2. What was the computer originally created for?
3. When was the first computer offered to the public and what was its name?
4. What were Robert Noyce and Jack Kilby known for?
5. What was the microprocessor'soriginal purpose?
6. In each of the 4 generations what was the cause for the increase of speed, power, or memory?
7. How do you think society will be different if scientists are able to create a chip that will perform a trillion operations in a singlesecond?
11. Watch a video review on computers:
http://www.brainpop.com/technology/computersandinternet/computerhistory/
12. Take a quiz at the end:
http://www.brainpop.com//technology/computersandinternet/computerhistory/quiz/
13.Topics for discussion.
1. How computers used to work.
2. How circuit boards work.
3. Computer generations.
14.  Prepare a presentation on the topic being discussed.
Prepare a presentation on the topic being discussed.

1. ‘Computer history in 140 seconds’ http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=uudHO9PBGRc
2. A Chronology of Digital Computing Machines (to 1952), by Mark Brader, 1994.
3. BIT by BIT, An Illustrated History of Computers, by Stan Augarten (1985).
4. ‘How computer works’, by Ron White, 2008, pp.8-9.
Unit 2
INFORMATION IS A FUNDAMENTAL PROPERTY OF THE WORLD AROUND
1. Match the words with their definitions:
| 1) condensed (adj.)
| [kən'den(t)st]
| a) relating to the sense of smell
|
| 2)acoustic(al) (adj.)
| [ə'kuːstɪkəl]
| b)spread out
|
| 3) olfactory (adj.)
| [ɔl'fækt(ə)rɪ]
| c) relating to sound or the sense of hearing
|
| 4)flavouring (adj.)
| [fleɪv(ə)rɪŋ]
| d) the arrival of a notable person or thing
|
| 5)demise (n.)
| [dɪ'maɪz]
| e) including or dealing with all or nearly all elements or aspects of something
|
| 6) deploy (v.)
| [dɪ'plɔɪ]
| f) relating to or expressed as a number or numbers
|
| 7)integrity (n.)
| [ɪn'tegrətɪ]
| g) of or connected with the sense of touch
|
| 8) advent (n.)
| ['ædvənt]
| h)the distinctive taste of a food or drink
|
| 9)comprehensive (adj.)
| [ˌkɔmprɪ'hen(t)sɪv]
| i) the quality or condition of being whole or undivided; completeness
|
| 10) tactile (n.)
| ['tæktaɪl]
| j) made shorter, usually by including only the most important parts.
|
| 11)numerical (n.)
| [njuː'merɪkl]
| k) the end of smth
|

1. Now watch a video ‘What is information?’ and mark True (T) or False (F).
| 1.
| We can touch information.
|
|
| 2.
| Information is used to convey a message from one person to another.
|
|
| 3.
| Information is stored, processed and retrieved by the brain
|
|
| 4.
| Information theory says that universe is made up of two substances.
|
|
| 5.
| Information dictates how matter and energy interact
|
|
| 6.
| Intelligence is necessary for information to exist.
|
|
| 7.
| Intelligence is only required when you are trying to describe information
|
|

Discuss with your partner the following questions.
· What do you know about the information?
· What are the reasons for storing information?
Skim the text to check your ideas.

WHAT IS INFORMATION?

 We live in the Information Age and we are surrounded by information. The information is everywhere: in human speech, books, magazines and newspapers, radio and TV messages, readings, etc. Information is stored on CD- and DVD-disks, special devices and data carriers. Thanks to new media like the Internet, the Web, blogs, email, cell phones, iPods, e-Readers, Blackberries and iPhones we are blanketed in information.
We live in the Information Age and we are surrounded by information. The information is everywhere: in human speech, books, magazines and newspapers, radio and TV messages, readings, etc. Information is stored on CD- and DVD-disks, special devices and data carriers. Thanks to new media like the Internet, the Web, blogs, email, cell phones, iPods, e-Readers, Blackberries and iPhones we are blanketed in information.
Information can be found in primary, secondary or tertiary sources depending on how original the materials are or how much they have been interpreted or condensed by others. Information can come from many sources and be obtained from everyday life such as watching the channel news or reading the Chicago Tribune and it can be distributed in several ways such as TV news, the Internet, newspaper, and through word of mouth. The farther away from the original source the information is found, the more likely it is to be filtered, interpreted, condensed or otherwise changed.
