ТЕХТ 1
HOW MATERIALS REACT TO EXTERNAL FORCES
Materials Science and Technology is the study of materials and how they can be fabricated to meet the needs of modern technology. Using the laboratory techniques and knowledge of physics, chemistry, and metallurgy, scientists are finding new ways of using metals, plastics and other materials.
Engineers must know how materials respond to external forces, such as tension, compression, torsion, bending, and shear. All materials respond to these forces by elastic deformation. That is, the materials return their original size and form when the external force disappears. The materials may also have permanent deformation or they may fracture. The results of external forces are creep and fatigue.
Compression is a pressure causing a decrease in volume. When a material is subjected to a bending, shearing, or torsion (twisting) force, both tensile and compressive forces are simultaneously at work. When a metal bar is bent, one side of it is stretched and subjected to a tensional force, and the other side is compressed.
Tension is a pulling force; for example, the force in a cable holding a weight. Under tension, a material usually stretches, returning to its original length if the force does not exceed the material’s elastic limit. Under larger tensions, the material does not return completely to its original condition, and under greater forces the material ruptures.
Fatigue is the growth of cracks under stress. It occurs when a mechanical part is subjected to a repeated or cyclic stress, such as vibration. Even when the maximum stress never exceeds the elastic limit, failure of the material can occur even after a short time. No deformation is seen during fatigue, but small localised cracks develop and propagate through the material until the remaining cross-sectional area cannot support the maximum stress of the cyclic force. Knowledge of tensile stress, elastic limits, and the resistance of materials to creep and fatigue are of basic importance in engineering.
Creep is a slow, permanent deformation that results from a steady force acting on a material. Materials at high temperatures usually suffer from this deformation. The gradual loosening of bolts and the deformation of components of machines and engines are all the examples of creep. In many cases the slow deformation stops because deformation eliminates the force causing the creep. Creep extended over a long time finally leads to the rupture of the material.
. Answer the questions:
What are the external forces that cause the elastic deformation of materials? Describe those forces that change the form and size of materials.
What are the results of external forces?
What kinds of deformation are the combinations of tension and compression?
What is the result of tension? What happens if the
Elastic limit of material is exceeded under tension?
What do we call fatigue? When does it occur? What are the results of fatigue?
What do we call creep? When does this type of permanent deformation take place? Whataretheresultsofcreep?


Find the following word combinations in
The text:
1. отвечать требованиям современной технологии.
Используя лабораторные методы.
Внешняя сила.
Постоянная деформация.
Уменьшение объема.
Разрушение материала.
Density (specific weight) is the amount of mass in a unit volume. It is measured in kilograms per cubic metre. The density of water is 1000 kg/m3 but most materials have a higher density and sink in water. Aluminium alloys, with typical densities around 2800 kg/m3 are considerably less dense than steels, which have typical densities around 7800 kg/m3. Density is important in any application where the material must not be heavy.
Stiffness (rigidity) is a measure of the resistance to deformation such as stretching or bending. The Young modulus is a measure of the resistance to simple stretching or compression* It is the ratio of the applied force per unit area (stress) to the fractional elastic deformation (strain). Stiffness is important when a rigid structure is to be made.
Strength is the force per unit area (stress) that a material can support without failing. The units are the same as those of stiffness, MM/m2, but in this case the deformation is irreversible. The yield strength is the stress at which a material first deforms plastically. For a metal the yield strength may be less than the fracture strength, which is the stress at which it breaks. Many t materials have a higher strength in compression than in tension.
Ductility is the ability of a material to deform without breaking. One of the great advantages of metals is their ability to be formed into the shape that is needed, such as car body parts. Materials that are not ductile are brittle. Ductile materials can absorb energy by deformation but brittle materials cannot.
Toughness is the resistance of a material to breaking ■ when there is a crack in it. For a material of given toughness, the stress at which it will fail is inversely proportional to the square root of the size of the largest defect present. Toughness is different from strength; the toughest steels, for example, are different from the ones with highest tensile strengths Brittle materials have low toughness: glass can be broken along a chosen line by first scratching it with a diamond. Composites can be designed to have considerably greater toughness than their constituent materials. The example of a very tough composite is fiberglass that is very flexible and strong.
