

Общие условия выбора системы дренажа: Система дренажа выбирается в зависимости от характера защищаемого...

Своеобразие русской архитектуры: Основной материал – дерево – быстрота постройки, но недолговечность и необходимость деления...

Общие условия выбора системы дренажа: Система дренажа выбирается в зависимости от характера защищаемого...

Своеобразие русской архитектуры: Основной материал – дерево – быстрота постройки, но недолговечность и необходимость деления...
Топ:
Определение места расположения распределительного центра: Фирма реализует продукцию на рынках сбыта и имеет постоянных поставщиков в разных регионах. Увеличение объема продаж...
Методика измерений сопротивления растеканию тока анодного заземления: Анодный заземлитель (анод) – проводник, погруженный в электролитическую среду (грунт, раствор электролита) и подключенный к положительному...
Выпускная квалификационная работа: Основная часть ВКР, как правило, состоит из двух-трех глав, каждая из которых, в свою очередь...
Интересное:
Аура как энергетическое поле: многослойную ауру человека можно представить себе подобным...
Берегоукрепление оползневых склонов: На прибрежных склонах основной причиной развития оползневых процессов является подмыв водами рек естественных склонов...
Наиболее распространенные виды рака: Раковая опухоль — это самостоятельное новообразование, которое может возникнуть и от повышенного давления...
Дисциплины:
|
из
5.00
|
Заказать работу |
|
|
|
|
Orthopedics is the medical specialty responsible for treating entire skeletal system. In the United States, orthopedic surgeons have typically completed four years of undergraduate education and four years of medical school. They then undergo residency training in orthopedic surgery. The American Board of Orthopaedic Surgery oversees the certification process for this specialty. Many go on to further specialize in specific areas, such as the spine, hand or sports injuries.
Milestones
Humans have been dealing with injuries and disease from the beginning of time. Some important milestones in the history of orthopedics include:
· In the Paleolithic period, early man engraved human bones after eating their owners. "Engraving is usually considered part of a modern behavior kit, a new way of expression typical of our species," said study lead author Silvia Bello, a paleoanthropologist at the Natural History Museum in London.
· Hippocrates, the ancient Greek father of medicine, develops splints for fractures of the tibia.
· During the Roman era, Galen (199-129 B.C.) describes the skeletal system and the surrounding muscles. Medical experts of the time also develop the first artificial prostheses.
· Ambroise Pare (1510-1590), the father of French surgery, develops techniques for amputations and artificial limbs.
· Antonius Mathysen (1805-1878), a Dutch military surgeon, in 1851 invents the plaster of Paris (POP) bandage. A POP cast remains the primary method of fracture immobilization today.
· In 1895, Wilhelm Conrad Roentgen accidentally discovers an image cast from his cathode ray generator, projected far beyond the possible range of the cathode rays. He wins the Nobel Prize for Physics in 1901 for his discovery of X-rays.
· Sir Reginald Watson-Jones (1902-1972) publishes "Fractures and Joint Injuries" in 1940, which remains a standard reference for several decades.
· In 1949, H. Lowry Rush (1879-1965) uses stainless steel pins to treat long bone fractures.
· Marijuana is found to possibly heal bone fractures, according to research by the Tel Aviv University's Sackler Faculty of Medicine in 2015.
· 2016 sees the creation of living bone grown from the cells of patients for the first time.
X rays

A German physicist named Wilhelm Conrad Röntgen discovered X rays in 1895. He found that these invisible rays had the ability to pass through the body and trace an image on a photographic plate placed on the other side of the body. While X rays can travel easily through soft organs like the skin and muscles, it is harder for them to penetrate denser material like bone. This results in an image showing white traces where the bones should be. Within months of Röntgen’s discovery, many doctors were using the mysterious rays to help them diagnose fractures. Röntgen was awarded the Nobel Prize for his discovery in 1901.
Sources:
https://www.livescience.com
Unit 6
|
|
Muscular system
T opic Muscular System
Grammar – ingforms (Present Participle, Gerund, Verbal Noun) Revision Passive Voice
Vocabulary Muscular system, Noun suffix -ure, prefix re- Revision Noun suffixes - tion, - ment, Adjective suffix – al, Adverb suffix - ly
Reading ‘Muscular System’, ‘Skeletal Muscles’, ‘Muscle Metabolism and Fatigue ’
Listening ‘Smooth Muscles’ (video)
Speaking Pair work (Description of Muscles), Summary

