N2 (g) + 3 H2 (g) ↔ 2 NH3 (g)
If hydrogen gas is added after the reaction has reached equilibrium, the reaction will:
A. shift to the right to produce more product
b. shift to the left to produce more reactants
c. stop. All the nitrogen gas has already been used up. d. Need more information.
Chemical Reaction Classification Practice Test
1 The chemical reaction: 2 H2O → 2 H2 + O2 is a
a. synthesis reaction b. decomposition reaction
c. single displacement reaction
d. double displacement reaction e. combustion reaction
2 The chemical reaction: 2 H2 + O2 → 2 H2O is a
a. synthesis reaction b. decomposition reaction
c. single displacement reaction
d. double displacement reaction e. combustion reaction
3 The chemical reaction: 2 KBr + Cl2 → 2 KCl + Br2 is a
a. synthesis reaction b. decomposition reaction
c. single displacement reaction
d. double displacement reaction e. combustion reaction
4 The chemical reaction: 2 H2O2 → 2 H2O + O2 is a
a. synthesis reaction b. decomposition reaction
c. single displacement reaction
d. double displacement reaction e. combustion reaction
5 The chemical reaction: Zn + H2SO4 → ZnSO4 + H2 is a
a. synthesis reaction b. decomposition reaction
c. single displacement reaction
d. double displacement reaction e. combustion reaction
6 The chemical reaction: AgNO3 + NaCl → AgCl + NaNO3 is a
a. synthesis reaction b. decomposition reaction
c. single displacement reaction
d. double displacement reaction e. combustion reaction
7 The chemical reaction: C10H8 + 12 O2 → 10 CO2 + 4 H2O is a
a. synthesis reaction b. decomposition reaction
c. single displacement reaction
d. double displacement reaction e. combustion reaction
8 The chemical reaction: 8 Fe + S8 → 8 FeS is a
a. synthesis reaction b. decomposition reaction
c. single displacement reaction
d. double displacement reaction e. combustion reaction
9 The chemical reaction: 2 CO + O2 → 2 CO2 is a
a. synthesis reaction b. decomposition reaction
c. single displacement reaction
d. double displacement reaction e. combustion reaction
10 The chemical reaction: Ca(OH)2 + H2SO4 → CaSO4 + 2 H2O is a
a. synthesis reaction b. decomposition reaction
c. single displacement reaction
d. double displacement reaction e. combustion reaction
Test questions
1. What is the equivalent weight of MgO
А. 20 В. 30 С. 10 D. 35 Е. 40
2. What is the equivalent weight of H3PO4
А. 20 В. 32 С. 10 D. 35 Е. 40
3. What is the equivalent weight of Fe2O3
А. 20 В. 32 С. 10 D. 35 Е. 26
4. What is the equivalent weight of HNO2
А. 20 В. 32 С. 47 D. 35 Е. 40
5. What is the equivalent weight of H2CrO4
А. 59 В. 32 С. 10 D. 35 Е. 40
6. What is the equivalent weight of H2ZnO2
А. 20 В. 32 С. 10 D. 35 Е. 49
7. What is the equivalent weight of CO
А. 20 В. 32 С. 14 D. 35 Е. 49
8. What is the equivalent weight of Al2O3
А. 20 В. 17 С. 10 D. 35 Е. 49
9. What is the equivalent weight of Fe(OH) 2
А. 20 В. 32 С. 10 D. 35 Е. 45
10. What is the equivalent weight of Fe(OH) 3
А. 20 В. 41 С. 10 D. 105 Е. 49
11. The elements of Group VII are known as the:
A. lanthanides B. noble gases C. halogens D. neutrons E. nonmetals
12. 30 64Zn and 30 68Zn are examples of:
A. isotopes B. allotropes C. phenemones D. neutrons E. nonmetals
13. An atom of strontium-90 (9038Sr) contains
А. 38 electrons, 38 protons, 52 neutrons
В. 38 electrons, 38 protons, 90 neutrons
С. 52 electrons, 52 protons, 38 neutrons
D. 52 electrons, 38 protons, 38 neutrons
E. 30 electrons, 30 protons, 38 neutrons
14. Which of the following pairs of species would have the greatest similarities in chemical properties?
А. 39K and 39K+ В. 39K and 23Na С. 39K and 40K
D. 40K and 40Ca E. 44K and 40Ca
15 The species 10444Ru contains
А. 44 neutrons and 44 electrons. В. 44 protons and 44 electrons.
