Urinary tract – urine - uric acid - urea, to secrete – secreted into the blood – secretion of gastric juice, to protect against the infection - protected by the lower ribs – protection of the internal organs, to extent along the spine - extension of the leg - extensive blood supply, empty system - to empty the cavity - emptied into the bladder – emptiness, to store nutrients – stored in the bones – storage of blood cells, mucous membrane- mucosal lining – submucosa, flat surface – to flatten the cavity – flattened transitional epithelium, to expel the urine - expelled from the body, to flow through capillaries - the flow of urine, a life circle - circular smooth muscle - to encircle the urethra, to cover the tissue – covered with epithelium – coverage of the muscle, to prevent the increase of blood pressure – the prevention of the disease – preventive measures.
4. Translate the following word combinations into Russian:
To eliminate waste from the body, by controlling levels of electrolytes and metabolites, consists of water and dissolved metabolic wastes, maintains the balance of chemicals and water in the body, removes liquid waste from the blood in the form of urine, a pair of bean-shaped organs found along the posterior wall of the abdominal cavity, is located slightly higher than the right kidney, surrounded by a layer of adipose tissue that holds them in place, have an extensive blood supply via the renal arteries, following filtration of blood and further processing, run on the left and right sides of the body parallel to the vertebral column, gravity and peristalsis of smooth muscle tissue in the walls of the ureters, are sealed at the point of entry to the bladder, prevent urine from flowing back towards the kidneys, consists of the inner circular and outer longitudinal smooth muscle, located along the body’s midline at the inferior end of the pelvis, varies with the pressure it receives from surrounding organs, a thin-walled tube that conveys urine from the floor of the urinary bladder, control the flow of urine through the urethra, to regulate blood volume and composition, to contribute to the production of red blood cells by the kidney.

5. Name five words or word combinations when you see the term ‘Urinary System’?
6. Try to answer the questions in Urinary Quiz:
Urinary Quiz
1. The urinary system maintains homeostasis by
a) secreting specific hormones
b) controlling levels of electrolytes, metabolites and regulating blood pH
c) controlling nerve impulses
2. The urine system helps in synthesizing:
a) Retinol (Vitamin A)
b) Ascorbic acid (Vitamin C)
c) Calcitrol (active form of Vitamin D)
3. The primary organs of the urinary system are
a) Kidneys 
b) Adrenal glands
c) Lungs
4. One of the kidneys’ function is
a) to produce hormones and to secrete enzymes
b) to control salivary secretion
c) to maintain the amount of Vitamin B12
5. The kidneys are surrounded by a layer of adipose tissue that
a) allows them to filtrate the blood
b) helps to maintain homeostasis
c) holds them in place and protects them from physical damage.
6. The central region of the kidney contains
a) renal pelvis
b) renal cortex
c) renal medulla
7. Every day, the kidneys filter about
a) 160 to 180 quarts of blood
b) 120 to 150 quarts of blood
c) 100 to 130 quarts of blood
7. Read the text and check your predictions. Translate the text into Russian paying your attention to special terms related to urinary system:
 Urinary System
Urinary System
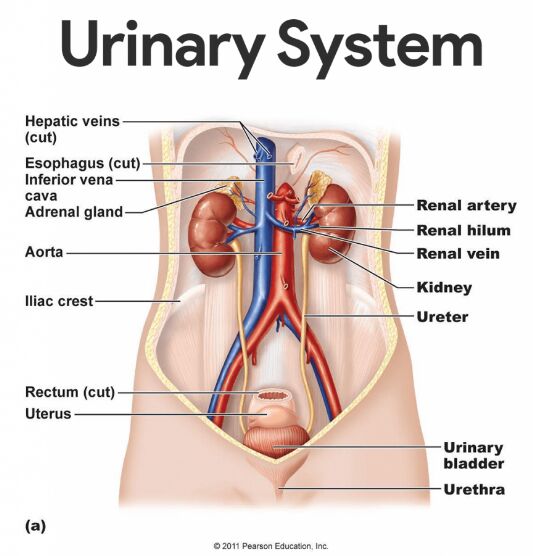
The urinary system, also known as the renal system or the urinary tract, is a part of the excretory system and consists of the kidneys, the ureters, the bladder, and the urethra. This system maintains homeostasis by controlling levels of electrolytes and metabolites, and regulating blood pH. The kidneys produce urine which consists of water and dissolved metabolic wastes such as nitrogenous compounds (urea and uric acid), excess ions and some drugs. To maintain the balance of chemicals and water in the body the urinary system interacts with the lungs, skin and intestines.
Kidneys. The kidneys are the primary organs of the urinary system. Their function is to remove liquid waste from the blood in the form of urine; to keep a stable balance of salts and other substances in the blood; to produce erythropoietin (a hormone that aids the formation of red blood cells), and to secrete renin (an important enzyme which controls blood pressure).
