

Кормораздатчик мобильный электрифицированный: схема и процесс работы устройства...

Типы сооружений для обработки осадков: Септиками называются сооружения, в которых одновременно происходят осветление сточной жидкости...

Кормораздатчик мобильный электрифицированный: схема и процесс работы устройства...

Типы сооружений для обработки осадков: Септиками называются сооружения, в которых одновременно происходят осветление сточной жидкости...
Топ:
Процедура выполнения команд. Рабочий цикл процессора: Функционирование процессора в основном состоит из повторяющихся рабочих циклов, каждый из которых соответствует...
Организация стока поверхностных вод: Наибольшее количество влаги на земном шаре испаряется с поверхности морей и океанов...
История развития методов оптимизации: теорема Куна-Таккера, метод Лагранжа, роль выпуклости в оптимизации...
Интересное:
Аура как энергетическое поле: многослойную ауру человека можно представить себе подобным...
Отражение на счетах бухгалтерского учета процесса приобретения: Процесс заготовления представляет систему экономических событий, включающих приобретение организацией у поставщиков сырья...
Что нужно делать при лейкемии: Прежде всего, необходимо выяснить, не страдаете ли вы каким-либо душевным недугом...
Дисциплины:
|
из
5.00
|
Заказать работу |
|
|
|
|
Many factors influence rates of chemical reactions, and these are summarized below.
1. Nature of Reactants. Acid-base reactions, formation of salts, and exchange of ions are fast reactions. Reactions in which large molecules are formed or break apart are usually slow. Reactions breaking strong covalent bonds are also slow.
2. Temperature. Usually, the higher the temperature, the faster the reaction. The temperature effect is discussed in terms of activation energy.
The rate constant k is affected by the temperature and this dependence may be represented by the Arrhenius equation:
E a/ RT
k = A e
where the pre-exponential factor A is assumed to be independent of temperature, R is the gas constant, and T the temperature in K.
3. Concentration Effect. The dependences of reaction rates on concentrations are called rate laws. Rate laws are expressions of rates in terms of concentrations of reactants. Keep in mind that rate laws can be in differential forms or integrated forms. They are called differential rate laws and integrated rate laws. The following is a brief summary of topics regarding rate laws.
The reaction rates of chemical reactions are the amounts of a reactant reacted or the amount of a product formed per unit time, (moles per second). Often, the amount can be expressed in terms of concentrations. Usually, the rate of a reaction is a function of the concentrations of reactants. For example, the rate of the reaction 2 NO + O2 = 2 NO2 has the form:
Rate = k [O2] [NO]2
The rate is proportional to the concentration of O2, usually written as [O2] and is proportional to the square of [NO], or [NO]2. The orders of 1 and 2 for [O2] and [NO] respectively has been determined by experiment, NOT from the chemical equation. The total order of this reaction is 3 (=2+1).
Rate laws apply to homogeneous reactions in which all reactants and products are in one phase (solution).
4. Heterogeneous reactions: reactants are present in more than one phase
For heterogeneous reactions, the rates are affected by surface areas.
5. Catalysts: substances used to facilitate reactions
By the nature of the term, catalysts play important roles in chemical reactions.
Chatelier's Principle. If you aren't sure about the words dynamic equilibrium or position of equilibrium you should read the introductory page before you go on
If a dynamic equilibrium is disturbed by changing the conditions, the position of equilibrium moves to counteract the change
Using Le Chatelier's Principle with a change of concentration
Suppose you have an equilibrium established between four substances A, B, C and D.
А + 2В «С + D
In case you wonder, the reason for choosing this equation rather than having just A + B on the left-hand side is because further down this page I need an equation which has different numbers of molecules on each side. I am going to use that same equation throughout this page.
|
|
Using Le Chatelier's Principle with a change of pressure
This only applies to reactions involving gases:
А (г) + 2В(г) «С(г) + D(г)
According to Le Chatelier, the position of equilibrium will move in such a way as to counteract the change. That means that the position of equilibrium will move so that the pressure is reduced again.
Pressure is caused by gas molecules hitting the sides of their container. The more molecules you have in the container, the higher the pressure will be. The system can reduce the pressure by reacting in such a way as to produce fewer molecules.
In this case, there are 3 molecules on the left-hand side of the equation, but only 2 on the right. By forming more C and D, the system causes the pressure to reduce.
Increasing the pressure on a gas reaction shifts the position of equilibrium towards the side with fewer molecules.
А (г) + 2В(г) «С(г) + D(г)
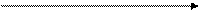
The position of equilibrium moves to the right if you increase the pressure on the reaction.
Using Le Chatelier's Principle with a change of temperature
For this, you need to know whether heat is given out or absorbed during the reaction. Assume that our forward reaction is exothermic (heat is evolved): А + 2В «С + D DH=-250 kJ mol-1
This shows that 250 kJ is evolved (hence the negative sign) when 1 mole of A reacts completely with 2 moles of B. For reversible reactions, the value is always given as if the reaction was one-way in the forward direction.
To cool down, it needs to absorb the extra heat that you have just put in. In the case we are looking at, the back reaction absorbs heat. The position of equilibrium therefore moves to the left. The new equilibrium mixture contains more A and B, and less C and D.
А + 2В «С + D DH=-250 kJ mol-1
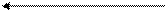
The position of equilibrium moves to the left if you increase the temperature.
If you were aiming to make as much C and D as possible, increasing the temperature on a reversible reaction where the forward reaction is exothermic isn't a good idea.
|
|
|

Архитектура электронного правительства: Единая архитектура – это методологический подход при создании системы управления государства, который строится...

Механическое удерживание земляных масс: Механическое удерживание земляных масс на склоне обеспечивают контрфорсными сооружениями различных конструкций...

Двойное оплодотворение у цветковых растений: Оплодотворение - это процесс слияния мужской и женской половых клеток с образованием зиготы...

Таксономические единицы (категории) растений: Каждая система классификации состоит из определённых соподчиненных друг другу...
© cyberpedia.su 2017-2024 - Не является автором материалов. Исключительное право сохранено за автором текста.
Если вы не хотите, чтобы данный материал был у нас на сайте, перейдите по ссылке: Нарушение авторских прав. Мы поможем в написании вашей работы!