General
The HF 1 AND HF 2 systems are the same. This example shows the HF 1 system.
When the tune sequence is complete, the HF system goes to the receive/operate mode and is ready to transmit. A PTT discrete starts the operation in the transceiver and antenna coupler.
Transmit Mode
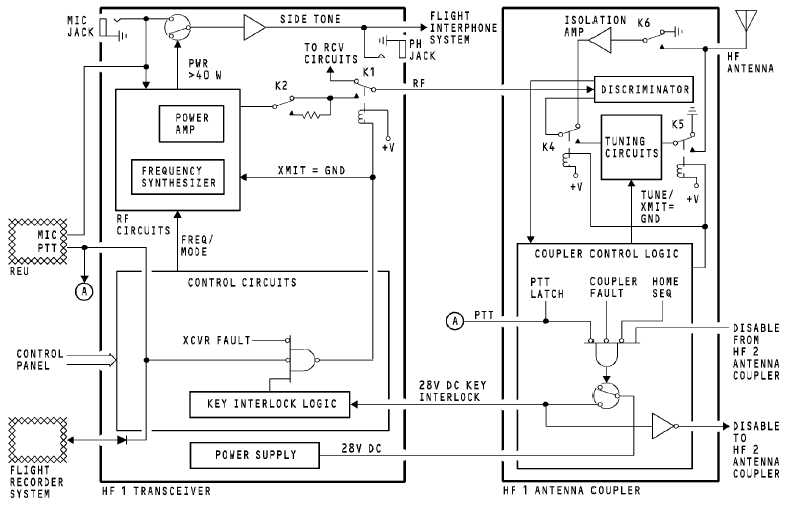
In the receive/operate mode, the PTT discrete from the REU to the transceiver and coupler control logic circuits starts the transmit mode. The coupler control logic circuits energize relays K4 and K5, and de-energize relay K6. This puts a ground on the input to the isolation amplifier. It connects the tuning elements in-line between the discriminator and the antenna.
The coupler control logic sends a ground to disable the off-side coupler. At the same time, it sends a key interlock signal to the HF transceiver. The coupler control logic does this only in these conditions:
· There is a ground on the PTT line
· There is no disable from the HF 2 antenna coupler
· The coupler control logic circuits are not in the home mode
· There are no coupler faults.
The control circuits in the transceiver energize relay K1 and tell
the RF circuits to transmit a carrier in these conditions:
· There is a ground on the PTT line
· There is no transceiver fault
· There is a key interlock signal from the coupler.
The RF circuits mix the carrier from the frequency synthesizer
with the mic audio. The RF signal goes through these:
· A power amplifier
· The relaxed contacts of relay K2
· The energized contacts of relay K1
· The discriminator in the coupler.
The RF signal then goes through these:
· Energized relays K4 and K5
· The tuning elements.
The antenna receives the RF from the tuning elements and transmits it.
Side Tone
When the output from the transceiver power amplifier is more than 40 watts in the AM mode, a switch connects the microphone audio to an audio amplifier. The amplified audio goes to the audio jack and to the flight interphone system for side tone. When the output is less than 40 watts, there is no side tone. When the output is less than 30 watts, an LRU fault occurs.
Key Event Output
The PTT discrete goes to the flight recorder system for key event marking.
OPERATION
General
You use these components to operate the HF radio:
· Hand microphone or headset
· Radio communication panel
· Control wheel mic switch
· Remote MIC switch
· Audio control panel.
Receive Operation
You use the radio communication panel and the audio control panel to receive transmissions on the HF radio.
On the audio control panel, push the receiver volume control for the HF radio. Turn the control to adjust the volume from the HF radio.
You hear audio on the headset and the flight interphone speakers. To hear sound from the flight interphone speakers, push the speaker (SPKR) volume control to turn on the speaker. Turn the control to adjust the volume of sound from the speaker.
Use the on/off control to turn on the radio communication panel. When you first turn it on, the radio communication panel tunes the VHF radio. Push the HF 1 switch to make the radio communication panel tune the HF radio. A light above the switch comes on to show which radio the panel controls. The frequency displays show HF radio frequencies (2.000 to 29.999 MHz). The HF radio uses the frequency in the active frequency display.
Use the frequency selectors to tune the radio to a new frequency. The standby frequency display shows the new frequency.
When you are sure the frequency is correct, push the frequency transfer switch. The active frequency display shows the new frequency. The HF radio uses the new frequency.
NOTE: When you select a new frequency, the HF coupler drives its tuning elements to the home position.
Listen for audio from the HF radio on the speaker or headset. Adjust the volume control switches on the audio control panel for a comfortable sound level.
Use the HF sensitivity (HF SENS) control on the radio communication panel to adjust the sensitivity of the HF radio receiver.
Transmit Operation
WARNING: MAKE SURE PERSONNEL STAY A MINIMUM OF SIX FEET AWAY FROM THE VERTICAL STABILIZER WHEN THE HF SYSTEM TRANSMITS. RF ENERGY FROM THE HF COMMUNICATION ANTENNA CAN CAUSE INJURIES TO PERSONNEL.
WARNING: DO NOT OPERATE THE HF COMMUNICATION SYSTEM WHILE FUEL IS PUT INTO THE AIRPLANE. INJURY TO PERSONS AND DAMAGE TO EQUIPMENT CAN OCCUR.
Make sure the active frequency display shows the frequency you want to transmit. Make sure the frequency you select is a valid transmit frequency.
Push the microphone selector switch on the audio control panel for the HF radio.
Listen for transmissions on the frequency you selected. When the frequency is clear, push and release the push-to-talk for the microphone. This causes the HF coupler to tune to the transmission frequency. While the coupler tunes, the HF transceiver supplies a 1 kHz tone. You hear this tone on the speaker and in the headset.
Normally, it takes several seconds for the coupler to tune. When the 1 kHz tone stops, the HF system is ready to transmit.
When the frequency is clear and you want to transmit a message, key the mic and speak into it. You hear sidetone in the headphone and muted sidetone from the flight interphone speaker. The flight interphone system mutes the sidetone to the speaker when you use the boom mic or the hand mic.
You can continue to transmit and receive on the frequency you selected.
When you select another frequency and key the mic to transmit, the HF coupler tunes again. You hear the 1 kHz tone while it tunes.
Non-Normal Indications
If you hear the 1 kHz tone for more than 15 seconds when the coupler tunes, there may be a coupler fault.
If the tone only lasts as long as you key the microphone, you may have tuned a frequency which is outside the frequency range for the HF transceiver.









