7. Decide if these statements are True or False:
1. The endocrine system is a complex network of glands and organs that secret hormones.
2. The response of the autonomic nervous system is faster than endocrine control.
3. The endocrine cells of the pancreas make up just about 1% of the total mass of the pancreas.
4. An adrenal gland, triangular-shaped glands, is located at the bottom of each kidney.
5. The parathyroid glands are one pair of small found on the anterior side of the thyroid gland.
6. Thyroid hormones also help to maintain normal blood pressure and heart rate.
7. The hypothalamus contains special cells called neurosecretory cells—neurons that secrete hormones.
8. Read the text and check your answers in task True or False:
 Endocrine System
Endocrine System
The endocrine system (endocrine derives via New Latin from the Greek words ἔνδον, endon, "inside, within") and "exocrine" from the κρίνω, krīnō, "to separate, distinguish") is a complex network of glands and organs that secret hormones to control and coordinate your body's internal metabolism (or homeostasis), energy level, reproduction, growth and development, tissue function, sleep, and mood, and response to injury, stress, and environmental factors.The endocrine system along with the autonomic nervous system is responsible for maintaining homeostasis. The response of the autonomic nervous system is faster than endocrine control but the latter is more precise.
Endocrine glands are glands of the endocrine system that secrete their products, hormones, directly into interstitial spaces which then are absorbed into blood. Hormones are chemical messengers used to communicate between organs and tissues for physiological