The person perceives the information by means of sense organs, stores and processes it by means of brain and the central nervous system. In addition to this everyday interaction with information by the users of computer-based digital new media there is the role that information plays in the sciences of AI and AL. The irony of our total immersion in information as well as the prominent role it plays in AI and AL is that for the most part we do not really have a clear understanding of exactly what information is.
The use of the word ‘information’ as a descriptive adjective has exploded to the point of near absurdity: information age, information society, information economy, information superhighway, information millennium, information revolution. But what does this word "information" mean in these constructions and how did it become the new keyword of our social formation’s self-definition? At first, it appears that the definition of "information" is clear and unproblematic: we all know, in common sense, what it is. But, immediately, it becomes evident that we can’t exactly specify the term in its everyday usage, and that the term is being used in some other way when attached to the words "society," "age," etc.
The word ‘information’ is derived from Latin informare which means "give form to the mind". The way the word information is used can refer to both "facts" in themselves and the transmission of the facts. There have been many descriptions and characterizations of information through the years, some very broad, some narrow and some humorous.
One of the earliest definition of information was produced by Shannon and Weaver. They defined information as what is known beyond random chance predictions. In this sense, information must surprise the recipient. It must reduce the uncertainty recipient has about the state of the world. Random chance events represent the state of complete uncertainty. To the extent that recipient can reduce his/her uncertainty, he/she is informed. If the conclusion of a report is known a priori, then it has no surprise value, and therefore it is not, according to this definition, informative.
It may be helpful to view information the way it is structured and used, namely: data, text, spreadsheets, pictures, voice and video. Data are discretely defined fields. Text is a collection of words. Spreadsheets are data in matrix (row and column) form. Pictures are lists of vectors or frames of bits. Voice is a continuous stream of sound waves. Video is a sequence of image frames.
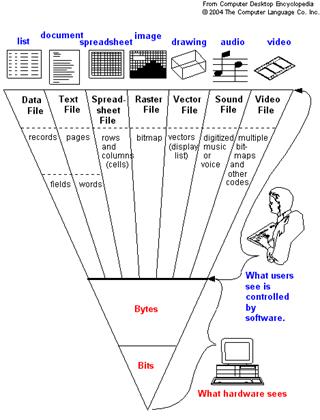
When information is stored electronically, it is structured according to the way it is used. Databases support all kinds of information.
Information may be hard to define but it can be categorized and divided into types by different criteria: on the validity - true, false; on ways of perception - visual, acoustical, tactile, olfactory, flavouring; on public value - mass, special, confidential, personal; under its form of representation, ways of its coding and storage - graphic, sound, text, numerical, a video information, etc.
Information is of value to decision makers if it is accurate, timely, complete, and relevant. These four criteria are used to distinguish valuable information from information that is of less value.
Accurate information provides a reliable and valid representation of reality. The cost of inaccurate or distorted information can be extremely high. Consider the demise of the multimillion dollar Mars Climate Orbiter launched by NASA in 1998. The tragic outcome of this mission was blamed on the failure of one scientific team to recognize and correct an error in information from another team. Findings indicate that one team used English units (e.g., inches, feet and pounds) while the other used metric units for key spacecraft operations affecting navigation. This oversight caused the orbiter to burn up in Mars atmosphere before it could deploy to the surface. Timely information is information that is available when it is needed. When information is needed almost always depends on the situation. In the fast-paced world of air travel, commercial airlines need virtually daily updates on what other commercial airlines are doing with their ticket prices. If one airline reduces its airfares from Newark International Airport to Los Angeles International Airport, other airlines flying the same route would find out quickly about it and respond in a similar manner. Other projects, such as real estate development, might require months of information gathering and assessment. Spending six months preparing a report on the environmental impacts of a real estate development project might be an acceptable timeframe in this situation. Complete information tends to be comprehensive in covering the issue or topic of interest. Complete information tells a complete story. Without complete information, a decision maker will get a distorted view of reality. Incomplete market information can lead businesses to introduce products and services that customers don't want. For example, the fashion site Boo.com was to be an international Internet fashion superstore that would offer street fashion on the web. Even though the site was designed for 18 different languages and currencies, the site was not user-friendly, the prices were too high in some cases, and you couldn't really get the true feel for the products. The initial concept was very good and did make some money, but like most Internet start-ups, they spent more than they made, which is just not good business. All is not lost; with the right strategy and a test market, Boo might have done quite well…had they had the complete information. Information is relevant if it has significance or can be applied to a specific situation, problem, or issue of interest. Here are some examples of relevant information. Human resource managers need information on hiring and employee turnover; operations managers need information on costs and productivity; marketing managers need information on sales projections and advertising rates; top executives need information on the strategic actions of their competitors. In contrast, product inventory information is not very relevant to a computer programmer.