Creep resistance is the resistance to a gradual permanent change of shape, and it becomes especially important at higher temperatures. A successful research has been made in materials for machine parts that operate at high temperatures and under high tensile forces without gradually extending, for example the parts of plane engines.
ДОПОЛНИТЕЛЬНЫЙСЛОВАРЬ;
ability [ a' biliti] способность absorb [ sb' zo: b] поглощать amount [ a' maunt] количество
application [,aepli'keijsn] применение brittle ['britl] хрупкий, ломкий
Car body кузовавтомобиля
constituent [кэп ' stitjuan t] компонент
crack [kraek] трещина creepresistance устойчивость к ползучести definition [,defTniJan] определение density ['densiti] плотность
ductility [dAk'tihti] ковкость, эластичность failure ['feiljs] повреждение, разрушение
gradualf'grasdjual] постепенный
rigid ['ri(%id] –жесткий. To sink - тонуть. squareroot[ skwea'rud]- квадратный корень
stiffness [' stifnis] жесткость strain [ strein]- нагрузка, напряжение, деформация
strength [ strepG] прочность stress [ stres]- давление, напряжение
Young modulus -модуль Юнга
1.8. Answer the questions:
What is Young modulus?
What is strength?
What is ductility?
What is toughness?
10. What properties of steel are necessary for the manufacturing of: a) springs, b) car body parts, c) bolts and nuts, d) cutting tools?
Тонна на кубический метр
Жесткая конструкция
Прочность на сжатие
Постепенное изменение формы
Повышенные температуры
WELDING
Welding is a process when metal parts are joined together by the application of heat, pressure, or a combination of both. The processes of welding can be divided into two main groups:
•pressure welding, when the weld is achieved by pressure and
•heat welding, when the weld is achieved by heat. Heat welding is the most common welding process used today.
Riveting in the construction of many types of structures, including bridges, buildings, and ships. It is also a basic process in the manufacture of machinery and in the motor and aircraft industries. It is necessary almost in all productions where metals are used.
The welding process depends greatly on the properties of the metals, the purpose of their application and the available equipment. Welding processes are classified according to the sources of heat and pressure used: gas welding, arc welding, and resistance welding. Other joining processes are laser welding, and electron-beam welding.
Gas Welding
Gas welding is a non-pressure process using heat from a gas flame. The flame is applied directly to the metal edges to be joined and simultaneously to a filler metal in the form of wire or rod, called the welding rod, which is melted to the joint. Gas welding has the advantage of using equipment that is portable and does not require an electric power source. The surfaces to be welded and the welding rod are coated with flux, a fusible material that shields the material from air, which would result in a defective weld.
Arc Welding
Arc-welding is the most important welding process for joining steels. It requires a continuous supply of either direct or alternating electrical current. This current is used to create an electric arc, which generates enough heat to melt metal and create a weld.
Arc welding has several advantages over other welding methods. Arc welding is faster because the concentration of heat is high. Also, fluxes are not necessary in certainmethods of arc welding. The most widely used arc-welding processes are shielded metal arc, gas-tungsten arc, gas- metal arc, and submerged arc.
Resistance Welding
In resistance welding, heat is obtained from the resistance of metal to the flow of an electric current. Electrodes are clamped on each side of the parts to be welded, the parts are subjected to great pressure, and a heavy current is applied for a short period of time. The point where the two metals touch creates resistance to the flow of current. This resistance causes heat, which melts the metals and creates the weld. Resistance welding is widely employed in many fields of sheet metal or wire manufacturing and is often used for welds made by automatic or semi-automatic [«semi «Ltq’mxtlk] machines especially in automobile industry.
\/ ДОПОЛНИТЕЛЬНЫЙ СЛОВАРЬ:
Gas welding- газосварка
arc welding- электродуговая сварка
Where is welding necessary?
