Operation purpose: to learn to determine painting masses of equivalents.
Devices and reactants: the burette, support with pads, rubber and glass tubes, test tubes, a clip, scales, a glass funnel, the crane, metal (iron, magnesium, zinc), the diluted hydrochloric acid.
Procedure. To collect the installation presented in fig. 1. It consists of a support (1) with holders, burettes (2), a reactionary test tube (3). The burette and test tube are connected among themselves by rubber tubes (4), test tubes to openings (5, 6) and glass tubes (7).

Fig. 1. Installation for determination of
painting weight of equivalents of metal
Calculate a metal hinge plate which needs to be taken for replacement of 20 or 50 ml of hydrogen (depending on burette volume). Weigh it on scales with an accuracy of 0,01 g and place in a test tube. The doubled amount of solution of acid or alkali, in comparison with calculated, place in the second knee of a test tube. Check the device on tightness. Turn a test tube so that acid it was poured in that knee of a test tube where there is a metal. Zinc and iron reaction with the diluted hydrochloric acid goes on the equation:
 Ме + 2HCl ® MeCl2 + H2
Ме + 2HCl ® MeCl2 + H2
Reaction with iron demands heating which should be carried out carefully and with breaks. The hydrogen which is allocating as a result of interaction of metal with acid, forces out water from the burette. The equalizer thus should be lowered a vessel and during experience to try to keep water in it and the burette at one level that gas pressure in the device all the time was close to atmospheric. When all metal will be dissolved, will stop water level falls in the burette.
Lead the volume of the emitted hydrogen by normal conditions (n.c.) Thus consider that hydrogen collected over water, contains water vapor and that the general pressure of gas in the burette, equal to atmospheric pressure, it consists of partsialny pressure of hydrogen and water vapor.
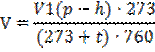
The mass of metal – m, g;
The volume of the forced-out gas in experimental conditions – V, ml;
Experience temperature – t, 0C.;
Atmospheric pressure on a barometer – P, Pa;
Pressure of saturated steam of water at an experience temperature - h, Pa.
Metal equivalent of the corresponding 1,008 g of hydrogen (on the volume of 11 200 ml) calculate on a formula: Eме=11200·m/V.
It is necessary to make experiment 3 times. The size of a chemical equivalent of metal calculate as an average from three definitions.
In the conclusions calculate mistake size as a percentage on a formula:
mistake=(Etheory– Eexperiment)/ Etheory ·100%.
Laboratory work № 2
Chemical thermodynamics
Operation purpose: Definition of thermal effect of reaction.
Experience 1. Thermal effect of interaction of potassium hydroxide with water.
Devices and reactants: Glass on 500 ml with a stick, a support, the thermometer, the potassium hydroxide, the distilled water.
Work course: In a glass almost to the bottom to lower the thermometer strengthened in a support. To weigh 25 g of potassium hydroxide and to place in a glass so that to close a thermometer ball. Then in a glass to pour in 50 ml of water and carefully to mix a glass stick. Solution will strongly be warmed, the thermometer will show temperature.
KOH + q=KOH + q, DH =-13,3 kcal
To define the maximum value of temperature.
Experience 2. Definition of thermal effect of reaction натрата ammonium with water.
Devices and reactants: Glass on 200 ml with a stick, a support with a pad, the thermometer, a test tube, the ammonium nitrate, the distilled water.
Work course: In a glass almost to the bottom to lower the thermometer strengthened in a support. To weigh 60 g of nitrate of ammonium and to place in a glass so that to close a thermometer ball. Then in a glass to pour in 100 ml of water and to place in it a test tube, on a quarter filled with water. Carefully to mix a glass stick. At dissolution of nitrate of ammonium in water temperature falls to - 200C and below. The glass outside becomes covered with hoarfrost.
NH4NO3 + q = NH4NO3 + q, DH = + 6.3 kcal.
To define the minimum value of temperature. To draw a conclusion.
Laboratory work № 3
Speed of chemical reaction
Operation purpose: To establish influence of various factors on the speed of chemical reaction.
Experience 1. Dependence of speed of reaction on concentration of reacting substances. Interaction of thiosulphate of sodium with sulfuric acid.
Devices and reactants: stop watch, glasses, the cylinder, the pipette, the distilled water, Na2S2O3 and H2SO4 solutions.
Procedure. In three test tubes to pour on 2 ml 0,5 N of solution of sulfuric acid, in three others to pour:
1. 2 ml 0,5 N solution of Na2S2O3 and 4 ml of H2O;
2. 4 ml 0,5 N solution of Na2S2O3 and 2 ml of H2O;
3. 6 ml 0,5 N solution of Na2S2O3.
Interaction of Na2S2O3 and H2SO4 proceeds on the equations:
Na2S2O3 + H2SO4 = Na2SO4
Na2S2O3 = H2SO3 + S¯
To merge in pairs prepared Na2S2O3 and H2SO4 solutions and to count time on a stop watch from the moment of draining prior to emergence of turbidity in each test tube. Emergence of dregs testifies to formation of the first molecules of sulfur which drops out in a deposit.
Results of experience enter in the table.
| №
| Volume, ml
| the Period from the reaction beginning before turbidity, sec.
| the Relative speed of the reaction, V
|
| Na2S2O3
| Н2О
| Na2SO4
|
| 1
| 2
| 4
| 2
|
|
|
| 2
| 2
| 2
| 4
|
|
|
| 3
| 2
| 0
| 6
|
|
|
Draw a conclusion on dependence of speed of reaction on concentration of reacting substances.
Experience 2. Dependence of speed of reaction on catalyst existence.
Devices and reactants: stop watch, glasses, the cylinder, the pipette, the distilled water, 0,5 N Na2S2O3 solution, 0,5 N Na2SO4 solution, 0,2 N CuSO4 solution.
Work course: In three test tubes pour on 2 ml 0,5 N solution of Na2S2O3 and add on 1, 2, 3 ml 0,2 N of CuSO4 solution. In the first two test tubes add 2 and 1 ml of water that the total amount of solution in all test tubes made 5 ml. In other three test tubes pour on 5 ml 0,5 N of solution of sulfuric acid. Mix in pairs Na2S2O3 solutions, and CuSO4 and define time before solution turbidity.
Results of experience enter in the table.
| №
| Volume, ml
| the Period from the reaction beginning before turbidity, sec.
| the Relative speed of the reaction, V
|
| Na2S2O3
| Н2О
| Na2SO4
| CuSO4
|
| 1
| 2
| 1
| 2
| 5
|
|
|
| 2
| 2
| 2
| 1
| 5
|
|
|
| 3
| 2
| 3
| 0
| 5
|
|
|
Compare value of speed of reaction of the corresponding test tubes to speed in experience 1. Draw a conclusion.
Laboratory work № 4




 Ме + 2HCl ® MeCl2 + H2
Ме + 2HCl ® MeCl2 + H2