It is important to ensure that financial plans are being implemented and to catch minor problems before they become major problems. Accordingly, the financial manager should establish a means of monitoring and evaluating financial performance. Interim budgets (weekly, monthly, or quarterly) may be prepared for comparison purposes. These comparisons point up areas that require additional or revised planning.

Exercises
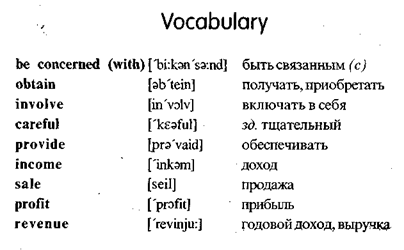
I. Translate into Russian.
Basis of financial management; goal; objective; sources of fi
nancing; funding; step; important task; financial performance;
budgeting; expenditure; revenue; sales revenue; equity capital;
debt capital; specific period; profit; assets; short-term borrowing;
long-term borrowing; merger; companywide budget; cash budget;
zero-base budgeting; income; source; share of ownership; assign
a cost; justify; meet needs; obtain; implement; modify; establish;
reduce; determine; evaluate. !:
II. Find the English equivalents. \
Финансовый план; бюджет; составление бюджета; наличный бюджет; бюджет всей компании; промежуточный бюджет; доход (годовой); доход; доход от продаж; заемный капитал; работа фирмы; активы; бюджетная статья; расход; источник денежных средств; доля собственности; акционерный капитал; средство; последнее спасительное средство; радикальный шаг; финансовая деятельность; определять стоимость; решать; оценивать; оправдывать; осуществлять; удовлетворять потребности; нести издержки; финансировать; занимать (брать в долг).
III. Fill in the blanks.
1. Financial planning begins with the establishment of... and
2. A budget is a financial statement that projects... and/or... over a specified future period of time.
3. Usually the budgeting process begins with the construction of individual budgets for each of the various types of....
4. Budgeting accuracy is improved when budgets are first constructed for individual... for shorter periods of time.
5. Departmental budgets can help managers... and financial performance throughout the period covered by the overall cash budget.
6. In the traditional approach, each new budget is based on the... contained in the budget for the... year.
7. This approach leaves room for the manipulation of......
to protect the interests of separate departments.
8. Zero-base budgeting is a budgeting approach in which every... must be justified in every budget.
9....... are the first type of funding.
10. The second type of funding is.......
11. The third type of funding is.......
12. The fourth type of funding is the... of....
13. Selling assets is a.......
14. The financial manager should establish a... of monitoring and... financial performance.
IV. Translate into English in a written form.
1. Финансовый план—это план получения и использования денег, необходимых для осуществления целей организации.
2. Финансовое планирование начинается с установления конечных целей и поэтапных целей.
3. Бюджет предусматривает доход и расходы за конкретный период времени.
4. Процесс составления бюджета (budgeting) начинается с составления отдельных бюджетов по продажам и по каждому виду расходов.
5. Эти бюджеты легко объединяются в наличный бюджет всей компании.
6. Многие фирмы используют один из двух подходов к построению бюджетов.
7. При традиционном подходе новый бюджет основывается на бюджете за предыдущий год и руководители обосновывают только новые расходы.
8. Это оставляет место для манипуляции бюджетными статьями.
9. Эта проблема в основном ликвидируется через бюдже
тирование нуля. -;••;
10. Четырьмя основными источниками финансирования являются: доход от продаж, акционерный капитал, заемный капитал и продажа активов.
11. Продажа активов — это последнее спасительное средство.
12. Финансовый руководитель должен обеспечить (establish) средство контроля и оценки финансовой деятельности.
V. Questions and assignments.
1. What is a plan?
2. What is a financial plan?
3. What does financial planning begin with?
4. State the difference between goals and objectives.
5. List the three steps involved in financial planning.
6. In what case financial planning cannot proceed?
7. State the meaning of the word "budget".
8. Give the examples of various types of expenses which must be considered (учтены) in budgeting process?
9. How can budgeting accuracy be improved?
10. What is the peculiarity (особенность) of the traditional approach to budgeting?
11. What is the problem with this approach?
12. What is the difference between the traditional budgeting approach and zero-base budgeting?
13. What is the problem with zero-base budgeting?
14. List the four primary sources of funding.
1 5. For what purpose (цель) is equity capital used?
16. Is selling assets a normal step?
17. In what case selling assets may be a reasonable last resort?
18. For what purpose may interim budgets be prepared?
VI. Make up a written abstract (краткое изложение) of the text.
VII. Retell the prepared abstract.
Unit 5
Outside Sources of Financing
Financial management consist of all those activities that are concerned with obtaining money and using it effectively. Effective financial management involves careful planning. It begins with a determination of the firm's financial needs.
Money is needed to start a business. Then the income from sales could be used to finance the firm's continuing operations and to provide a profit.
But sales revenue does not generally flow evenly. Income and expenses may very from season to season or from year to year. Temporary financing may be needed when expenses are high or income is low. Then, the need to purchase a new facility or expand an existing facility may require more money than is available within a firm. In these cases the firm must look for outside sources of financing. Usually it is short- or long-term financing.