regulation and behavioral activities. They may affect one or several organs throughout the body.Endocrine glands consist of groups of secretory cells which are surrounded by capillary networks. Special features of endocrine glands are their ductless nature, their vascularity, and commonly the presence of intracellular vacuoles or granules that store their hormones.
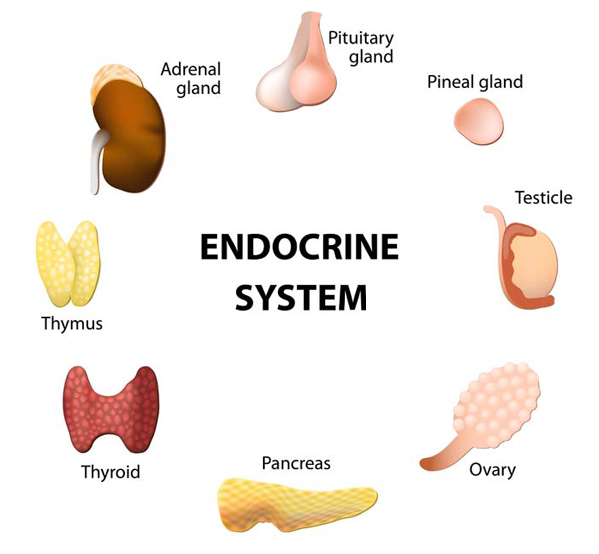
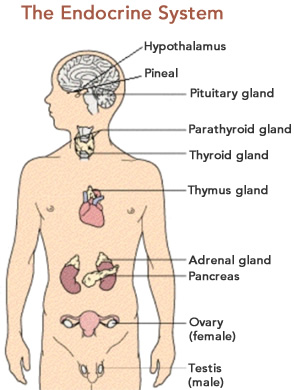
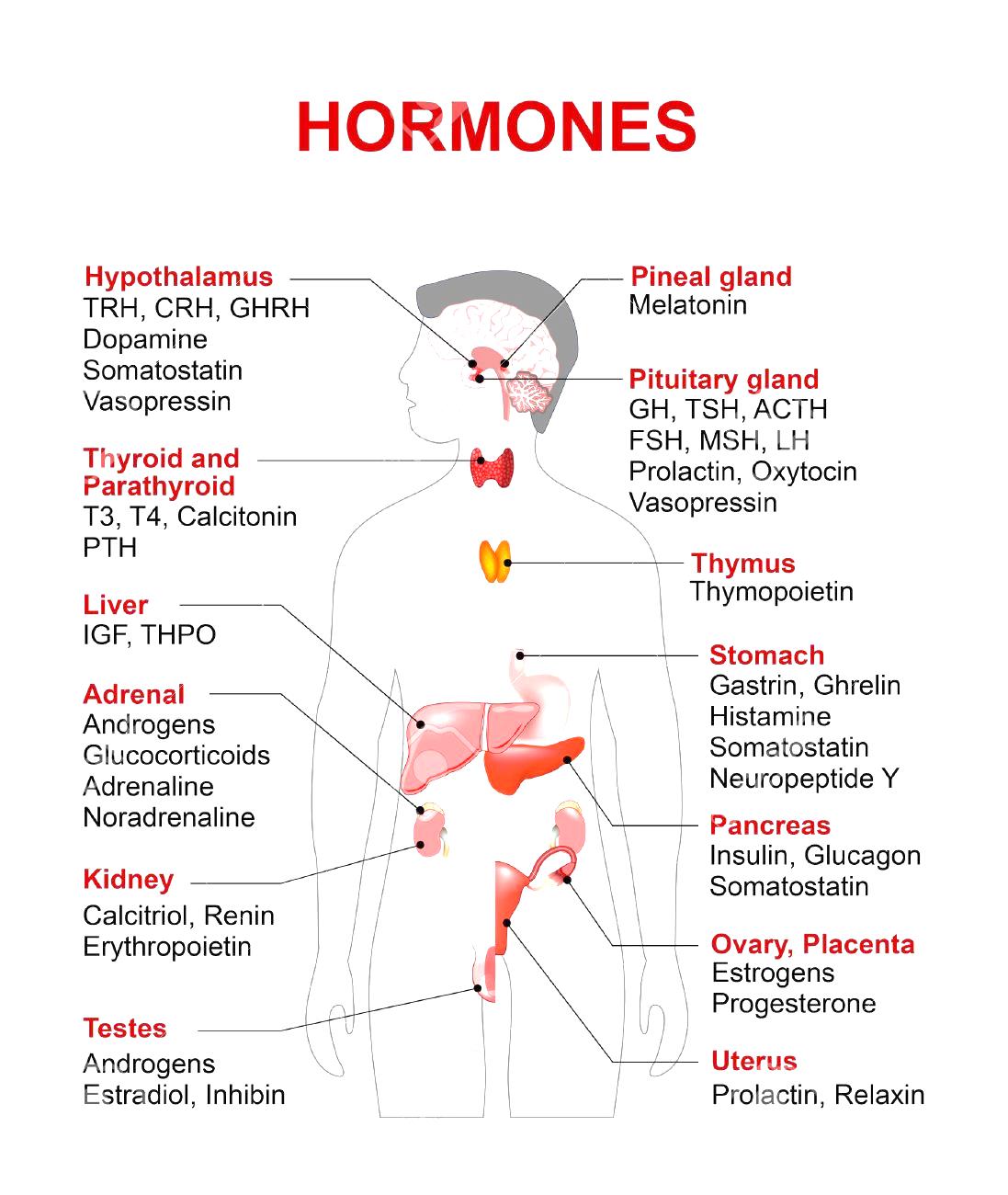
Endocrine glands are widely separated from each other and are not physically connected. The major glands of the endocrine system include the pineal gland, pancreas, ovaries, testes, thyroid gland, parathyroid gland, hypothalamus and adrenal glands. The hypothalamus and pituitary gland are neuroendocrine organs.The pancreas has a role in hormone production as well as in digestion.
In addition to the specialized endocrine organs mentioned above, many other organs that are part of other body systems, such as bone, kidney, liver, heart, adipose tissue, placenta, have secondary endocrine functions.
Hypothalamus. The hypothalamus is a part of the brain located superior and anterior to the brain stem and inferior to the thalamus. It serves many different functions in the nervous system, and is also responsible for the direct control of the endocrine system through the pituitary gland. The hypothalamus contains special cells called neurosecretory cells—neurons that secrete hormones. The hypothalamus secretes hormones that stimulate or suppress the release of hormones in the pituitary gland, in addition to controlling food intake, weight regulation, fluid intake and balance, thirst, body heat, and the blood pressure.
