

Археология об основании Рима: Новые раскопки проясняют и такой острый дискуссионный вопрос, как дата самого возникновения Рима...

Семя – орган полового размножения и расселения растений: наружи у семян имеется плотный покров – кожура...

Археология об основании Рима: Новые раскопки проясняют и такой острый дискуссионный вопрос, как дата самого возникновения Рима...

Семя – орган полового размножения и расселения растений: наружи у семян имеется плотный покров – кожура...
Топ:
Марксистская теория происхождения государства: По мнению Маркса и Энгельса, в основе развития общества, происходящих в нем изменений лежит...
Процедура выполнения команд. Рабочий цикл процессора: Функционирование процессора в основном состоит из повторяющихся рабочих циклов, каждый из которых соответствует...
Установка замедленного коксования: Чем выше температура и ниже давление, тем место разрыва углеродной цепи всё больше смещается к её концу и значительно возрастает...
Интересное:
Средства для ингаляционного наркоза: Наркоз наступает в результате вдыхания (ингаляции) средств, которое осуществляют или с помощью маски...
Финансовый рынок и его значение в управлении денежными потоками на современном этапе: любому предприятию для расширения производства и увеличения прибыли нужны...
Распространение рака на другие отдаленные от желудка органы: Характерных симптомов рака желудка не существует. Выраженные симптомы появляются, когда опухоль...
Дисциплины:
|
из
5.00
|
Заказать работу |
|
|
|
|
Content
Preface
Introduction
Recommended literature
Topic 1. Philosophy, its subject and role in society
Table 1. Philosophy and pre-philosophical worldview systems
Table 2. The main question of philosophy
Table 3. Historical forms of materialism
Table 4. The relationship between philosophy and the individual Sciences
Basic concepts of the topic
Topic 2. The history of philosophy as a source of philosophical ideas
Table 5. The main stages of the development of Western European philosophy
Basic concepts of the topic
Topic 3. Philosophy of the Ancient East
Table 6. Philosophy of Ancient India and Ancient China
Basic concepts of the topic
Topic 4. Ancient philosophy
Table 7. Stages of development and characteristic features of ancient philosophy
Basic concepts of the topic
Topic 5. Philosophy of the Middle Ages
Table 8. Stages of development of medieval philosophy
Table 9. The dispute about universals in the philosophy of the Middle Ages
Basic concepts of the topic
Topic 6. Philosophy of the Renaissance
Table 10. General characteristics of Renaissance philosophy
Table 11. The principle of humanism in the culture of the Renaissance
Basic concepts of the topic
Topic 7. Philosophy of the New Age
Table 12. General characteristics of the philosophy of Modern times...Twenty nine
Table 13. Francis bacon was the founder of empiricism in the philosophy of the New time
Table 14. Rationalism in Modern Philosophy
Table 15. Subjective idealism in Modern Philosophy
Basic concepts of the topic
Topic 8. German classical philosophy
Table 16. The main representatives of German classical philosophy
Table 17. Hegel's Philosophy
Basic concepts of the topic
Topic 9. The philosophy of Marxism
Table 18. The main sources
of Marxist philosophy
Basic concepts of the topic
Topic 10. Western philosophy of the twentieth century
Table 20. Conditions of formation, characteristic features and main directions of Western philosophy of the twentieth century
Basic concepts of the topic
Topic 11. Russian Philosophy
Table 21. The main stages of the development of philosophy in Russia.
Table 22. Russian Religious Philosophy
Table 23. The materialist tradition in Russian philosophy
Table 24. The philosophy of Russian Cosmism
Basic concepts of the topic
TOPIC 1. PHILOSOPHY, ITS SUBJECT AND ROLE IN SOCIETY
Table 1. Philosophy and pre-philosophical worldview systems
| Basic worldview systems | Socio-historical conditions of formation | Features of the worldview | Form of reflection of reality | ||||
| Mythology | Ancient society: adaptation to nature, subsistence farming, collective labor, lack of social inequality. | Syncretism of world perception. The idea of the unity of the world, the inseparable relationship of man and nature. | Fantastic performances, emotional-figurative form. | ||||
| Religion | Formation of the social division of labor and the system of social inequality. The emergence of privileged social strata (priests, ministers of worship). | The world is divided into 2 parts:
1) earthly, natural, perceived by the senses,
2) heavenly, supernatural, inaccessible to sensory perception
the basis of the religious worldview is the belief in the supernatural. | Illusory representations, emotional-figurative form. | ||||
| Philosophy | A class-organized society. The emergence of groups of people who are free from physical labor and have the opportunity to professionally devote themselves to spiritual activities. | The concept of the unity of being, in which two basic types of reality are distinguished: material and spiritual. | Rational, logical-conceptual form. |
Table 2.
The «main question» of philosophy,
its two sides are the wording 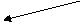
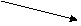
| Ontological (what is primary?) | Epistemological (is the world cognizable?) | Main philosophical directions | |||
 The primary material principle
The primary material principle
| the world is cognizable, a person is able to reveal the laws of nature and society, to make a reliable picture of the world (epistemological optimism). | materialism | |||
The primary spiritual (ideational) principle:
a) objective, i.e. existing independently of the human will and consciousness;
b) subjective-individual human consciousness  
|
usually: the world is knowable, but within certain limits;
usually: reliable knowledge about the objective world cannot be obtained (agnosticism) | idealism: objective subjective | |||
 Material and spiritual-equal, independent of each other principles
Material and spiritual-equal, independent of each other principles
| usually: the world is cognizable | dualism |
|
|
|

Семя – орган полового размножения и расселения растений: наружи у семян имеется плотный покров – кожура...

Биохимия спиртового брожения: Основу технологии получения пива составляет спиртовое брожение, - при котором сахар превращается...

Архитектура электронного правительства: Единая архитектура – это методологический подход при создании системы управления государства, который строится...

Наброски и зарисовки растений, плодов, цветов: Освоить конструктивное построение структуры дерева через зарисовки отдельных деревьев, группы деревьев...
© cyberpedia.su 2017-2024 - Не является автором материалов. Исключительное право сохранено за автором текста.
Если вы не хотите, чтобы данный материал был у нас на сайте, перейдите по ссылке: Нарушение авторских прав. Мы поможем в написании вашей работы!