Сварка давлением
Тепловая сварка
Процесс сварки
Имеющееся оборудование
Сварочный электрод
Плавкий материал
Дефектный сварной шов
Электрическая дуга
Text 4
Types of welding
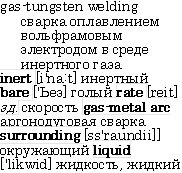
As a non-consumable electrodes tungsten or carbon electrodes can be used. In gas-tungsten arc welding a tungsten electrode is used in place of the metal electrode used in shielded metal-arc welding. A chemically inert gas, such as argon, helium, or carbon dioxide is used to shield the metal from oxidation. The heat from the arc formed between the electrode and the metal melts the edges of the metal. Metal for the weld may be added by placing a bare wire in the arc or the point of the weld. This process can be used with nearly all metals and produces a high-quality weld. However, the rate of welding is considerably slower than in other processes.
Shielded Metal Arc welding
In shielded metal-arc welding, a metallic electrode, which conducts electricity, is coated with flux and connected to a source of electric current. The metal to be welded is connected to the other end of the same source of current. An electric arc is formed by touching the tip of the electrode to the metal and then drawing it away. The intense heat of the arc melts both parts to be welded and the point of the metal electrode, which supplies filler metal for the weld. This process is used mainly for welding steels.
Gas-Metal Arc welding
In gas-metal welding, a bare electrode is shielded from the air by surrounding it with argon or carbon dioxide gas and sometimes by coating the electrode with flux. The electrode is fed into the electric arc, and melts off indroplets that enter the liquid metal of the weld seam. Most metals can be joined by this process.
Submerged Arc welding
Submerged-arc welding is similar to gas-metal arc welding, but in this process no gas is used to shield the weld. Instead of that, the arc and tip of the wire are submerged beneath a layer of granular, fusible material that covers the weld seam. This process is also called eiectroslag welding. It is very efficient but can be used only with steels.

Answer the questions:
Вольфрамовыйэлектрод
Инертный газ
Окисление
Скорость сварки
Жидкий металл
Листовой металл
10. полуавтоматические сварочные станки
Translate into Russian:
ТЕХТ 1
HOW MATERIALS REACT TO EXTERNAL FORCES
Materials Science and Technology is the study of materials and how they can be fabricated to meet the needs of modern technology. Using the laboratory techniques and knowledge of physics, chemistry, and metallurgy, scientists are finding new ways of using metals, plastics and other materials.
Engineers must know how materials respond to external forces, such as tension, compression, torsion, bending, and shear. All materials respond to these forces by elastic deformation. That is, the materials return their original size and form when the external force disappears. The materials may also have permanent deformation or they may fracture. The results of external forces are creep and fatigue.
Compression is a pressure causing a decrease in volume. When a material is subjected to a bending, shearing, or torsion (twisting) force, both tensile and compressive forces are simultaneously at work. When a metal bar is bent, one side of it is stretched and subjected to a tensional force, and the other side is compressed.
Tension is a pulling force; for example, the force in a cable holding a weight. Under tension, a material usually stretches, returning to its original length if the force does not exceed the material’s elastic limit. Under larger tensions, the material does not return completely to its original condition, and under greater forces the material ruptures.
Fatigue is the growth of cracks under stress. It occurs when a mechanical part is subjected to a repeated or cyclic stress, such as vibration. Even when the maximum stress never exceeds the elastic limit, failure of the material can occur even after a short time. No deformation is seen during fatigue, but small localised cracks develop and propagate through the material until the remaining cross-sectional area cannot support the maximum stress of the cyclic force. Knowledge of tensile stress, elastic limits, and the resistance of materials to creep and fatigue are of basic importance in engineering.
Creep is a slow, permanent deformation that results from a steady force acting on a material. Materials at high temperatures usually suffer from this deformation. The gradual loosening of bolts and the deformation of components of machines and engines are all the examples of creep. In many cases the slow deformation stops because deformation eliminates the force causing the creep. Creep extended over a long time finally leads to the rupture of the material.
. Answer the questions:










