 Speaking
Speaking
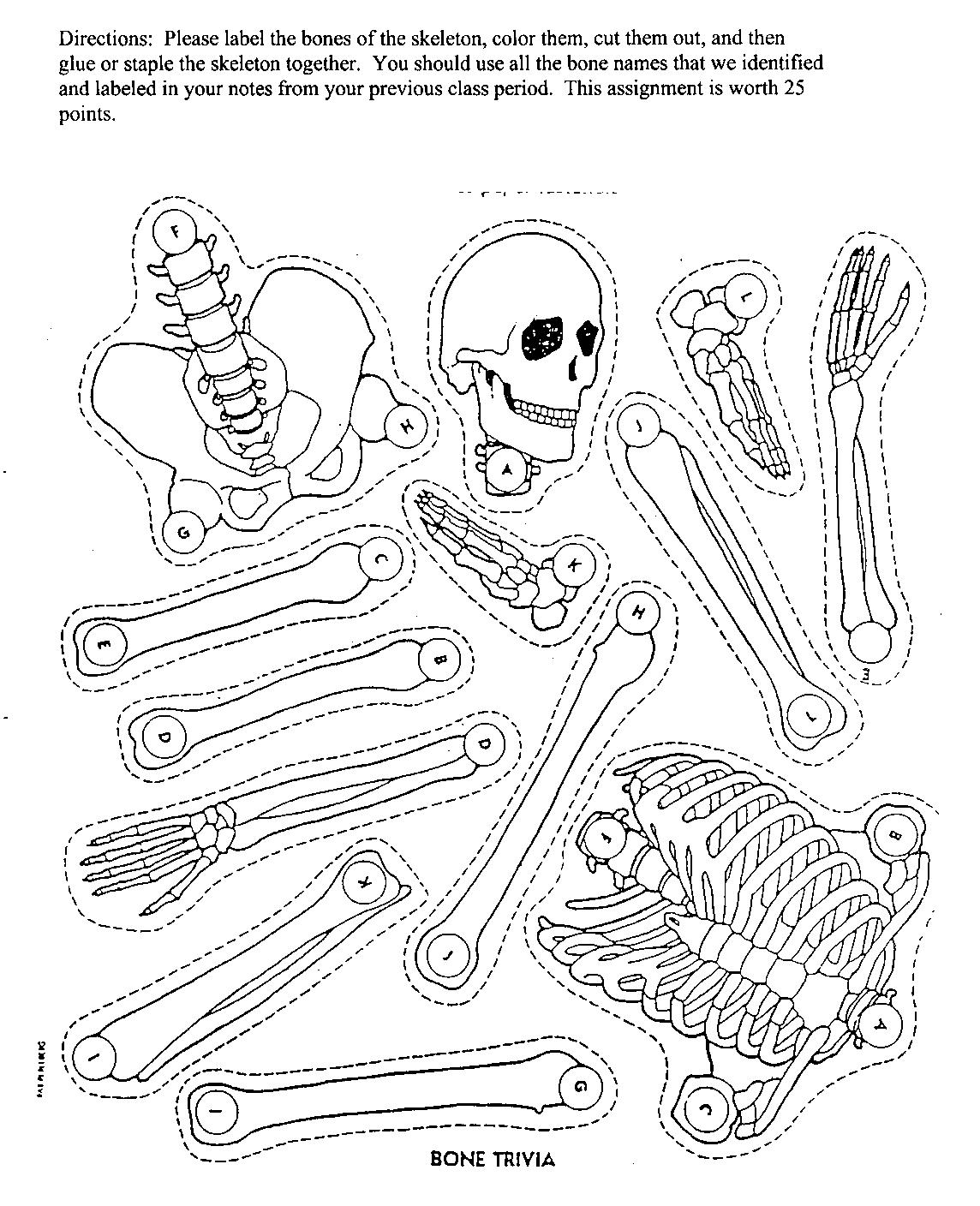
Make a model of human skeleton anddescribe the structure pointing to all the parts of the human skeleton.

