called instrument transformers. Voltage transformers alter the voltage input to the device and output a voltage that is proportional to the input voltage. Current transformers do the same for amperage.
In the broadest terms, there are two types of transformers. There are voltage transformers, which are typically what people are talking about when they simply say ‘transformer’, and there are current transformers, often times called instrument transformers. Voltage transformers alter the voltage input to the device and output a voltage that is proportional to the input voltage. Current transformers do the same for amperage. The step-down transformer converts the high voltage (HV) and low current from the primary side to the low voltage (LV) and high current value on the secondary side. This transformer type has a wide application in electronic devices and electrical systems. When it comes to the operation voltage, the step-up transformer application can be roughly divided in two groups: LV (voltages up to 1 kV) and HV application (voltages above 1 kV).
The step-down transformer converts the high voltage (HV) and low current from the primary side to the low voltage (LV) and high current value on the secondary side. This transformer type has a wide application in electronic devices and electrical systems. When it comes to the operation voltage, the step-up transformer application can be roughly divided in two groups: LV (voltages up to 1 kV) and HV application (voltages above 1 kV). Transformers are among the most basic electrical components in use. These devices contain few parts, but they perform a vital role in many different electrical applications. From the large plugs on most electronic charging devices for cellular phones and tablet computers to the huge transformers mounted to power poles and located at substations, these devices are so common precisely because they are so useful.
Transformers are among the most basic electrical components in use. These devices contain few parts, but they perform a vital role in many different electrical applications. From the large plugs on most electronic charging devices for cellular phones and tablet computers to the huge transformers mounted to power poles and located at substations, these devices are so common precisely because they are so useful.