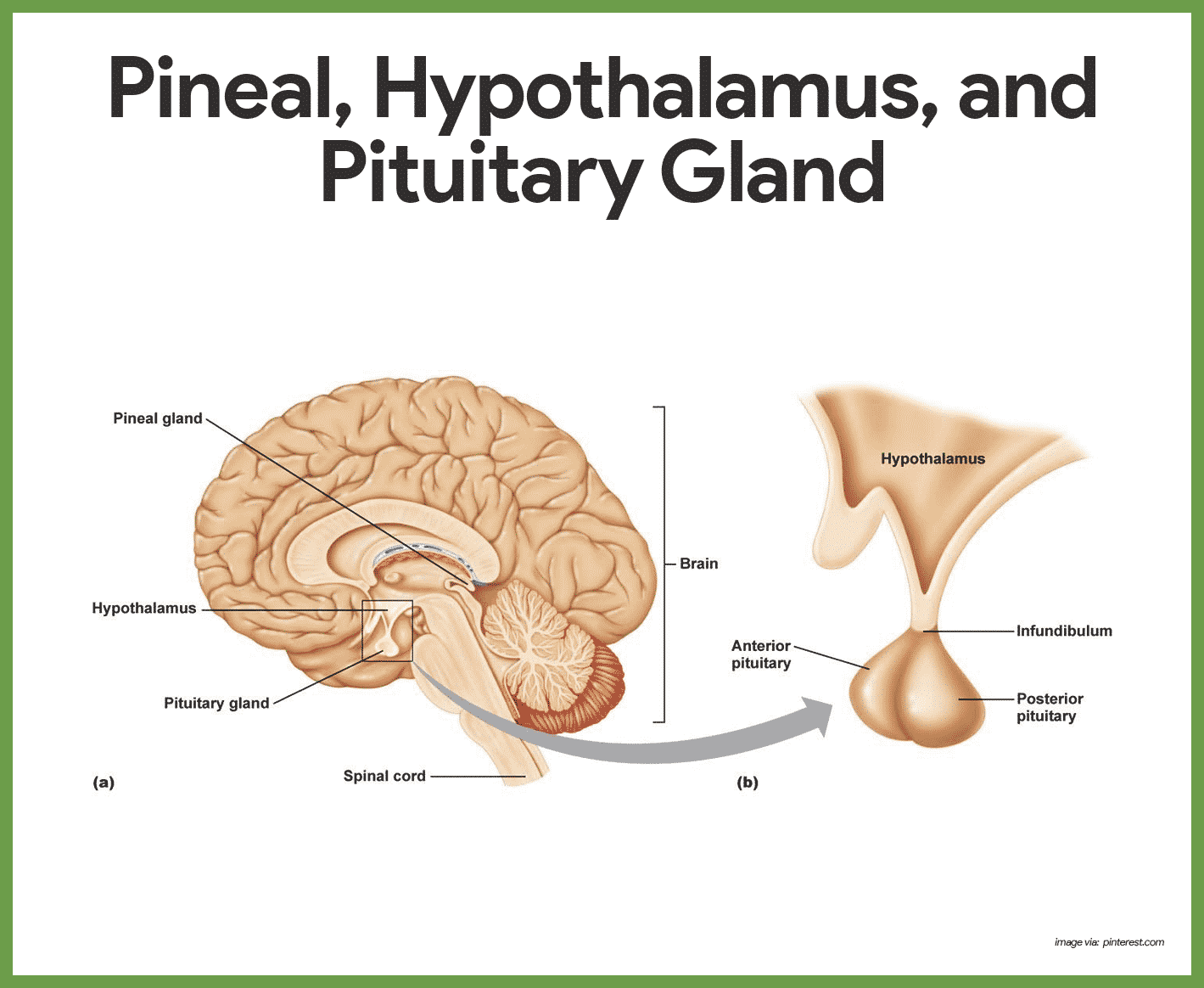 Pineal body. The pineal body, or pineal gland, is a small pinecone-shaped mass of glandular tissue located below the corpus callosum, just posterior to the thalamus of the brain. It produces the hormone melatonin, which may help regulate the wake-sleep cycle of the body known as the circadian rhythm. The activity of the pineal gland is inhibited by stimulation from the photoreceptors of the retina. The pineal gland may play a significant role in sexual maturation and the circadian rhythm.
Pineal body. The pineal body, or pineal gland, is a small pinecone-shaped mass of glandular tissue located below the corpus callosum, just posterior to the thalamus of the brain. It produces the hormone melatonin, which may help regulate the wake-sleep cycle of the body known as the circadian rhythm. The activity of the pineal gland is inhibited by stimulation from the photoreceptors of the retina. The pineal gland may play a significant role in sexual maturation and the circadian rhythm.
Pituitary. The pituitary gland, also known as the hypophysis, is located at the base of the brain beneath the hypothalamus and is no larger than a pea. It is often considered the most important part of the endocrine system because it produces hormones that control many functions of other endocrine glands. The pituitary gland is divided into two parts: the anterior lobe and the posterior lobe. The posterior pituitary gland is actually not glandular tissue at all, but nervous tissue instead. The anterior pituitary gland is the true glandular part of the pituitary gland. The function of the anterior pituitary gland is controlled by the releasing and inhibiting hormones of the hypothalamus. Pituitary hormones stimulate growth, sexual cell development, milk secretion.