Review your progress

Test for self-control
Vocabulary
50. Complete the table from the words given below:
vertebra (vertebrae), coccyx, sternum, mandible, clavicle, scapula (scapulae), humerus, radius, ulna, femur, tibia, patella, fibula, talus, skull, shoulder girdle, pelvis, chest, rib, breastbone, facial bone, elbow joint, forearm, wrist joint, hand, finger, phalange, thumb, hip bone, hip joint, knee joint, kneecap, ankle joint, foot, heel, toe (big toe)
| Head
| Trunk
| Upper extremity
| Low extremity
|
|
|
|
|
|
51. Label the picture with the words given below:
vertebra (vertebrae), coccyx, sternum, mandible, clavicle, scapula (scapulae), humerus, radius, ulna, femur, tibia, patella, fibula, talus, skull, shoulder girdle, pelvis, chest, rib, breastbone, facial bone, elbow joint, forearm, wrist joint, hand, finger, phalange, thumb, hip bone, hip joint, knee joint, kneecap, ankle joint, foot, heel, toe (big toe)
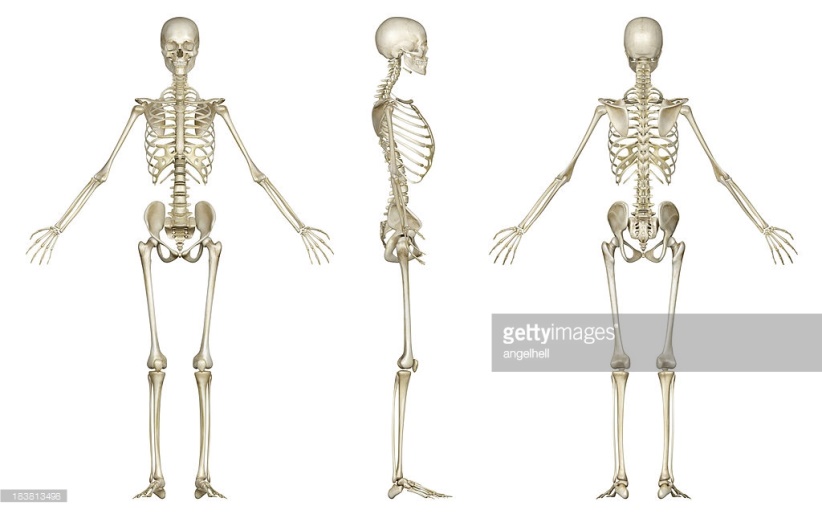
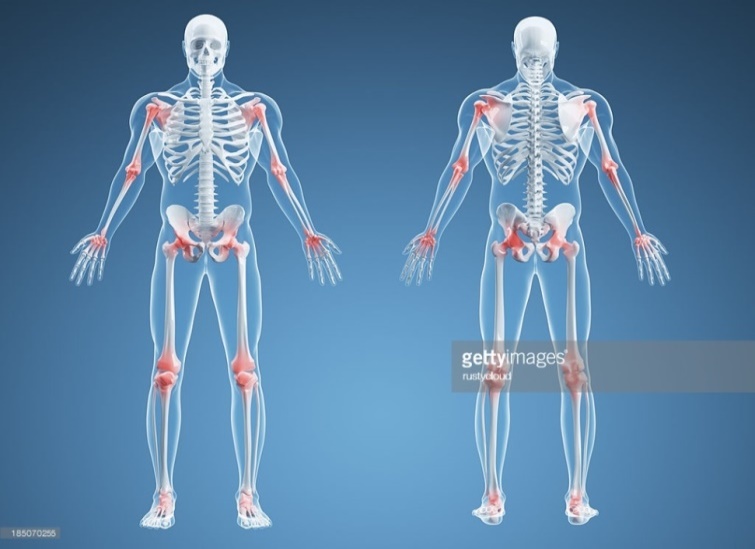
To what type of joint does each joint in the picture refer to?
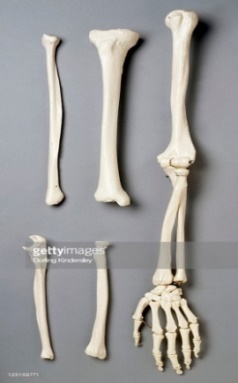
Name the bones in the picture and put them down.
Listening
54. Watch the video ‘Human Skeleton. Types of Joints’ and answer the questions:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=UXtG052Klkg
ü What are the main functions of the human skeleton?
ü What are 4 types of the bones?
ü What bones does the axial skeleton consist of?
ü What bones does the skull consist of?
ü What main regions are the vertebrae divided into?
ü What organs does a rib cage protect?
Grammar
55. Rewrite the sentences in the Passive:
1) Herophilosdissected human corpses in Alexandria.
2) Antonio Pollaiuolo performed dissections for better understanding of the body.
3) Many doctors used X rays for diagnostics the fractures.
4) 270 bones compose a skeleton at birth.
5) The shoulder girdle, the pelvic girdle and the bones of the upper and lower limbs or extremities form the appendicular skeleton.
6) The tarsals form the posterior end of the foot and heel.