Getting started
1. Look at the picture and try to answer the following questions:
ü What’s the man doing?
ü How is the man feeling? Put down three words or phrases to describe his feelings.
ü How does the picture make you feel?
ü Do you go in for sports? What kind of sports?
ü How do you feel after a training session? Do you feel your muscles have got tired?
ü Give your reasons for going in for sports being important for a human being.
Vocabulary for help ing you to cope with texts and tasks:
Word building:

Noun suffixes - tion, - ment, -ure
Adjective suffix - al
Adverb suffix - ly
Prefix re-
See Unite 2 for the noun suffixes -tion, - ment and adverb suffix - ly
See Unite 5 for the suffix – al
Suffix - ure forms a noun being added to a verb. For example, “mixture” is a noun which is formed by adding the - (t)ure suffix to the end of the verb, “mix”: a dventure, pressure, pleasure.
Preffix re- – being added to nouns, verbs and adjectives is used with the meaning “again” or “again and again” to indicate repetition, or with the meaning “back” or “backward” to indicate withdrawal or backward motion: regenerate; refurbish; retype; retrace; revert, re-election, revised,
2. Define the part of the speech of the words given below and translate them into Russian:
Skeletal, fundamental.contraction, function, motion, posture, locomotion, movement, internal, connection, action, approximately, consciously, structure, usually, stimulation, oxidation, reaction, identical, bilateral, insertion, location, direction, anatomical, abdominal, transversely, situation respiration, fermentation, finally, quickly, exertion, intrinsically, react, release, diagonally, directly, actually, regeneration, re-write, rebuild, mitral
3. Read and translate the anatomical terms of Latin-Greek origin. Pay your attention to the pronunciation of the words:
Peristalsis[,perI`stxlsIs], esophagus[J’sOfqgqs], bronchus [‘brONkqs] (pl. bronchi[‘brONkaI]), uterus[`jHt(q)rqs], urethra[juq’rJTrq], tetanus[‘tet(q)nqs], rectusabdominis[`rektqsxb`dOmInIs], transverseabdominis[trxnz`vE:sxb`dOmInIs], tibialisanterior[,tIbI`eIlIsxn`tIqrIq], brachioradialis[`brakIq(V)`reIdIqlIs], sternocleidomastoid[,stWnq(V),klAIdq(V)`mastOId], sternum[`stE:nqm], clavicle[`klxvIkl], mastoidprocess[`mastOId `prquses], occipitofrontalis[Ok`sIpItqV`frAnt(q)lIs], occipitalbone[Ok’sIpItlbqun], biceps[`baIseps], triceps[`traIseps], quadriceps[`kwOdrIseps], deltoid[`deltOId], serratusmuscle[sI’reItqsmAsl], rhomboidmajor[`rOmbOId `meIGq], rhombus[`rOmbqs], gluteusmaximus[`glHtIqs `mxksImqs], gluteusmedius[`glHtIqs `mJdIqs], gluteusminimus[`glHtIqs `mInImqs], lacticacid[`lxktIk `xsId], myocardium[,maIqu`kRdIqm], hormone[`hLmqun]
Useful vocabulary
 muscle[mAsl] - мышца
muscle[mAsl] - мышца
toconstruct[kqn’strAkt] – составлять, строить
discrete[dI’skrJt] – прерывистый, прерывный
|
|
bloodvessel[blAd ‘ves(q)l]– кровеносныйсосуд
tocontract[‘kOntrxkt]- сокращаться
contraction[kqn’trxkS(q)n]– сокращение, укорочение
tochange[CeInG]- менять, изменять
length[leNT]– длинна, протяжённость
shape[SeIp]– форма, очертание
motion[‘mquS(q)n] - движение, телодвижение
tomaintain[meIn’teIn] - поддерживать, сохранять
posture [‘pOsCq]– поза, положение, осанка
locomotion[,lqukq’mquS(q)n]- передвижение
internalorgans[In’tE:n(q)l‘Lgqnz]– внутренниеорганы
heart[hRt] - сердце
digestivesystem [daI’GestIv‘sIstqm] - пищеварительнаясистема
toderive[dI’raIv] – получать, производить
tomean[mJn]– означать, иметь ввиду
tomove[mHv] - двигаться, перемещаться
voluntarymuscle[‘vOlqnt(q)rImAsl]– произвольно сокращающаяся мышца
involuntarymuscle[In‘vOlqnt(q)rImAsl]– непроизвольно сокращающаяся мышца
cardiacmuscle[‘kRdIxkmAsl]– сердечная мышца, миокард
smoothmuscle[smHT mAsl]– гладкаямышца
skeletalmuscle[‘skelIt(q)l mAsl] – скелетнаямышца
toanchor[‘xNkq] – закреплять, привязывать
average[‘xv(q)rIG] – средний, усреднённый