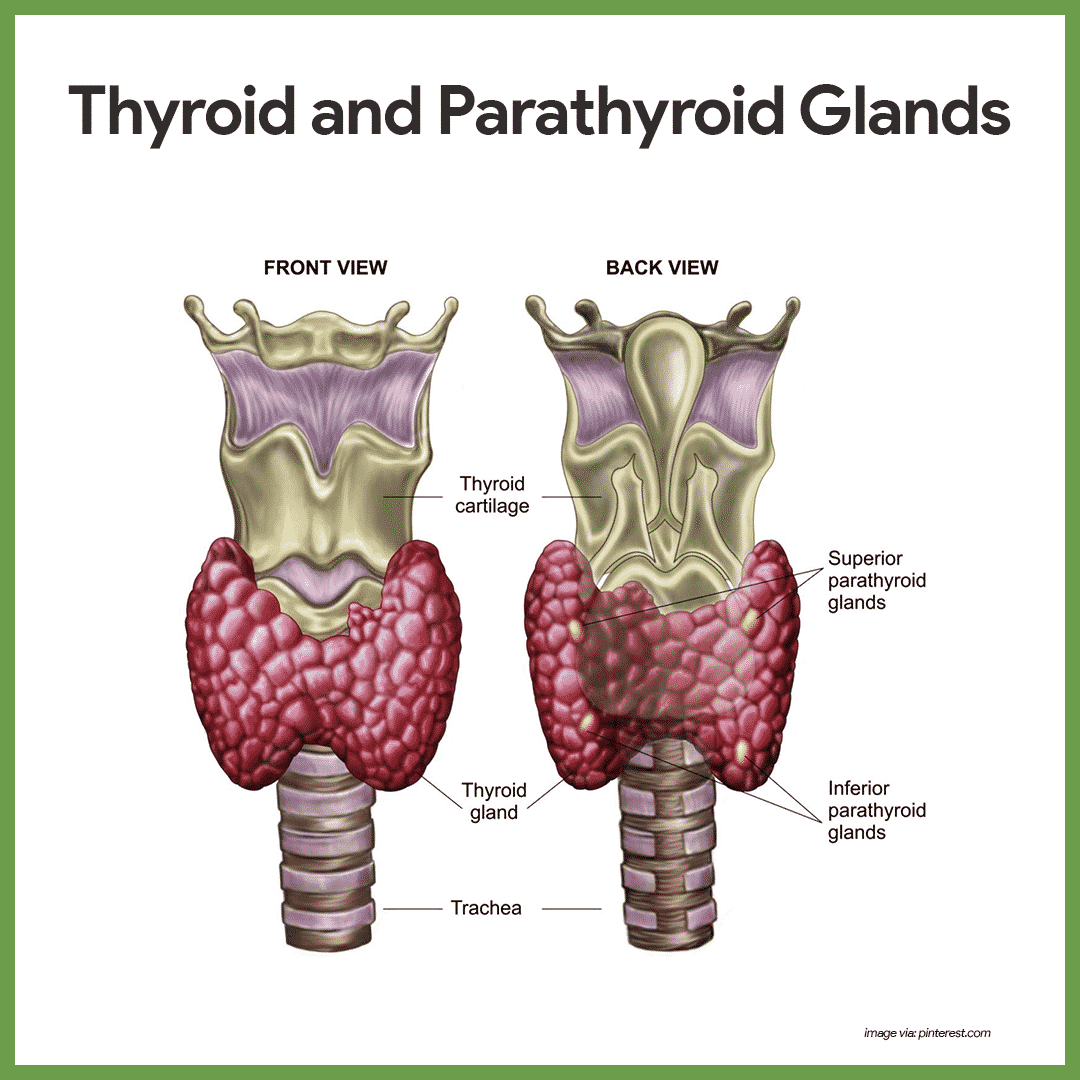 Thyroid. The thyroid gland, a butterfly-shaped gland, is located in the lower front part of the neck, below the larynx. It produces thyroid hormones that regulate the body's metabolism. It also plays a role in bone growth and development of the brain and nervous system in children. Thyroid hormones also help to maintain normal blood pressure, heart rate, digestion, muscle tone, and reproductive functions, regulates the metabolic rate of tissues, and are necessary for normal growth and brain development before birth and during infancy.