1. Short-term financing is money that will be used for one year or less and then repaid.
There are many short-term financing needs. Two deserve special attention. First, certain necessary business practices may affect a firm's cashflow and create a need for short-term financing.
Cashflow is the movement of money into and out of an organization. The ideal is to have sufficient money coming into the firm, in any period, to cover the firm's expenses during that period. But the ideal is not always achieved. For example, a firm that offers credit to its customers may find an imbalance in its cash flow. Such credit purchases are generally not paid until thirty or sixty days (or more) after the transaction. Short-term financing is then
needed to pay the firm's bills until customers have paid their bills. Unanticipated expenses may also cause a cash-flow problem.
A second major need for short-term financing that is related to a firm's cash-flow problem is inventory.
Inventory requires considerable investment for most manufactures, wholesalers, and retailers. Moreover, most goods are manufactured four to nine months before they are sold to the ultimate customer. As a result, manufacturers often need short-term financing. The borrowed money is used to buy materials and supplies, to pay wages and rent, and to cover inventory costs until the goods are sold. Then, the money is repaid out of sales revenue. Additionally, wholesalers and retailers may need short-term financing to build up their inventories before peak selling periods. Again, the money is repaid when the merchandise is sold.
2. Long-term financing is money that will be used for longer period than one year. Long-term financing is needed to start a new business. It is also needed for executing business expansions and mergers, for developing and marketing new products, and for replacing equipment that becomes obsolete or inefficient.
The amounts of long-term financing needed by large firms can be very great.
Exercises
I. Translate into Russian.
Income; profit; facility; sales revenue; expense; source; term; short-term financing; long-term financing; cash; cash flow; expand; provide; obtain; purchase; affect; be available; repay; borrow; transaction; supplies; marketing; equipment; merger; retailer; wholesaler; manufacturer; imbalance; merchandise; inventory; rent; sales revenue.
II. Find the English equivalents.
Финансовые потребности; арендная плата; стоимость; изготовитель; оптовый торговец; розничный торговец; (торговая) сделка; доход от продажи; припасы; товары; слияние (предприятий); определение; товарные запасы; оборудование; продажа; доход; прибыль; расход; срок; краткосрочное финансирование; долгосрочное финансирование; денежная наличность; движение наличности; обеспечивать; изменяться; покупать; быть в наличии; предлагать; заменять; влиять (на); конечный; устарелый; неэффективный; непредвиденный; тщательный.
III. Fill in the blanks.
1. Financial management begins with a determination of the firm's....
2. Temporary financing may be needed when... are high and... is low.
3. In these cases the firm must look for outside... of financing.
4. Short-term financing is... that will be used for one year or less and then....
5. Cash flow is the movement of... into and out of an organization.
6. A firm that offers credit to its customers may find an imbalance in its....
7. A second major need for... financing that is related to a firm's cash-flow problem is....
8. The borrowed money is used to buy... and..., to pay... and to cover... until the goods are sold.
IV. Translate into English.
1. Финансовый менеджмент состоит из тех видов деятельности (activities), которые относятся к получению денег и эффективному их использованию.
2. Краткосрочное финансирование — это деньги, которые будут использоваться в течение одного года или менее (less).
3. Существуют (there are) многие потребности краткосрочного финансирования, но движение наличности и товарные запасы представляют (are) две основные проблемы.
4. Товарные запасы требуют значительного инвестирования для большинства производителей, оптовых торговцев и розничных торговцев.
5. Занятые деньги возвращаются (is repaid) из дохода от продаж.
V.. Answer the questions.
1. Is money needed to start a business?
2. When may temporary financing be needed?
3. What kinds (виды) of financing do you know?
4. What is short-term financing?
5. What is cash flow?
6. What is the ideal cash flow?
7. What can cause a cash flow problem?
8. Does inventory require considerable investment for most manufacturers, wholesalers and retailers?
9. Why do manufacturers often need short-term financing?
10. For what purpose (цель) is the borrowed money often used by the manufacturers?
11. When is the borrowed money usually repaid?
12. What is long-term financing? ,.:
13. For what purpose is long-term financing needed?
14. Are the amounts of long-term financing greater than those of short-term financing?
VI. Make up a written abstract of the above text.
VII. Retell the prepared abstract.
Unit 6
Sources of Unsecured Financing
Unsecured financing is financing for which collateral is not required. Most short-term financing is unsecured. Sources of unsecured short-term financing include trade credits, promissory notes, bank loans, commercial papers, and commercial drafts.
TRADE CREDIT
Wholesalers may provide financial aid to retailers by allowing them thirty to sixty days (or more) in which to pay for merchandise. This delayed payment, which may also be granted by manufacturers, is a form of credit known as trade credit or the open account. More specifically, trade credit is a payment delay that a supplier grants to its customers.
Between 80 and 90 percent of all transactions between businesses involve some trade credit. Typically, the purchased goods are delivered along with a bill (or invoice) that states the credit terms. If the amount is paid on time, no interest is generally charged. In fact, the seller may offer a cash discount to encour-. age prompt payment. The terms of a cash discount are specified on the invoice.