The kidneys are a pair of bean-shaped organs found along the posterior wall of the abdominal cavity and protected by the lower ribs. The paired kidneys are located between the twelfth thoracic and third lumbar vertebrae, one on each side of the vertebral column. The left kidney is located slightly higher than the right kidney because the right side of the liver is much larger than the left side. The kidneys are surrounded by a layer of adipose tissue that holds them in place and protects them from physical damage. In the adult, each kidney is approximately 3 cm thick, 6 cm wide, and 12 cm long. It has an indentation, called a hilum, on the medial side. The hilum leads to a large cavity, called the renal sinus, within the kidney. The kidneys have an extensive blood supply via the renal arteries entering the kidney at the hilum which leaves the kidneys via the renal vein. The cortex and medulla make up the parenchyma, or functional tissue, of the kidney. The central region of the kidney contains the renal pelvis located in the renal sinus, and is continuous with the ureter. The renal pelvis is a large cavity that collects the urine as it is produced.
The kidneys remove urea from the blood through tiny filtering units called nephrons. Each nephron consists of a ball formed of small blood capillaries, called a glomerulus, and a small tube called a renal tubule. Urea, together with water and other waste substances, forms the urine as it passes through the nephrons and down the renal tubules of the kidney. Every day, the kidneys filter about 120 to 150 quarts of blood to produce about 1 to 2 quarts of urine.
In adult humans about 1-2 liters of urine is produced per day. The amount of urine produced depends on many factors such as the state of hydration, activity level, environmental factors, weight, and the individual’s health. 
Ureters. Following filtration of blood and further processing, urine exits the kidney via the ureters, a pair of tubes that carry urine from the kidneys to the urinary bladder. The ureters are about 25 cm long and run on the left and right sides of the body parallel to the vertebral column. Gravity and peristalsis of smooth muscle tissue in the walls of the ureters carry urine from the renal pelvis to the urinary bladder. The ends of the ureters extend slightly into the urinary bladder and are sealed at the point of entry to the bladder by the ureterovesical valves. These valves prevent urine from flowing back towards the kidneys.About every 10 to 15 seconds, small amounts of urine are emptied into the bladder from the ureters. The wall of the ureter consists of three layers. The outer layer, the fibrous coat, is a supporting layer of fibrous connective tissue. The middle layer, the muscular coat, consists of the inner circular and outer longitudinal smooth muscle. The main function of this layer is peristalsis: to propel the urine. The inner layer, the mucosa, is transitional epithelium1. This layer secretes mucus, which coats and protects the surface of the cells.
Bladder. The urinary bladder is a triangle-shaped, hollow organ located in the lower abdomen is used for the storage of urine. The urinary bladder is located along the body’s midline at the inferior end of the pelvis. It is held in place by ligaments attached to other organs and the pelvic bones. The size and shape of the urinary bladder varies with the amount of urine it contains and with the pressure it receives from surrounding organs. The inner lining of the urinary bladder is a mucous membrane of transitional epithelium. The second layer in the walls is the submucosa, which supports the mucous membrane. The next layer is the muscularis, which is composed of smooth muscle. Contraction of this muscle expels urine from the bladder. The bladder's walls relax and expand to store urine, and contract and flatten to empty urine through the urethra. Urine entering the urinary bladder from the ureters slowly fills the hollow space of the bladder and stretches its elastic walls. The walls of the bladder allow it to stretch to hold anywhere from 600 to 800 milliliters of urine. The urine is stored and subsequently expelled from the body by urination (voiding).
Urethra. The urethra is a thin-walled tube that conveys urine from the floor of the urinary bladder to the outside. In females urethra is around 3-4 cm long while in males it is around 20 cm long. The mucosal lining of the urethra is transitional epithelium. The wall also contains smooth muscle fibers and is supported by connective tissue. The internal urethral sphincter surrounds the beginning of the urethra, where it leaves the urinary bladder. This sphincter is smooth (involuntary) muscle. Another sphincter, the external urethral sphincter, is skeletal (voluntary) muscle and encircles the urethra where it goes through the pelvic floor. These two sphincters control the flow of urine through the urethra.
The main functions of the urinary system and its components are:
· to regulate blood volume and composition (e.g. sodium, potassium and calcium)
· to regulate blood pressure
· to regulate pH homeostasis of the blood
· to contribute to the production of red blood cells by the kidney
· to help in synthesizing calcitrol (the active form of Vitamin D)
· to store waste product (mainly urea and uric acid) before it and other products are removed from the body.
1 Under microscopy, the urinary system is covered in a unique lining called urothelium, a type of transitional epithelium. Unlike the epithelial lining of most organs, transitional epithelium can flatten and distend. Urothelium covers most of the urinary system, including the renal pelvis, ureters, and bladder.





 Urinary System
Urinary System