Thyroid. The thyroid gland, a butterfly-shaped gland, is located in the lower front part of the neck, below the larynx. It produces thyroid hormones that regulate the body's metabolism. It also plays a role in bone growth and development of the brain and nervous system in children. Thyroid hormones also help to maintain normal blood pressure, heart rate, digestion, muscle tone, and reproductive functions, regulates the metabolic rate of tissues, and are necessary for normal growth and brain development before birth and during infancy.
Parathyroid glands. The parathyroid glands are two pairs of small found on the posterior side of the thyroid gland. They release parathyroid hormone, which plays a role in regulating calcium levels in the blood and bone metabolism. The thyroid plays an important role in the body's metabolism, in the regulation of the body's calcium balance.It also regulates phosphorus, and magnesium levels.
Thymus. The thymus is a soft, triangular-shaped organ found in the chest posterior to the sternum and produces T-lymphocytes.
Adrenal gland. An adrenal gland, triangular-shaped glands, is located on top of each kidney. The adrenal glands are made up of two parts. The outer part is called the adrenal cortex, and the inner part is called the adrenal medulla. The outer part produces hormones called corticosteroids, which regulate the body's metabolism, the balance of salt and water in the body, the immune system, and sexual function. The inner part, or adrenal medulla, produces hormones called catecholamines (e.g. adrenaline). These hormones help the body cope with physical and emotional stressby increasing the heart rate and blood pressure.
Pancreas. The pancreas, an elongated organ, is located across the back of the abdomen, behind the 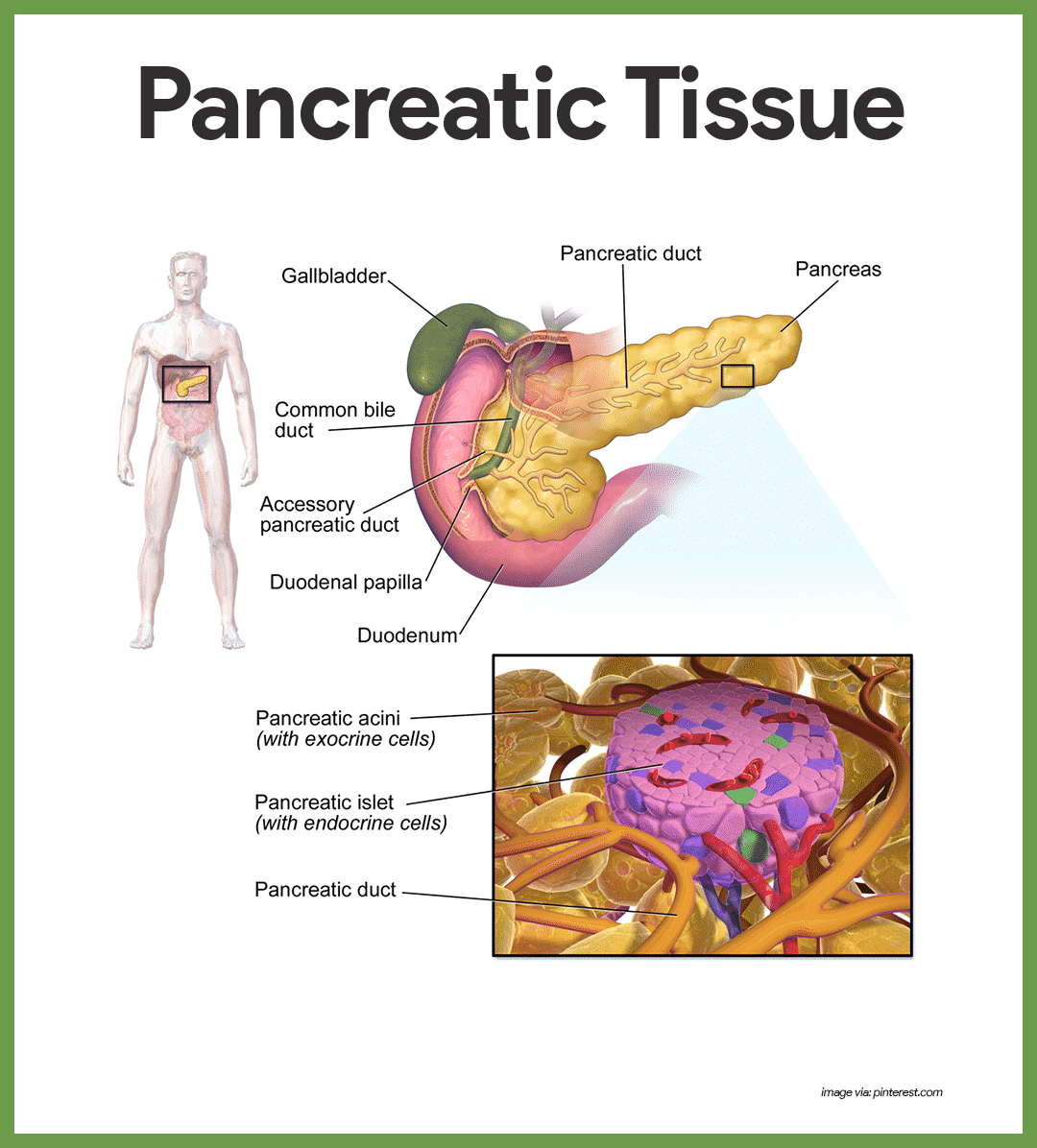 stomach. The pancreas has digestive and hormonal functions. The pancreas is considered to be a heterocrine gland as it contains both endocrine and exocrine tissue. The endocrine cells of the pancreas make up just about 1% of the total mass of the pancreas and are found in small groups throughout the pancreas called islets of Langerhans. Within these islets are 2 types of cells—alpha and beta cells. The alpha cells produce the hormone glucagon, which is responsible for raising blood glucose levels. The beta cells produce the hormone insulin, which is responsible for lowering blood glucose levels after a meal. Both types of cells regulate levels of blood sugar.
stomach. The pancreas has digestive and hormonal functions. The pancreas is considered to be a heterocrine gland as it contains both endocrine and exocrine tissue. The endocrine cells of the pancreas make up just about 1% of the total mass of the pancreas and are found in small groups throughout the pancreas called islets of Langerhans. Within these islets are 2 types of cells—alpha and beta cells. The alpha cells produce the hormone glucagon, which is responsible for raising blood glucose levels. The beta cells produce the hormone insulin, which is responsible for lowering blood glucose levels after a meal. Both types of cells regulate levels of blood sugar.