male[meIl]– мужчина, мужского пола, самец
female[‘fJmeIl]– женщина, женского пола, самка
consciously[‘kOnSqslI]- сознательно
twitch[twIC]- мышечное сокращение
esophagus[J’sOfqgqs]- пищевод
stomach[‘stAmqk] - желудок
intestines[In’testIns]- кишечник
bronchus[‘brONkqs] (pl. bronchi[‘brONkaI]) – бронх (бронхи)
urethra[juq’rJTrq]– уретра, мочеиспускательный канал
bladder[‘blxdq]– мочевой пузырь
skin[skIn]– кожа
topump[pAmp]– накачивать, прокачивать, нагнетать
heartbeat[hRtbJt]– цикл сокращения сердечной мышцы
rate[reIt] of contraction – частотасокращений
fat[fxt]- жир
carbohydrate[,kRbq’haIdreIt] - углевод
cause[kLz]- причина
tocause[kLz]– быть причиной, вызывать
tetanus[‘tet(q)nqs]– длительное сокращение скелетной мышцы, судорога
bilateral muscle[baI’lxt(q)r(q)lmAsl]– билатеральная (двусторонняя) мышца
toresultin[rI’zAlt]– приводить к (чему-либо), заканчиваться (чем-либо)
a number of [‘nAmbq] - ряд
the number of [‘nAmbq] - число
torelateto[rI’leIt]– иметьотношениек
trunk[trANk] – туловище, корпус
topull[pul] – тянуть, тащить
origin[‘OrIGIn]– началомышцы
insertion[In’sE:S(q)n]– местоприкрепления (мышцы), инсерция
fleshy[‘fleSI]- мясистый
abdominalregion[xb’dOmIn(q)l ‘rJG(q)n]– областьживота
toidentify[aI’dentIfaI] - определять, устанавливать
occipitalbone[Ok’sIpItl bqun] – затылочнаякость
serrated[sI’reItId] – зубчатый, зазубренный
oblique[q`blJk]- косой
flexor[`fleksq] – сгибающаямышца
4. Translate the following word combinations paying your attention to the word formation:
Skeletal muscle - muscular system, to construct an organ system - constructed of elastic tissue – construction of a cell, to contract in response - rate of contraction - contracting muscle, a long muscle – the length of bone – prolonged contraction, to move throughout the whole body - food moving through esophagus - movement of internal organs, to pump - pumping the blood, the cause of the disease – to cause the symptoms, a number of muscles - the number of males, to relate to muscular system – related to skull, insertion of muscle – to insert into the socket, tomean - the meaning of the word – by means of, tomaintain a skeleton - maintaining posture, to produce force - producing a contraction – blood production, to act consciously - muscle action, conscious control – unconscious - unconsciously, to term – termed as – terminology, to connect to the skeleton – connection of bones, to conduct the impulse - conduction system, to stimulate cardiac muscle cells - self-stimulation, power of contraction - powered by the oxidation
|
|
5. Translate the following word combinations into Russian:
Organ system consisting of muscles, blood vessels, muscular tissue, a contraction changing both the length and the shape of the cell, force and motion, maintaining and changing posture, look like mice moving under the skin, being either voluntary or involuntary, contract without conscious thought, contract upon command, anchored by tendons, average adult male, a percentage of body mass, skeletal muscles in the human body, voluntary muscle tissue, muscle serves to move parts of bones, smooth muscle, one layer of muscle, cardiac muscle, more similar in structure, found only in the heart, to make the heart beat, cells called cardiocytes, forming a network, cardiac muscle tissue, natural pacemaker of the heart, the oxidation of fats and carbohydrates, anaerobic chemical reactions, fast twitch fibers, muscle twitch, result from tetanus.
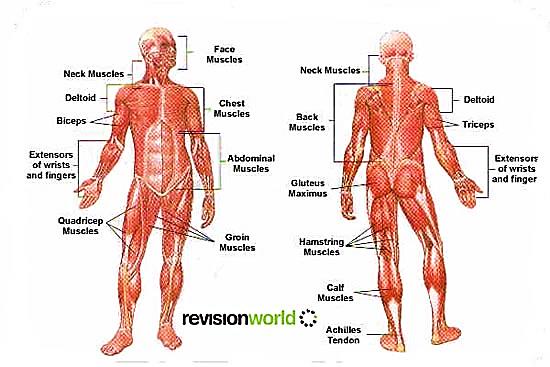
6. Look at the picture given bellow. Give your ideas for the following: 
ü What muscles and groups of muscles can you name?
ü What is the function of muscular system in a human body?
7. Muscle Quiz. Try to answer these questions: 
a) How many types of muscles are there in a human body?
One type - Four types - Three types
b) Muscle function is:
to produce force and motion – to support a human skeleton – to store proteins and acids
