

Двойное оплодотворение у цветковых растений: Оплодотворение - это процесс слияния мужской и женской половых клеток с образованием зиготы...

Кормораздатчик мобильный электрифицированный: схема и процесс работы устройства...

Двойное оплодотворение у цветковых растений: Оплодотворение - это процесс слияния мужской и женской половых клеток с образованием зиготы...

Кормораздатчик мобильный электрифицированный: схема и процесс работы устройства...
Топ:
Методика измерений сопротивления растеканию тока анодного заземления: Анодный заземлитель (анод) – проводник, погруженный в электролитическую среду (грунт, раствор электролита) и подключенный к положительному...
Характеристика АТП и сварочно-жестяницкого участка: Транспорт в настоящее время является одной из важнейших отраслей народного хозяйства...
Процедура выполнения команд. Рабочий цикл процессора: Функционирование процессора в основном состоит из повторяющихся рабочих циклов, каждый из которых соответствует...
Интересное:
Мероприятия для защиты от морозного пучения грунтов: Инженерная защита от морозного (криогенного) пучения грунтов необходима для легких малоэтажных зданий и других сооружений...
Средства для ингаляционного наркоза: Наркоз наступает в результате вдыхания (ингаляции) средств, которое осуществляют или с помощью маски...
Берегоукрепление оползневых склонов: На прибрежных склонах основной причиной развития оползневых процессов является подмыв водами рек естественных склонов...
Дисциплины:
|
из
5.00
|
Заказать работу |
Содержание книги
Поиск на нашем сайте
|
|
|
|
Electricity is something we do not notice until we do not have it. However, few people understand what it is and still fewer can explain it. Let us try it anyway.
So, what is electricity? Electricity is the set of physical phenomena associated with the presence of electric charge.
Electricity is a secondary energy source which means that we get it from the conversion of other sources of energy into flowing electrons at the power plant. The type of power plant depends on the source of energy used: thermal power (coal, oil, gas, nuclear, underground steam), solar power (photovoltaic), kinetic power (water, wind) and chemical power (fuel cell). These sources of energy are called primary sources. The energy sources used to make electricity can be renewable and non- renewable, but electricity itself is neither renewable nor non-renewable.
The basic notions in electricity include the following.
 An Amp (A) is a unit measure of the amount of current in a circuit. An ammeter is a measuring instrument used to measure the current in a circuit. The majority of ammeters are connected in series. The current passes through the meter.
An Amp (A) is a unit measure of the amount of current in a circuit. An ammeter is a measuring instrument used to measure the current in a circuit. The majority of ammeters are connected in series. The current passes through the meter.
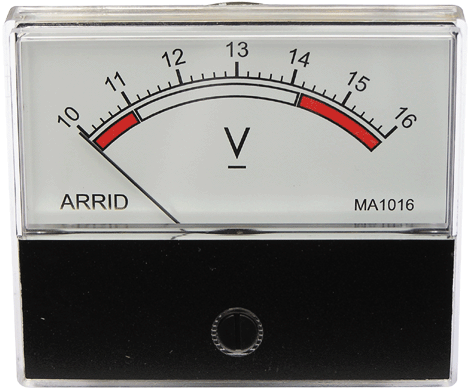 The pressure that forces the current to flow is measured in Volts (V). A transformer is used to change the voltage of electricity. This allows electricity to be transmitted over long distances at high voltages, but safely used at a lower voltage. A Watt (W) is a unit measure of electric power that depends on amps and volts. The more watts the bulb uses the more light is produced.
The pressure that forces the current to flow is measured in Volts (V). A transformer is used to change the voltage of electricity. This allows electricity to be transmitted over long distances at high voltages, but safely used at a lower voltage. A Watt (W) is a unit measure of electric power that depends on amps and volts. The more watts the bulb uses the more light is produced.
A voltmeter, also known as a voltage meter, is an instrument used for measuring the potential difference, or voltage, between two points in an electrical or electronic circuit. Some voltmeters are intended for use in direct current circuits; others are designed for alternating current circuits.
An Ohm (Ω) is a unit measure of materials resistance to a flowing current.
 An ohmmeter is an electricalinstrument that measures electrical resistance, the opposition to an electric current. Micro-ohmmeters make low resistance measurements. Megoohmmeters measure large values of resistance. The filament in the light bulb glows because its high resistance makes it hot. Low resistance of the support wires does not let them glow. The glass has a resistance so high that it does not allow the current to move through it – this property makes glass a good insulator.
An ohmmeter is an electricalinstrument that measures electrical resistance, the opposition to an electric current. Micro-ohmmeters make low resistance measurements. Megoohmmeters measure large values of resistance. The filament in the light bulb glows because its high resistance makes it hot. Low resistance of the support wires does not let them glow. The glass has a resistance so high that it does not allow the current to move through it – this property makes glass a good insulator.
An electric current is a flow of electric charge. In electric circuits this charge is often carried by moving electrons in a wire. The electrons, which flow through this wire, carry a negative charge. A lightning discharge is the same idea, just without the wire.
There are two different kinds of electrical current. One is called direct current because electrons are made to move in one direction only. It is usually abbreviated to DC. This kind of electricity is produced by a battery.
AC stands for alternating current where the electrons in the circuit reverse the direction of their flow. Alternating current is the form in which electric power is delivered to businesses and residences, and it is the form of electric energy that consumers typically use when they plug kitchen appliances, televisions and electric lamps into a wall socket.
Nowadays electricity is transmitted over long distances and the length of transmitting power lines varies from area to area.
 A wire system is termed a power line in case “it has no parallel branches” and “a power network” in case it has parallel branches. According to their functions, power lines and networks are subdivided into transmission and distribution lines. After electricity is made, it is sent into a system of cables and wires called a transmission grid. This system enables power plants and end users to be connected together.