Reproductive glands. The reproductive glands (gonads) are the main source of sex hormones. In males, the testes, secrete hormones called androgens; the most important of which is testosterone. These hormones affect many male characteristics (for example, sexual development, growth of facial hair, etc.). In females, the ovariesproduce estrogen and progesterone. These hormones control the development of female characteristics (for example, breast growth), and they are also involved in reproductive functions.

9. Choose the right answer for the question:
1. How are the main organs of the endocrine system called?
Internal organs - Glands - Vessels
2. What does the endocrine system secrete?
Hormones - Enzymes - Proteins
3. What is a special feature of the endocrine glands?
Few in number - Are not paired - Their ductless nature and vascularity
4. What glands are neuroendocrine organs?
Hypothalamus and pituitary gland – Thyroid and parathyroid glands – Reproductive glands
5. What endocrine gland contains neurosecretory cells?
Pancreas - Pituitary gland - Hypothalamus
6. What endocrine gland may help regulate the wake-sleep cycle of the body?
Thymus - Pineal gland - Adrenal glands
7. What endocrine gland plays a role in regulating calcium levels in the blood and bone metabolism?
Adrenal glands - Pineal gland - Parathyroid gland
8. What endocrine glands secrete hormones helping the body to cope with physical and emotional stress?
Adrenal glands - Reproductive glands - Pancreas and gallbladder
9. What endocrine glands secrete hormones helping the body to regulate levels of blood sugar?
Hypothalamus - Thymus - Pancreas
10. What endocrine glands secrete hormones helping the body to control the development of male and female characteristics?
Reproductive glands - Thyroid and parathyroid glands - Adrenal glands
10. Correct the statements according to the text:
A. ‘Endocrine’ derives from the German language.
B. Nervous system is a complex networks of glands and organs that secret hormones to control and coordinate your body's internal metabolism.
C. Hormones may affect one organ in the body.
D. Endocrine glands are not widely separated from each other and are physically connected.
E. Bones, kidneys, liver, heart, adipose tissue, placenta have primary endocrine functions.
F. Hypothalamus is responsible for the direct control of the endocrine system through the pineal gland.
G. Both posterior and anterior parts of pituitary gland are the true glandular parts.
H. Thyroid gland plays a role in bone growth and development of the brain and nervous system in adults.
I. The alpha cells of pancreas produce the hormone insulin, which is responsible for lowering blood glucose levels after a meal.