From the point of view of computer science the information has a number of fundamental properties: integrity, reliability, availability, up-to-dateness, pertinency, privacy, usability etc.
Integrity – the quality or condition of being whole or undivided; completeness;
Reliability – is the ability of system to perform and maintain its functions in routine circumstances;
Availability of data, data channels, and input-output devices in computers is the condition of being ready for use and not immediately committed to other tasks;
Up-to-dateness – being in accord with consumer needs just-in-time;
Pertinency – having logical precise relevance to the matter at hand;
Privacy – the state of being free from unsanctioned intrusion or altering;
Usability – fit for use, convenient to use.
The type, quality and amount of information has changed greatly through the ages, but a human's ability to process the information has remained the same, creating what some call information overload.
With the advent of the Information age it seems that there is way too much information for us to absorb. The increase in publishing, the growth of news and other media, the advances in worldwide communications and now the explosion of information on the Internet all contribute to the sense that finding the information we need is just about impossible.
Despite the massive change in information storage and retrieval technology over time, our capacity to understand and synthesize information has remained constant.
On the assumption of the aforesaid, the information is data of the objects and of the environment phenomena, their parameters, properties and condition, which are perceived information systems (the live organisms, operating cars, etc.) in the course of ability to live and work.
Information obviously fuels most of our daily activities. Knowledge workers who understand the importance of information will have a unique advantage over those who do not. And even more importantly, those who understand the difference between good information sources and poor ones will become knowledge leaders.
1. Find and learn Russian equivalents for the following words and expressions:
| 1) data carriers
| a)
|
| 2) artificial intelligence
| b)
|
| 3) silicon-based
| c)
|
| 4) distorted information
| d)
|
| 5) pertinency
| е)
|
| 6) altering
| f)
|
| 7) privacy
| g)
|
| 8) availability
| h)
|
| 9)information sources
| i)
|
| 10) information gathering and assessment
| j)
|
2. Find and learn English equivalents for the following words and expressions:
| 1) специальное приспособление
| a)
|
| 2) полное погружение
| b)
|
| 3) передаваемый из уст в уста
| c)
|
| 4) концепция, моделируемая в системах машин и воспроизводящая их поведение по типу взаимодействия живых организмов
| d)
|
| 5) удобный для пользователя (дружественный)
| e)
|
| 6)недавно созданная фирма
| f)
|
| 7) эргономичность
| g)
|
| 8)актуальность
| h)
|
| 9) достоверность
| i)
|
| 10) полнота
| j)
|

(AI) Artificial Intelligence
AI is used in games for everything from making a computer opponent behave believably like a human opponent to having automated units perform tasks in a realistic manner. In AI intelligence is posited to be a form of information that can be downloaded from the human brain onto a computer.
(AL) Artificial Life In AL life is posited to be a form of information that first became embodied in carbon-basedchemicals but now can exist in silicon-based computers. Some AL scientists like EdwardFredkin insist that the universe is a computer and that life including human life ismerely a programme running on that computer.
Information
It is the summarization of data. Technically, data are raw facts and figures that are processed into information, such as summaries and totals. But since information can also be the raw data for the next job or person, the two terms cannot be precisely defined, and both are used interchangeably.
Silicon
A brownish crystalline semi metal used tomake the majority of semiconductor wafers.
Semiconductor
A material (such as silicon) that
can be altered to either conduct electrical current
or block its passage. Microchips are typically fabricated on semiconductor materials such as silicon, germanium, or gallium arsenide.
User friendly
A system that is easy to learn and easy to use. In the past, this term was so abused in the software business that vendors became reluctant to use it today. Except for mobile phone applications, which due to their tiny screens forces developers to design concisely, a great amount of desktop software is downright "user hostile." It is the rarest of desktop applications that can be used by someone immediately who has never worked with a similar program.
Wafer
In semiconductor technology, a very thin
piece of silicon that functions as the base material
for building microchips. Also called a "slice."
! Study the following sentence: If the conclusion of a report is known a priori, it will nothave any surprise value.
