 CirculatorySystem
CirculatorySystem
The circulatory system, also called the cardiovascular system or the vascular system, is an organ system that permits blood to circulate and transport nutrients, oxygen, carbon dioxide, hormones, and blood cells to and from the cells in the body to provide nourishment and help in fighting diseases, stabilizing temperature and pH, and maintaining homeostasis.The circulatory system includes the lymphatic system, which circulates lymph.Blood is a fluid consisting of plasma, red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets that is circulated by the heartthrough the vascular system, carrying oxygen and nutrients to and waste materials away from all body tissues.
The cardiovascular (from Latin words meaning "heart" and "vessel") system comprises the blood, heart, and blood vessels. Humans have a closed cardiovascular system, meaning that the blood never leaves the network of arteries, veins and capillaries. The circulatory system of the blood is seen as having two components, a systemic circulation (systemic circuit) and a pulmonary circulation (pulmonary circuit). This system includes the pulmonary circulation, a "loop" (‘a circulatory loop’) through the lungs where blood is oxygenated; and the systemic circulation, a "loop" through the rest of the body to provide oxygenated blood.
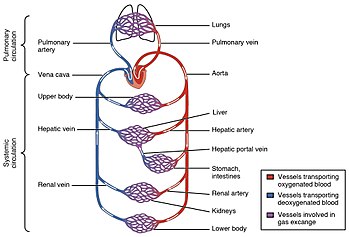
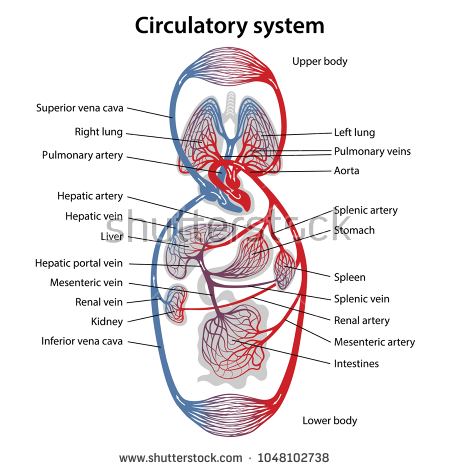
The first part of the systemic circulation is the aorta, a massive and thick-walled artery. The aorta arches and gives branches supplying the upper part of the body after passing through the aortic opening of the diaphragm at the level of the thoracic tenth vertebra, it enters the abdomen. Later it descends down and supplies branches to abdomen, pelvis, perineum and the lower limbs. When the aorta receives almost five liters of blood from the heart, it recoils and is responsible for pulsating blood pressure. Moreover, as aorta branches into smaller arteries, their elasticity goes on decreasing and their compliance goes on increasing.Twenty major arteries make a path through your tissues. The main arteries which branch off the aorta and take blood to specific parts of the body are:
· Carotid arteries, which take blood to the neck and head
· Coronary arteries, which provide blood supply to the heart itself
· Hepatic artery, which takes blood to the liver with branches going to the stomach
· Mesenteric artery, which takes blood to the intestines
· Renal arteries, which takes blood to the kidneys
· Femoral arteries, which take blood to the legs
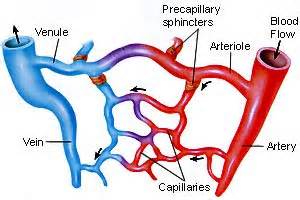
Arteries branch into smaller passages called arterioles and then into the capillaries. They are the smallest vessels. The capillaries merge into venules to bring blood into the venous system.Venules continue to merge into veins. The venous system finally coalesces into two major veins: the superior vena cava (roughly speaking draining the areas above the heart) and the inferior vena cava (roughly speaking from areas below the heart). These two great vessels empty into the right atrium of the heart. There are many valves found in veins throughout the body. However, there are no valves found in any of the other arteries besides the aorta and pulmonary trunk.
Hepatic Portal Circulation. The veins of the stomach and intestines perform a unique function: instead of carrying blood directly back to the heart, they carry blood to the liver through the hepatic portal vein. Blood leaving the digestive organs is rich in nutrients and other chemicals absorbed from food. The liver removes toxins, stores sugars, and processes the products of digestion before they reach the other body tissues. Blood from the liver then returns to the heart through the inferior vena cava.