11. Complete words with missing letters:
End_cr_ne, netw__k, gl_nd, th_mus, adr_n_l, h_pot_alam_s, s_cret_, ho_mon_, b_hav_oral, p_ysiolo_ical, ne_roendocr_ne, ant_ri_r, b_lance, pre_sur_, th_ro_d, p_ncr_as, gl_cos_, k_dne_
12. Make a word combination, match the words:
endocrinetissue
secretsecretion
chemicalcortex
bloodsystem
glandularhormones
circadianmessengers
milkpressure
adrenal cells
betarhythm
13. See the given list of verbs. Choose nouns that can form word combinations with these verbs:
to secrete, to respond to, to be responsible for, to affect, to suppress, to release, to involve
organs, tissues, chemical substances, cold, heat, hormones, chemical reactions, enzymes, human body, endocrine system
14. Using the information from the text choose the right variant:
1. The endocrine is a complex network of glands and organs that secrets\destroys hormones.
2. Hormones are chemical messengers used to communicate between organs and tissues\cells and intracellular fluid for physiological regulation.
3. The hypothalamus secretes hormones that stimulate or suppress the release of hormones in the pituitary gland\pineal gland.
4. The pineal gland produces the hormone melatonin\estrogen.
5. The pituitary gland is divided into two\three parts.
6. The thyroid gland is located in the upper\lower front part of the neck, below\above the larynx.
7. The thymus is found in the chest anterior\posterior to the sternum.
8. The outer part of adrenal gland produces hormones called corticosteroids, which regulate the body's metabolism\blood pressure.
9. The alpha cells produce the hormone insulin\glucagon.
10. Gonads\adrenal glands are the main source of sex hormones
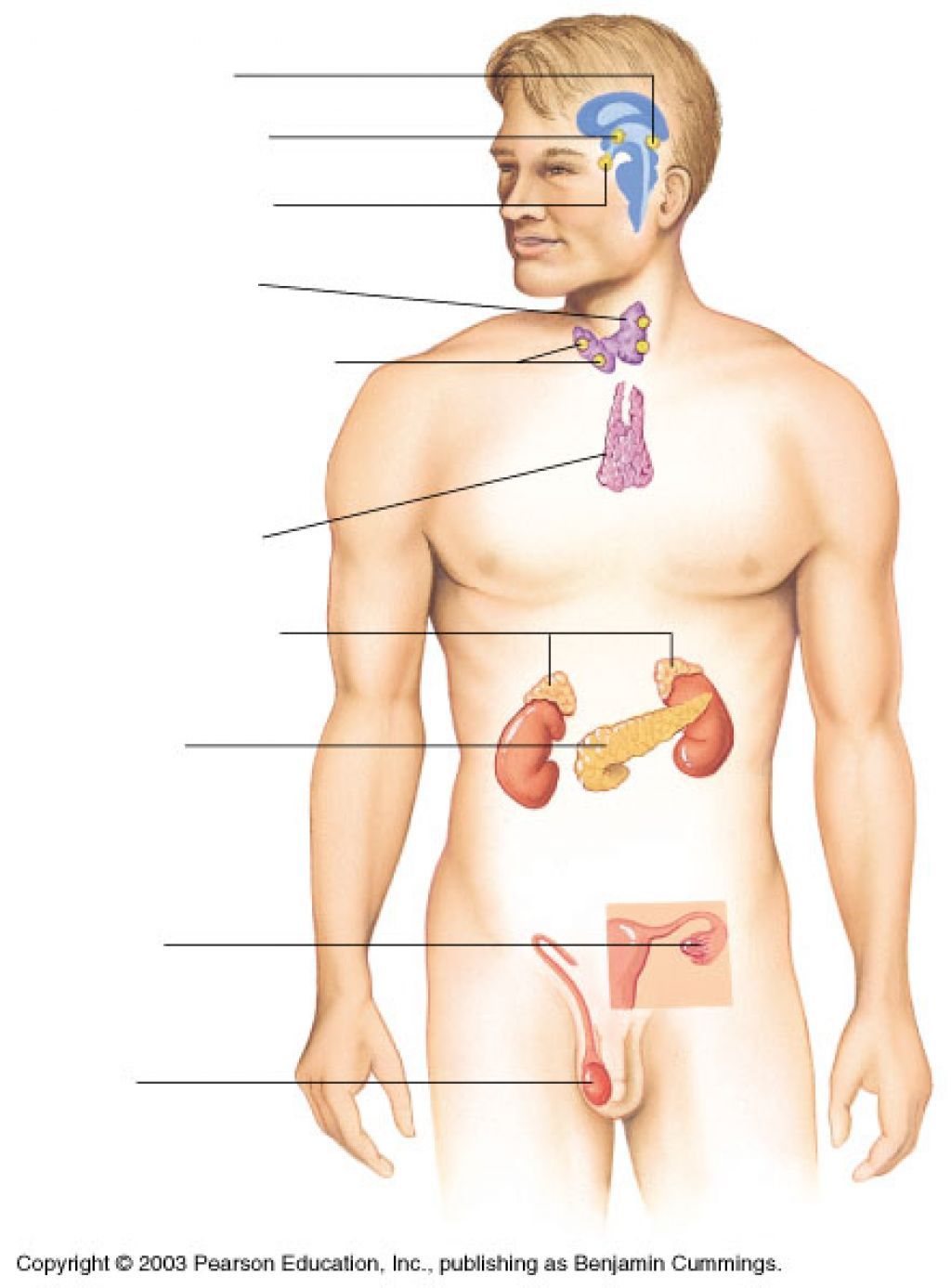
15. Fill in the diagram with the words from Word Bank:
Word bank:
Pancreas, adrenal glands, ovary, thymus, thyroid gland, parathyroid glands, testes, pineal gland, hypothalamus, pituitary gland




 Endocrine System
Endocrine System Pineal body. The pineal body, or pineal gland, is a small pinecone-shaped mass of glandular tissue located below the corpus callosum, just posterior to the thalamus of the brain. It produces the hormone melatonin, which may help regulate the wake-sleep cycle of the body known as the circadian rhythm. The activity of the pineal gland is inhibited by stimulation from the photoreceptors of the retina. The pineal gland may play a significant role in sexual maturation and the circadian rhythm.