This is the example of a conditional clause (if + subject + present simple, future/modal/imperative + bare infinitive/V1/base form), the 1st type of adverbial clause (real present).
The first (type 1) conditional is used to talk about things that are possible and may happen in the future. It is used to express different attitudes and ideas, or it is used for particular purposes. These different attitudes, ideas and purposes are sometimes called functions. You can either use other conjunctions: unless (if not), provided/ing that, so long as, as long as, on condition that.
| | If
| Subject
| Present simple (passive/active)
| Subject
| Will not
| bare infinitive/V1/ base form
|
| –
| If
| the conclusion of a report
| is not known a priori,
| it
| will not
| have any surprise value….
|
| +
| If
| the conclusion of a report
| is known a priori,
| it
| will
| have a surprise value…
|
|
| If
| Subject
| Present simple (passive/active)
| W ill (not)
| Subject
| Have
|
| ?
| If
| the conclusion of a report
| is known a priori,
| will
| it
| have any surprise value…?
|
! Study the following sentence: If Sarah didn’t have the Internet, she wouldn’t chat with her friends.
This is the example of a conditional clause (if + subject + past simple, would + bare infinitive/V1), the 2nd type of adverbial clause (unreal present). (didn’t have) is V2, but in this sentence it is NOT a Past tense, for it does NOT refer to past time. We know that Sarah, at the time when she is speaking, HAS the Internet, and she is able to chat with her friends.
The second (type 2) conditional is used to talk about things that are unlikely, impossible or contrary to facts. This is similar to the way we use the second conditional when we are talking about the present. Although the examples in the task refer to the future, the subordinate if clause is formed with the past simple and the main clause uses would not will.
|
| If
| Subject
| Past simple
| Subject
| would (not)
| bare infinitive/V1/ base form
|
| +
| If
| Sarah
| had the Internet,
| she
| would
| chat with her friends.
|
| –
| If
| Sarah
| didn’t have the Internet,
| she
| wouldn’t
| chat with her friends.
|
| ?
| If
| Subject
| Past simple
| Would (not)
| Subject
| bare infinitive/V1/ base form
|
| ?
| If
| Sarah
| had the Internet,
| Would
| she
| chat with her friends?
|
You can say this sentence about Sarah in 3 ways:
If Sarah didn’t have the Internet, she wouldn’t chat with her friends.
If Sarah didn’t have the Internet, she might not chat with her friends.
If Sarah didn’t have the Internet, she could not chat with her friends.
There is a difference in meaning:
wouldn’t chat - it is certain that she wouldn’t chat
might not chat - perhaps she wouldn’t chat
could not chat - it wouldn’t be possible for her to chat
Sometimes in American English, especially in spoken English, the form of the second conditional is different, with would being used in both the main clause and the subordinate clause.
|
| If
| Subject
| would
| Base form
| Subject
| would (not)
| Base form
|
| +
| If
| Sarah
| would
| have the Internet,
| she
| would
| chat.
|
! Study the following sentence: If one scientific team of NASA hadn’t made a mistake, they wouldn’t have been blamed on the demise of the multimillion dollar Mars Climate Orbiter.
This is the example of a conditional clause (if + subject + past perfect, would + have + Pii/V3), the 3rd type of adverbial clause (unreal past). We use this conditional to reflect on things that happened or didn’t happen in the past and how changing these events might have made a difference. It is often used to express regret or to criticise.
The team didn’t recognize and correct an error in information from another team, in 1998. We suppose the opposite, using the Past Perfect tense (hadn’t made). We use wouldn’t have been blamed to express the past possible result.
| | If
| Subject
| Past perfect
| Subject
| Would(not)
| Have
| Past participle
|
| –
| If
| team of NASA
| hadn’t made a mistake,
| they
| would not
| have been
| blamed….
|
| +
| If
| team of NASA
| had made a mistake,
| they
| would
| have been
| blamed….
|
|
| If
| Subject
| Past perfect
| Would (not)
| Subject
| Have
| Past participle
|
| ?
| If
| team of NASA
| had made a mistake,
| would
| they
| have been
| blamed …?
|
Sometimes in American English and in colloquial British English, the form of the third conditional is different, with would being used in both the main clause and the subordinate if clause.
|
| If
| Subject
| would
(not)
| have
| Past participle
| Subject
| would (not)
| have
| Past participle
|
| +
| If
| he
| would
| have
| known that information
| he
| would
| have
| used it properly
|
! Study the following sentence: When he left school in 1980, he was offered a job in a bank, but he didn’t take it. If he had taken the job, he would ( or might) be a bank manager now.