56. Put the verbs in brackets into the Passive or the Active (pay your attention to the form of the verb):
Anatomists (use) a number of anatomical terms to portray the appearance, shape and function of bones. Other anatomical terms also (use) to specify the bone location.Many terms(derive) from Latin and Greeklanguages. Some anatomists still (use) Latin. The term "osseous", and the prefix "osteo-", related to bone, still (use) commonly today. Examples of terms used to describe bones (include) the term "foramen" to describe a hole through which something (pass). In general, long bones(have) three parts, namely a "head", "neck", and "body". When two bones (join) together, they are said to "articulate". If the two bones have a fibrous connection and are relatively immobile, then the joint (call) a "suture".
57. Translate the following text into English:
В составе скелета взрослого человека около 205—207 костей. Почти все они объединяются в единое целое с помощью суставов, связок и других соединений. 23 кости образуют череп, 32—34 — позвоночный столб, 25 — ребра и грудину, 64 — скелет верхних конечностей, 62 — скелет нижних конечностей. Каждая кость является органом. Кости скелета образованы костной и хрящевой тканями, относящиеся к соединительным тканям. Состоят кости из клеток. Состав кости стабилен. В ней содержится 45 % минеральных солей (соли кальция, калия, натрия и других элементов), 25 % воды и 30 % органических веществ.

Additional Information:
Skeletal System Physiology
Growth and Development
The skeleton begins to form early in fetal development as a flexible skeleton made of hyaline cartilage and dense irregular fibrous connective tissue. These tissues act as a soft, growing framework and placeholder for the bony skeleton that will replace them. As development progresses, blood vessels begin to grow into the soft fetal skeleton, bringing stem cells and nutrients for bone growth. Osseous tissue slowly replaces the cartilage and fibrous tissue in a process called calcification. The calcified areas spread out from their blood vessels replacing the old tissues until they reach the border of another bony area. At birth, the skeleton of a newborn has more than 300 bones; as a person ages, these bones grow together and fuse into larger bones, leaving adults with only 206 bones.
Flat bones follow the process of intramembranous ossification where the young bones grow from a primary ossification center in fibrous membranes and leave a small region of fibrous tissue in between each other. In the skull these soft spots are known as fontanels, and give the skull flexibility and room for the bones to grow. Bone slowly replaces the fontanels until the individual bones of the skull fuse together to form a rigid adult skull.
Long bones follow the process of endochondral ossification where the diaphysis grows inside of cartilage from a primary ossification center until it forms most of the bone. The epiphyses then grow from secondary ossification centers on the ends of the bone. A small band of hyaline cartilage remains in between the bones as a growth plate. As we grow through childhood, the growth plates grow under the influence of growth and sex hormones, slowly separating the bones. At the same time the bones grow larger by growing back into the growth plates. This process continues until the end of puberty, when the growth plate stops growing and the bones fuse permanently into a single bone. The vast difference in height and limb length between birth and adulthood are mainly the result of endochondral ossification in the long bones.
History
The study of human bones probably started in ancient Greece under Ptolemaic kings due to their link to Egypt. Herophilos, through his work by studying dissected human corpses in Alexandria is credited to be the pioneer of the field. His works are lost but are often cited by notable persons in the field such as Galen and Rufus of Ephesus. Galen himself did little dissection though and relied on the work of others like Marinus of Alexandria,[13] as well as his own observations of gladiator cadavers and animals.[14] According to Katherine Park, in medieval Europe dissection continued to be practiced, contrary to the popular understanding that such practices are taboo and thus completely banned.[15] The practice of holy autopsy, such as in the case of Clare of Montefalco further supports the claim.[16] Alexandria continued as a center of anatomy under Islamic rule, with Ibn Zuhr a notable figure. Chinese understandings are divergent, as the closest corresponding concept in the medicinal system seem to be the meridians, although given that Hua Tuo regularly performs surgery, there must be some distance between medical theory and actual understanding.
The Renaissance
Leonardo Da Vinci, among his many talents also contributed to the study of the skeleton, albeit unpublished in his time.[17] Many artists, Antonio Pollaiuolo being the first, performed dissections for better understanding of the body, although they concentrated mostly on the muscles.[18] Vesalius, regarded as the founder of modern anatomy authored the book De humani corporis fabrica, which contained many illustrations of the skeleton and other body parts, correcting some theories dating from Galen, such as the lower jaw being a single bone instead of two.[19] Various other figures like Alessandro Achillini also contributed to the further understanding of the skeleton.