c) The term muscle is derived from:
German origin – Russian origin – Latin origin
d) There are approximately ………. skeletal muscles in a human body.
639 - 720 - 206
e) Cardiac muscle is located in ………
skull - tarsals - heart
8. Read the text and check your predictions. Translate the text into Russian paying your attention to special terms related to the muscular system:
Muscular system
The muscular system is an organ system consisting of muscles. The term muscle is derived from the Latin musculus meaning "little mouse" perhaps because of the shape of certain muscles or because contracting muscles look like mice moving under the skin. Each of these muscles is a discrete organ constructed of skeletal muscle tissue, blood vessels, tendons, and nerves. Muscle tissue is a soft tissue, and is one of the four fundamental types of tissue. Muscle cells contain protein filaments of actin and myosin that slide past one another, producing a contraction that changes both the length and the shape of the cell. Muscles function to produce force and motion. They are primarily responsible for maintaining and changing posture, locomotion, as well as movement of internal organs, such as the contraction of the heart and the movement of food through the digestive system via peristalsis.
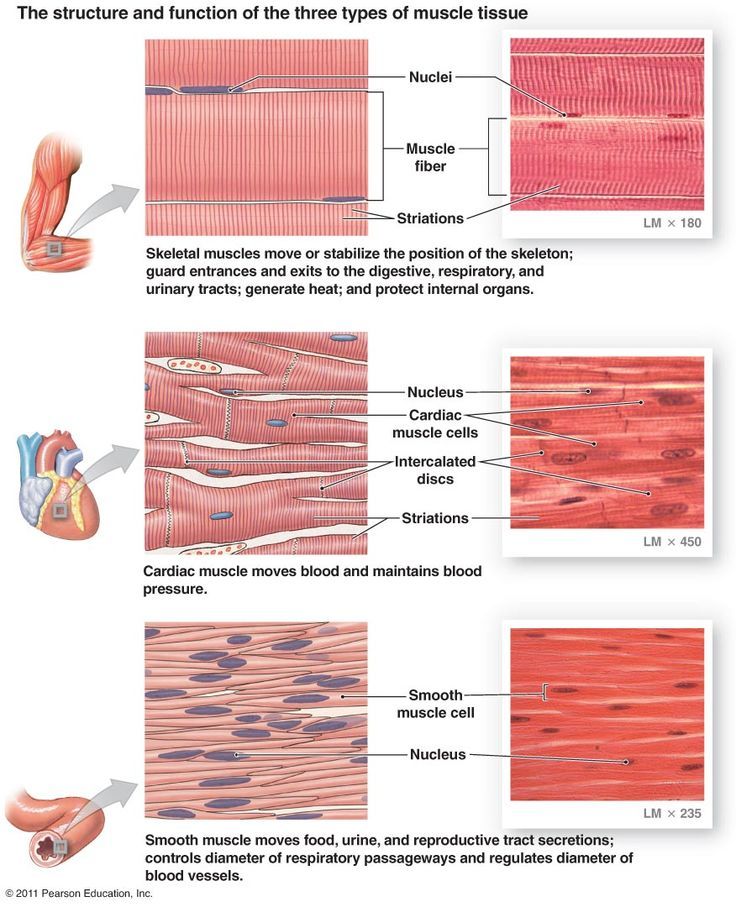
There are three types of muscle, skeletal or striated, cardiac, and smooth. Muscle action can be classified as being either voluntary or involuntary. Cardiac and smooth muscles contract without conscious thought and are termed involuntary, whereas the skeletal muscles contract upon command.
Skeletal muscle or "voluntary muscle" is anchored by tendons (or by aponeuroses at a few places) to bone and is used to effect skeletalmovement such as locomotion and in maintaining posture. Skeletal muscle fibers are very strong. Skeletal muscle derives its name from the fact that these muscles always connect to the skeleton in at least one place. There are approximately 639 skeletal muscles in the human body. An average adult male is made up of 42% of skeletal muscle and an average adult female is made up of 36% (as a percentage of body mass). Skeletal muscle is the only voluntary muscle tissue in the human body, it is controlled consciously. Every physical action that a person consciously performs (e.g. speaking, walking, or writing) requires skeletal muscle. The function of skeletal muscle is to contract
|
|
to move parts of the body closer to the bone that the muscle is attached to. Most skeletal muscles are to attach two bones across a joint, so the muscle serves to move parts of those bones closer to each other. Skeletal muscles in turn can be divided into fast and slow twitch fibers.
Smooth muscle or "involuntary muscle" is found within the walls of organs and structures such as the esophagus, stomach, intestines, bronchi, uterus, urethra, bladder, blood vessels, and the arrector pili in the skin. They are usually in sheets, or layers, with one layer of muscle behind the other. Unlike skeletal muscle, smooth muscle is not under conscious control.
Cardiac muscle (myocardium), is also an "involuntary muscle" but is more similar in structure to skeletal muscle. This type of muscle is responsible for pumping blood throughout the body. Cardiac muscle, found only in the myocardium, contracts in response to signals from the cardiac conduction system to make the heart beat. Cardiac muscle is made from cells called cardiocytes. Cardiocytes are branched, allowing them to connect with several other cardiocytes, forming a network that facilitates coordinated contraction. Cardiac muscle tissue cannot be controlled consciously, so it is an involuntary muscle. While hormones and signals from the brain adjust the rate of contraction, cardiac muscle stimulates itself to contract. The natural pacemaker of the heart is made of cardiac muscle tissue that stimulates other cardiac muscle cells to contract. Because of its self-stimulation, cardiac muscle is considered to be autorhythmic or intrinsically controlled.
