- tissue system of a plant organ
- the structure of a plant organ
- the diversity of plant organs
- the structure of a plant
Look at the examples made by some student of the Institute of Natural Sciences
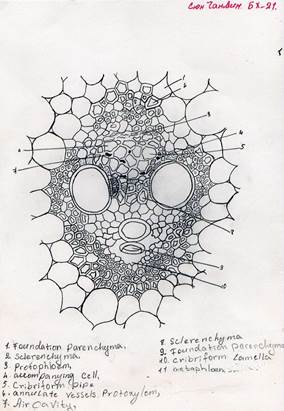
- tissue system of a plant organ (by Chanvin Grechikhina)
 Pic.1.
Pic.1.
Pic. 2.

-
- the diversity of plant organs, here the morphology of a leaf (by Chanvin Grechikhina Pic.1 and Christina Balakireva Pic.2
 Pic.3.
Pic.3.
Pic.4 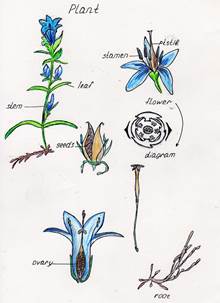
- the diversity of plant organs, here the morphology of a leaf (by Chanvin Grechikhina Pic.1 and Christina Balakireva Pic.2)
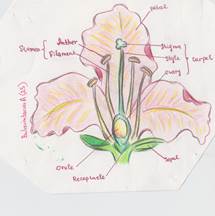
- the structure of a plant organ, here a flower (Pic.3 by Alexandra Bulavintseva)
- the diversity of plant organs (Pic.4 by Anastasia Kuzina)
II. Render the whole text
III.
a) While walking in the forest your friend finds an interesting leaf. He asks you to identify the tree. Imagine any leaf and make a little research of it, describing its morphology and thus making conclusions about the class, the family and probably about the genus and species of the plant (7 sentences).
b) You are a fifth-year student that is taking part in a botany practice of the first-year students. You are walking through flood lands of Kaluga region. Tell the students about some flowers and grass that you meet while walking (15 sentences). Speak to them as your botany professor usually does.
IV. Speak about your practice in Botany. The following pictures may help you.


Unit 3 Animals
Animals.
I
Read the text about animals. Find the passage which contains the information about the kind of food animals eat and the way they get it. Read and translate the passage.
Animal are multicellular organisms that obtain energy by eating food. They live in a vast range of habitats, from deserts and Arctic tundra to the deep-sea floor.
Like all living things, animals show similarities and differences that enable them to be classified into groups. Birds, for example, are the only animals that have feathers, while mammals are the only ones that have fur. Animals are also classified according to other characteristics, including their internal anatomy, patterns of development, and genetic makeup. Scientists divide the animal kingdom into approximately 30 groups, each called a phylum.
One phylum of animals, the chordates, has been more intensively studied than has any other, because it comprises nearly all the world’s largest and most familiar animals as well as humans. This phylum includes mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, and fish together with a collection of lesser-known organisms. Some invertebrate phyla contain relatively few species. Vertebrates are customarily divided into cold-blooded (an animal whose temperature is dictated by its surroundings) and warm-blooded animals (is one that keeps its body at a constant warm temperature by generating internal heat).
Few parts of Earth’s surface are entirely devoid of animal life. Animals cannot survive in places where water is unavailable or permanently frozen, or where temperatures regularly exceed 55° C. However, in all habitats that lie between these extremes, animal life abounds. In the seas and oceans, the greatest diversity of animal life is found in habitats close to shores. On land, animal habitats are strongly influenced by climate, the combination of precipitation and temperature conditions experienced in a region. For land animals, the most testing habitats are ones that experience intense drought or extreme cold.
Animals all feed on organic matter, but their diets and way of obtaining food vary enormously. Some animals are omnivores, meaning that they are capable of surviving on a very wide range of foods. Many other animals have extremely precise requirements and cannot deviate from their highly specialized diet. In general, animals eat plants, other animals, or the remains of living things. Plant-eaters, or herbivores, often do not have to search far to find things to eat, and in some cases—for example wood-boring insects—they are entirely surrounded by their food. But plant food can be difficult to digest and is often low in nutrients. Carnivores live on flesh from other animals that is often nutrient-rich and easy to digest but difficult to obtain. Finding and capturing this kind of food calls for keen senses. Some mammalian predators increase their chances of success by hunting in groups. Some position themselves in a suitable location and wait for their prey to come within striking distance. In predatory animals, teeth or other mouthparts often play a part in catching and subduing food as well as in preparing it for digestion.
Wherever they live, animals need oxygen in order to survive. By breathing, or respiring, they extract oxygen from their surroundings and dispose of carbon dioxide waste. Very small animals do not need any special adaptations for obtaining oxygen. Oxygen simply diffuses in through their body surface, with carbon dioxide traveling out the same way. To obtain sufficient oxygen, large animals have to boost their oxygen intake by using special respiratory organs. In water, many animals breathe by using gills.
Vocabulary
To obtain, habitat, desert, tundra, bird, feather, fur, internal anatomy, chordates, to comprise, reptile, amphibian, fish, invertebrates/ vertebrates, cold-blooded, warm-blooded, to abound, diversity, climate, precipitation, condition, drought, carnivores/ omnivores/ herbivores, keen senses, predator, prey, to hunt, teeth, to subdue, to breathe, gills, to extract, to dispose.




 Pic.1.
Pic.1.
 Pic.3.
Pic.3.