Pineal body. The pineal body, or pineal gland, is a small pinecone-shaped mass of glandular tissue located below the corpus callosum, just posterior to the thalamus of the brain. It produces the hormone melatonin, which may help regulate the wake-sleep cycle of the body known as the circadian rhythm. The activity of the pineal gland is inhibited by stimulation from the photoreceptors of the retina. The pineal gland may play a significant role in sexual maturation and the circadian rhythm. Thyroid. The thyroid gland, a butterfly-shaped gland, is located in the lower front part of the neck, below the larynx. It produces thyroid hormones that regulate the body's metabolism. It also plays a role in bone growth and development of the brain and nervous system in children. Thyroid hormones also help to maintain normal blood pressure, heart rate, digestion, muscle tone, and reproductive functions, regulates the metabolic rate of tissues, and are necessary for normal growth and brain development before birth and during infancy.
Thyroid. The thyroid gland, a butterfly-shaped gland, is located in the lower front part of the neck, below the larynx. It produces thyroid hormones that regulate the body's metabolism. It also plays a role in bone growth and development of the brain and nervous system in children. Thyroid hormones also help to maintain normal blood pressure, heart rate, digestion, muscle tone, and reproductive functions, regulates the metabolic rate of tissues, and are necessary for normal growth and brain development before birth and during infancy. stomach. The pancreas has digestive and hormonal functions. The pancreas is considered to be a heterocrine gland as it contains both endocrine and exocrine tissue. The endocrine cells of the pancreas make up just about 1% of the total mass of the pancreas and are found in small groups throughout the pancreas called islets of Langerhans. Within these islets are 2 types of cells—alpha and beta cells. The alpha cells produce the hormone glucagon, which is responsible for raising blood glucose levels. The beta cells produce the hormone insulin, which is responsible for lowering blood glucose levels after a meal. Both types of cells regulate levels of blood sugar.
stomach. The pancreas has digestive and hormonal functions. The pancreas is considered to be a heterocrine gland as it contains both endocrine and exocrine tissue. The endocrine cells of the pancreas make up just about 1% of the total mass of the pancreas and are found in small groups throughout the pancreas called islets of Langerhans. Within these islets are 2 types of cells—alpha and beta cells. The alpha cells produce the hormone glucagon, which is responsible for raising blood glucose levels. The beta cells produce the hormone insulin, which is responsible for lowering blood glucose levels after a meal. Both types of cells regulate levels of blood sugar.