Muscles are predominantly powered by the oxidation of fats and carbohydrates,but anaerobic chemical reactions are also used, particularly by fast twitch fibers. (An impulse from a nerve cell causes calcium release and brings about a single, short muscle contraction called a muscle twitch. If there is a problem at the neuromuscular junction, a very prolonged contraction may occur, such as the muscle contractions that result from tetanus. Also, a loss of function at the junction can produce paralysis.)
Мышечная система-это система органов, состоящая из мышц. Термин мышца происходит от латинского musculus, означающего "маленькая мышь", возможно, из-за формы некоторых мышц или потому, что сокращающиеся мышцы выглядят как мыши, движущиеся под кожей. Каждая из этих мышц представляет собой отдельный орган, состоящий из скелетной мышечной ткани, кровеносных сосудов, сухожилий и нервов. Мышечная ткань является мягкой тканью и является одним из четырех основных типов тканей. Мышечные клетки содержат белковые нити актина и миозина, которые скользят мимо друг друга, производя сокращение, которое изменяет как длину, так и форму клетки. Мышцы функционируют, чтобы производить силу и движение. Они в первую очередь отвечают за поддержание и изменение позы, передвижение, а также движение внутренних органов, таких как сокращение сердца и движение пищи через пищеварительную систему через перистальтику.
Существует три типа мышц: скелетные или поперечно-полосатые, сердечные и гладкие. Мышечное действие может быть классифицировано как произвольное или непроизвольное. Сердечные и гладкие мышцы сокращаются безсознательно и называются непроизвольными, тогда как скелетные мышцы сокращаются по команде.
|
|
Скелетная мышца или" произольная мышца " прикрепляется сухожилиями (или апоневрозами в нескольких местах) к кости и используется для осуществления скелетных движений, таких как локомоция и поддержание осанки. Скелетные мышечные волокна очень прочны. Скелетная мышца получила свое название из-за того, что эти мышцы всегда соединяются со скелетом хотя бы в одном месте. В человеческом теле насчитывается около 639 скелетных мышц. Средний взрослый мужчина состоит из 42% скелетных мышц, а средняя взрослая женщина состоит из 36% (в процентах от массы тела). Скелетная мышца является единственной произвольной мышечной тканью в организме человека, она управляется сознательно. Каждое физическое действие, которое человек сознательно выполняет (например, речь, ходьба или письмо), требует скелетных мышц. Функция скелетной мышцы заключается в сокращении
для перемещения частей тела ближе к кости, к которой прикреплена мышца. Большинство скелетных мышц прикрепляют две кости поперек сустава, поэтому мышца служит для перемещения частей этих костей ближе друг к другу. Скелетные мышцы, в свою очередь, можно разделить на быстрые и медленные дергающиеся волокна.
Гладкая мышца или" непроизвольная мышца " находится в стенках органов и структур, таких как пищевод, желудок, кишечник, бронхи, матка, мочеиспускательный канал, мочевой пузырь, кровеносные сосуды и arrector pili в коже. Они обычно находятся в листах или слоях, с одним слоем мышц за другим. В отличие от скелетных мышц, гладкие мышцы не находятся под сознательным контролем.