A wire system is termed a power line in case “it has no parallel branches” and “a power network” in case it has parallel branches. According to their functions, power lines and networks are subdivided into transmission and distribution lines. After electricity is made, it is sent into a system of cables and wires called a transmission grid. This system enables power plants and end users to be connected together.
Transmission lines serve to deliver power from a station to distribution centres (substations). Power should be transmitted with minimal energy losses. It is cheaper and easier to carry a very high voltage but low current, over long distances. It can be done with the help of.high-voltagethinner overhead conductor wires, with an air gap between them to act as an insulator. The voltage of an AC power source can be easily changed by means of a power transformer. This allows the voltage to be stepped up (increased) for transmission and distribution. High-voltage transmission is more efficient than low-voltage transmission over long distances, because the loss caused by conductor resistance decreases as the voltage increases. Substations have transformers that change the high-voltage electricity into lower voltage electricity.
 Distribution lines deliver power from distribution centres (substations) to the loads, i. e. homes, offices, factories, which require low voltage electricity.
Distribution lines deliver power from distribution centres (substations) to the loads, i. e. homes, offices, factories, which require low voltage electricity.
Lines are also classed into: 1) overhead; 2) indoor; 3) cable (underground).
Overhead lines include line conductors, insulators, and supports. The conductors are connected to the insulators, and these are connected to the supports. The greater the resistance, the higher are the heating losses in the conducting wires. In order to reduce the losses, a step-down transformer can be used.
Indoor lines include conductors, cords, and buses. The conductor may include one wire or a combination of wires not insulated from one another. They deliver electric current to the consumers.
As to underground lines, they are used in city areas. Accordingly, they are used in cities and towns, and in the areas of industrial enterprises.
When electricity enters your home it must pass through a meter. A utility company worker reads the meter so the company will know how much electricity you have used and can bill you for the cost. After being metered, the electricity goes through a fuse box into your home. The fuse box protects the house in case of problems.
 (A) Exercise 1. Choose the correct answer.
(A) Exercise 1. Choose the correct answer.
1. What is electricity?
a) Electricity is the set of physical phenomena associated with the absence of electric charge.
b) Electricity is the set of physical phenomena associated with the presence of electric charge.
2. How is electricity made?
a) Electricity is made by the conversion of primary sources of energy into flowing electrons.
b) Electricity is made by the transmission of primary sources of energy at the power plant.
3. What are the basic notions in electricity?
a) The basic notions in electricity are primary and secondary sources of energy.
b) The basic notions in electricity include amps, volts, watts and ohms.
4. What is an electric current?
a) An electric current is a flow of electric charge.
b) An electric current is the set of physical phenomena associated with the presence of electric charge.
5. What is the difference between direct current and alternating current?
a) In direct current electrons move in one direction only while in alternating current the electrons move around.
b) In direct current electrons are made to move in one direction only while in alternating current the electrons in the circuit reverse the direction of their flow.
6. How are power lines and networks subdivided?
a) They are subdivided into transmission and distribution lines.
b) They are subdivided into transmission and generation lines.
7. How can power be transmitted with minimal energy losses over long distances?
a) It is not easy to transmit power with minimal energy losses using very high voltage electricity.
b) It is easier to transmit power with minimal energy losses using very high voltage electricity.
8. What is the function of distribution lines?
a) Distribution lines enable power plants and end users to be connected together.
b) Distribution lines deliver power from distribution centres (substations) to the loads.
9. How are lines classed into?
a) Lines are classed into overhead; indoor and cable (underground).
b) Lines are classed into overhead and indoor.
10. What happens when electricity enters our home?
a) When electricity enters our home it must pass through a meter, a utility company worker reads the meter and the company bill you for the cost.
b) When electricity enters our home it goes through a fuse box.
(A) Exercise 2. Divide the text into logical parts. Find the key sentences of each part and make a plan of the text.
(A) Exercise 3. Using the plan retell the text in Russian/Belarusian.
(B) Exercise 4. Put the questions into the correct order according to the text. Answer the questions.
 1. What is the fuse box used for?
1. What is the fuse box used for?
2. How does a utility company know how much electricity you have used?
3. What is an Ohm? What electricalinstrument is used for measuring?
4. Is electricity a secondary or a primary energy source?
5. What is electricity?
6. How can electricity be transmitted efficiently and with minimum energy losses?
7. What do the basic notions in electricity include?
8. What is a unit measure of the amount of current in a circuit?
9. What does the type of power plant depend on?
10. What is an electric current?
11. Where is electricity generated?
12. What does an ammeter measure?
13. How are power lines and networks subdivided?
14. What is measured in Volts and Watts?
15. What do an electric current and lightning have in common?
16. What is the difference between transmission and distribution lines?
17. How are overhead, indoor and underground lines used?
(B) Exercise 5. Make up a summary of the text in English.