· MORE
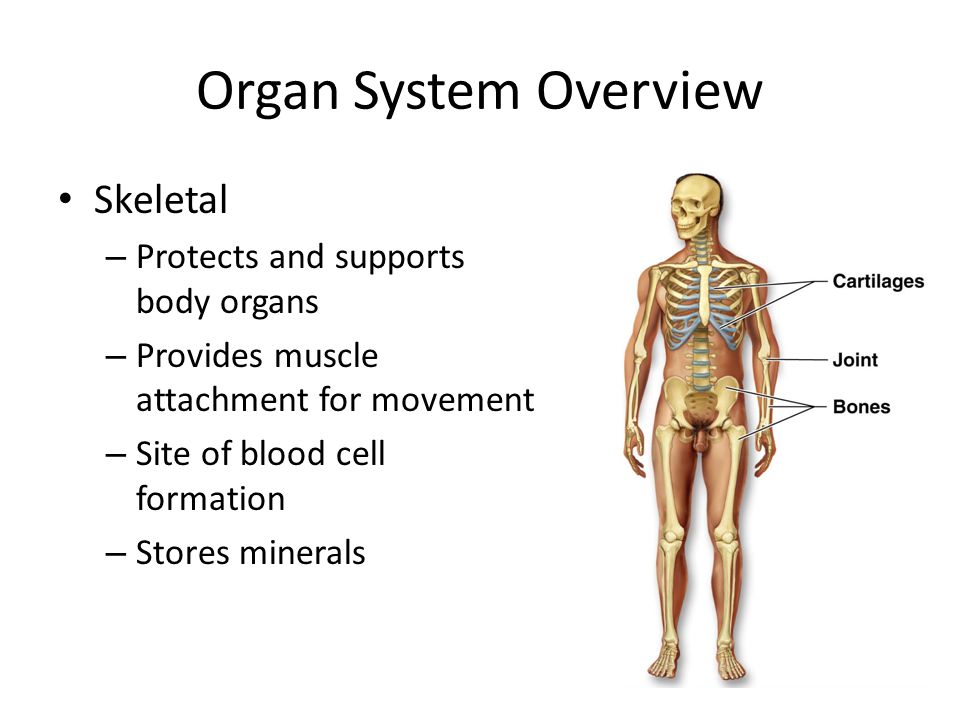
The adult human skeletal system consists of 206 bones, as well as a network of tendons, ligaments and cartilage that connects them. The skeletal system performs vital functions — support, movement, protection, blood cell production, calcium storage and endocrine regulation — that enable us to survive.
Animals with internal skeletons made of bone, called vertebrates, are actually the minority on Earth. As much as 98 percent of all animals are invertebrates, meaning they do not have internal skeletons or backbones.
The amount of bones a person is born with isn't the final tally later on. Human infants are born with about 300 bones, some of which fuse together as the body develops. By the time humans reach adulthood, they have 206 bones, according to Arizona State University’s School of Life Sciences. Human males grow until their late teens and females grow until two years after the beginning of their menstrual cycle, typically. This is when the growth plates on bones usually close, halting bone expansion.
The skeletons of adult males and females have some variation, primarily to accommodate childbirth. The female pelvis is flatter, more rounded and proportionally larger, for example. A male's pelvis is about 90 degrees or less of angle, whereas a female's is 100 degrees or more. [ Image Gallery: The BioDigital Human ]
While they become brittle when outside of the body, bones are very much alive inside the body, being fed by a network of blood vessels from the circulatory system and nerves from the nervous system, according to Healthline.
A typical bone has a dense and tough outer layer. Next is a layer of spongy bone, which is lighter and slightly flexible. In the middle of some bones is jelly-like bone marrow, where new cells are constantly being produced for blood, according to the Merck Manuals.
Teeth are considered part of the skeletal system but they are not counted as bones. Teeth are made of dentin and enamel, which is strongest substance in your body. Teeth also play a key role in the digestive system.
The skeletal system has two distinctive parts: the axial skeleton and the appendicular skeleton, according to the U.S National Library of Medicine(NLM).
The axial skeleton, with a total of 80 bones, consists of the vertebral column, the rib cage and the skull. The axial skeleton transmits the weight from the head, the trunk and the upper extremities down to the lower extremities at the hip joints, which help humans maintain our upright posture, the NLM noted.
The appendicular skeleton has a total of 126 bones, and is formed by the pectoral girdles, the upper limbs, the pelvic girdle and the lower limbs, according to the NLM. Their functions are to make walking, running and other movement possible and to protect the major organs responsible for digestion, excretion and reproduction.



 Speaking
Speaking