Сердечная мышца (миокард), также является "непроизвольной мышцей", но более похожа по структуре на скелетную мышцу. Этот тип мышц отвечает за перекачку крови по всему телу. Сердечная мышца, находящаяся только в миокарде, сокращается в ответ на сигналы от сердечной проводящей системы, чтобы заставить сердце биться. Сердечная мышца состоит из клеток, называемых кардиоцитами. Кардиоциты разветвляются, что позволяет им соединяться с несколькими другими кардиоцитами, образуя сеть, которая облегчает координированное сокращение. Сердечная мышечная ткань не может управляться сознательно, поэтому это непроизвольная мышца. В то время как гормоны и сигналы от мозга регулируют скорость сокращения, сердечная мышца стимулирует себя сокращаться. Естественный кардиостимулятор сердца состоит из ткани сердечной мышцы, которая стимулирует другие клетки сердечной мышцы сокращаться. Из-за своей самостимуляции сердечная мышца считается ауторитмичной или внутренне контролируемой.
Мышцы в основном питаются окислением жиров и углеводов,но анаэробные химические реакции также используются, в частности, быстрыми волокнами подергивания. (Импульс от нервной клетки вызывает высвобождение кальция и вызывает одно короткое мышечное сокращение, называемое мышечным подергиванием. Если есть проблема в нервно-мышечном соединении, может произойти очень длительное сокращение, такое как мышечные сокращения, которые являются результатом столбняка. Кроме того, потеря функции на стыке может привести к параличу.)
9. According to the text name the type of muscles which:
- contracts without conscious thought.
- contracts upon command.
- is anchored by tendons to bone.
- is an "involuntary muscle" but is more similar in structure to skeletal muscle.
- is found within the walls of organs and structures.
- is made from cells called cardiocytes.
- derives its name from the fact that these muscles always connect to the skeleton.
- is responsible for pumping blood throughout the body
- is the only voluntary muscle tissue.
- is usually in layers.
- serves to move parts of those bones closer to each other.
- can be divided into fast and slow twitch fibers.
- is not under conscious control.
- is found only in the heart.
10. Give the name of muscle type according to the description (cardiac muscle, skeletal muscle, smooth muscle):
1. _____________________________________________________
· Only found in the heart
· Contract and relax continuously
· Work without conscious effort
2. ______________________________________________________
· Around organs like the intestines
· Work without conscious effort
3. _______________________________________________________
· Attached to the skeleton
· Under your control
11.Make the following statements as true (T) or false (F):
a) The muscular system is an organ system consisting of muscles.
b) Muscle tissue is a hard tissue.
c) Muscle cells produce a contraction that changes both the length and the shape of the tendons.
d) Muscles function to produce force and motion.
e) The term muscle is derived from the Arabian musculus meaning "little mouse"
f) Muscle action can be classified only as being voluntary.
g) Skeletal muscle is anchored by tendons and ligaments to bone.
h) Smooth muscle is not under conscious control.
i) Because of its self-stimulation, cardiac muscle is considered to be autorhythmic.
j) A loss of function at the junction can produce the contraction.
|
|
|

Механическое удерживание земляных масс: Механическое удерживание земляных масс на склоне обеспечивают контрфорсными сооружениями различных конструкций...

Поперечные профили набережных и береговой полосы: На городских территориях берегоукрепление проектируют с учетом технических и экономических требований, но особое значение придают эстетическим...

Типы сооружений для обработки осадков: Септиками называются сооружения, в которых одновременно происходят осветление сточной жидкости...

Организация стока поверхностных вод: Наибольшее количество влаги на земном шаре испаряется с поверхности морей и океанов (88‰)...
© cyberpedia.su 2017-2024 - Не является автором материалов. Исключительное право сохранено за автором текста.
Если вы не хотите, чтобы данный материал был у нас на сайте, перейдите по ссылке: Нарушение авторских прав. Мы поможем в написании вашей работы!