Cardiovascular system has the following functions:
· to circulate oxygen and removes carbon dioxide.
· to provide cells with nutrients.
· to remove the waste products of metabolism to the excretory organs for disposal.
· to protect the body against disease and infection.
· clotting stops bleeding after injury.
· to transport hormones to target cells and organs.
· to help to regulate body temperature.
Heart
The cardiovascular system is powered by the body’s hardest-working organ — the heart, which is only about the size of a closed fist and is roughly cone-shaped. It is about 12cm long, 9cm across the broadest point and about 6cm thick. The heart is a muscular pumping organ located medial to the lungs along the body’s midline in the thoracic region. The bottom tip of the heart, known as its apex, is turned to the left, so that about 2/3 of the heart is located on the body’s left side with the other 1/3 on right. The top of the heart, known as the heart’s base, connects to the great blood vessels of the body: the aorta, vena cava, pulmonary trunk, and pulmonary veins. The heart has three layers; the endocardium (inner layer), the epicardium (middle layer), and myocardium (outer layer). The heart is protected by the pericardium, which is the protective membrane surrounding it.
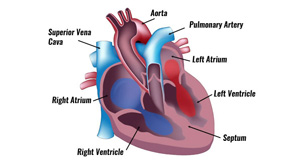

The heart pumps oxygenated blood to the body and deoxygenated blood to the lungs. In the human heart there is one atrium and one ventricle for each circulation, and with both a systemic and a pulmonary circulation there are four chambers, enclosed by thick, muscular walls, in total: left atrium, left ventricle, right atrium and right ventricle. A wall called the interventricular septum divides the ventricles. A wall called the interatrial septum divides the atria, which are separated from the ventricles by the atrioventricular valves. Valves are fibrous flaps of tissue found between the heart chambers and in the blood vessels. Valves between the atria and ventricles are known as the right and left atrioventricular valves, otherwise known as the tricuspid and mitral valves respectively. Valves between the ventricles and the great arteries are known as the semilunar valves. The aortic valve is found at the base of the aorta, while the pulmonary valve is found at the base of the pulmonary trunk.
The coronary circulation system provides a blood supply to the heart muscle itself.
Useful to know:
Cardiologists are medical professionals specializing in the heart, and cardiothoracic surgeons specialize in operating on the heart and its surrounding areas. Vascular surgeons focus on other parts of the circulatory system. Cardiologists are specialists who are certified to diagnose, treat and prevent disease of the heart, arteries and veins. Cardiologists are certified by the American Board of Internal Medicine (ABIM) after meeting educational and practice requirements. Before being certified as cardiologists, those aspiring to the specialty must be certified in internal medicine. Then cardiologists can become certified in one of several cardiology subspecialties, including transplant cardiology, cardiovascular disease, clinical cardiac electrophysiology and interventional cardiology.
Extension https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=OFMsvgUivvI Circulatory Cycle (video)
9. Fill in gaps with the given words and word combination according to the text:
Make a word combination, match the words:
Circulatory, artery,blood supply, vessels, interatrial septum, pulmonary, capillaries, fluid, pumping organ
1. The __________ system is an organ system. 2. Blood is a ________consisting of plasma, red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. 3. Cardiovascular system forms a network of ________ of different types such as arteries, veins and capillaries. 4. __________ circulation is a circulatory loop going through the lungs where blood is oxygenated. 5. Aorta is a massive and thick-walled_________. 6. Arteries branch into small passages called arterioles and then into the __________. 7. The heart is a muscular ____________ located between the lungs in the thoracic region. 8. A wall called the ____________divides the atria, which are separated from the ventricles by the atrioventricular valves. 9. The coronary circulation system provides a ______________ to the heart muscle itself.
10. Make a word combination, match the words:
circulatory vena cava
carbon loop
systemic valve
circulatory blood
femoral system
superior trunk
pulmonary septum
interventricular artery
semilunar circulation
oxygenated dioxide
11. See the given verb list. Choose noun(s) or noun + adjectives from the list below that can form word combinations with these verbs:



 CirculatorySystem
CirculatorySystem