(C) Exercise 6. Fill in the diagram and speak on the topic “Electricity basics”.
| POWER PLANT |
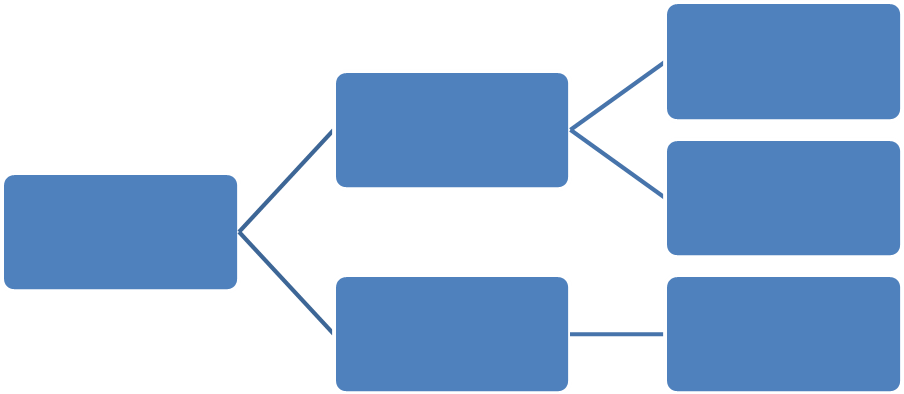
| SOURCE OF ENERGY |
| LINES |
| NOTIONS |
| ELECTRICITY |
| ELECTRIC CURRENT |
TEXT C

|
|
|

Двойное оплодотворение у цветковых растений: Оплодотворение - это процесс слияния мужской и женской половых клеток с образованием зиготы...

Автоматическое растормаживание колес: Тормозные устройства колес предназначены для уменьшения длины пробега и улучшения маневрирования ВС при...

Своеобразие русской архитектуры: Основной материал – дерево – быстрота постройки, но недолговечность и необходимость деления...

Наброски и зарисовки растений, плодов, цветов: Освоить конструктивное построение структуры дерева через зарисовки отдельных деревьев, группы деревьев...
© cyberpedia.su 2017-2025 - Не является автором материалов. Исключительное право сохранено за автором текста.
Если вы не хотите, чтобы данный материал был у нас на сайте, перейдите по ссылке: Нарушение авторских прав. Мы поможем в написании вашей работы!