This is the example of a mixed conditional clause (if + subject + past perfect, would + infinitive/V1). Mixed conditional is used when things that happened in the past have a result or a consequence in the present.
He didn’t take the job in 1980, in the past. We suppose the opposite, and express this with the Past Perfect tense had taken. The present result is expressed by the Conditional tense would be (certain) or might be (perhaps).
The subordinate if clause of this conditional is a third (type 3) conditional that we use to talk about the past and the main clause is a second (type 2) conditional that we use to talk about the present. If he had taken the job, he would ( or might) be a bank manager now.
|
| If
| Subject
| Past perfect
| Subject
| would (not)
| |
Base form
| –
| If
| he
| hadn’t taken the job,
| he
| would not
| be a bank manager now.
|
| +
| If
| he
| hadn taken the job,
| he
| would
| be a bank manager now.
|
| ?
| If
| Subject
| Past perfect
| Question word
| would (not)
| Subject
| Past participle
|
| ?
| If
| he
| had taken the job,
| who
| would
| he
| be now?
|
3. Find and underline other examples in the text.
4. Find the mistakes and correct the sentence.
1) If I see wrong information, I would correct it.
2) If you found an article that provides relevant information for your research topic, you should be taken care to investigate the source to make sure it is valid and reliable.
3) If you have identified your device as a first generation iPhone, to click here see the iPhone 2G jailbreak page.
4) He said that if they are running up-to-date, patched versions they should not face increased risk.
5) If start-up idea been did really well and we don't know about it, then would it has been did well?
5. Use the prompts to make conditional sentences.
1) If the information on the ticket _____________________ (to be incorrect) such as a misspelling on the name or the car color _____________________ (be wrong this _____________________ (to void/abolish) the ticket. (unreal past)
2) Can a car license_____________________ (be dismissed) if the police officer _____________________ (to write) the wrong info on it? (mixed)
3) If your documents_____________________ (to be) in the glove box or console, _____________________ (to get) them and close the compartment. (real present, imperative)
4) If your vehicle _____________________ (to have) smoke pouring out and _____________________ (to smell) like a Cheech and Chong reunion, he the officer_____________________ (to search) it without asking. (unreal past)
5) If you _____________________ (not/get) a reply or the information is still wrong, you_____________________ (may/wish) to contact the credit reference agency from where you obtained your file. (real present)
6. Translate the following sentences into Russian.
1) Total Immersion, Inc. is an Atlanta based computer consulting firm specializing in software development, systems support and network security.
2) Altering computer input in an unauthorized way requires little technical expertise and is not an uncommon form of theft by employees altering the data before entry or entering false data, or by entering unauthorized instructions or using unauthorized processes.
3) Each time a user chooses a document as being of interest he is making a statement about the pertinence of the document and the martial contained within the document.
4) A key aspect of Information Security is to preserve the confidentiality, integrity and availability of an organisation's information.
7. Translate the following sentences into English.
1) Если интерфейс не удобен для пользователя, он с ним не будет работать.
2) Если бы ты тогда использовал специальное приспособление, у тебя бы все получилось.
3) Если бы сбор и оценка информации проходили бы в быстром режиме, у нас не было бы сейчас проблем.
4) Если бы носители информации были созданы не на основе кремния, было бы не очень удобно их использовать.




 Prepare a presentation on the topic being discussed.
Prepare a presentation on the topic being discussed.





 We live in the Information Age and we are surrounded by information. The information is everywhere: in human speech, books, magazines and newspapers, radio and TV messages, readings, etc. Information is stored on CD- and DVD-disks, special devices and data carriers. Thanks to new media like the Internet, the Web, blogs, email, cell phones, iPods, e-Readers, Blackberries and iPhones we are blanketed in information.
We live in the Information Age and we are surrounded by information. The information is everywhere: in human speech, books, magazines and newspapers, radio and TV messages, readings, etc. Information is stored on CD- and DVD-disks, special devices and data carriers. Thanks to new media like the Internet, the Web, blogs, email, cell phones, iPods, e-Readers, Blackberries and iPhones we are blanketed in information.