С. 44 protons and 104 neutrons. D. 60 neutrons and 60 electrons.
E. 80 neutrons and 60 electrons.
16. An atom of strontium-90 (9038Sr) contains
А. 38 electrons, 38 protons, 52 neutrons В. 38 electrons, 38 protons, 90 neutrons
С. 52 electrons, 52 protons, 38 neutrons D. 52 electrons, 38 protons, 38 neutrons
E.59 electrons, 38 protons, 40 neutrons
17. The nucleus of a radon atom, 22286Rn, contains
А. 222 protons and 86 neutrons. В. 86 protons and 140 neutrons.
С. 86 protons and 222 neutrons. D. 86 protons, 136 neutrons and 86 electrons.
E. 86 protons, 136 neutrons.
18. The species 10444Ru contains
А. 44 neutrons and 44 electrons. В. 44 protons and 44 electrons.
С. 44 protons and 104 neutrons. D. 60 neutrons and 60 electrons.
E. 86 protons, 136 neutrons
19. What is the order of decreasing radii of species S, S2+ and S2-?
A. S >S2->S2+ B. S2->S2+>S C. S2->S>S2+ D. S2+>S>S2- E. S>S2+>S
20. Which subtance does not have the correct formula?
A. iron(lll) sulfate Fe2(SO4)3 B. iron(ll) oxide Fe2O
C. copper(l) sulfate Cu2SO4
D. copper(ll) nitrite Cu(NO3)2 E. Carbon dioxide CO
21. Тhe smallest particle of an element is ….
A. Atom B. Molecule C. Ion D. Elements
E. Substanses
22. The smallest particle of a substance that can have an independent existence.
A.Atom B. Molecule C. Ion D. Elements
E. Substanses
23. Pure substances, that make up everything in the universe
A. Atom B. Molecule C. Ion D. Elements
E. Substanses
24 Law of equivalent proportions - law stating that …
A. the proportions in which two elements separately combine with a third element are also the proportions in which they combine together.
B. The mass of the substances entering into a reaction equal the mass of the substances formed as a result of the reaction.
C. On mole of any substance in the gaseous state occupies the same volume at the same temperature and pressure.
D. One mole of any gas in standard conditions (0°C = 273°K, 1 atm = 101.3 kPa) occupies a volume of 22.4 litres.
25. Law of mass conversation - law stating that …
A. the proportions in which two elements separately combine with a third element are also the proportions in which they combine together.
B. The mass of the substances entering into a reaction equal the mass of the substances formed as a result of the reaction.
C. On mole of any substance in the gaseous state occupies the same volume at the same temperature and pressure.
D. One mole of any gas in standard conditions (0°C = 273°K, 1 atm = 101.3 kPa) occupies a volume of 22.4 litres.
26. Equal volumes of all gases at the same conditions (temperature, pressure) contain the same number of molecules.
A. Law of constant composition. B. Law of multiple proportions C. Avogadro law
D. Law of combining volumes
28 The elements in the Periodic Table are arranged in order of increasing
A. Ionization energy B. Atomic volume C. Relative atomic mass D. Nuclear charge
Е. Relative molecular mass
29 Which pair of elements has the most similar chemical properties?
A. As and Br B. As and Se C. As and P D. C and F
E. Cu and P
30 Which subtance does not have the correct formula?
A. iron(lll) sulfate Fe2(SO4)3 B. iron(ll) oxide Fe2O3
C. copper(l) sulfate Cu2SO4 D. copper(ll) nitrite Cu3(NO3)2
E. copper(ll) nitrite CuSO4
31 Which is not a property of metallic solids?
A. conduct electricity B. usually high melting
C. high freezing point
D. They are all properties of metallic solids
32. Oxygen gas can be produced by the decomposition of all of the following substances expect:
A. mercury(II) oxide B. hydrogen peroxide C. Ozone
D. copper E. iron
33. Which one of the following combinations of names and formulas is incorrect?
A. H3PO4 phosphoric acid B. HNO3 nitric acid
C. NaHCO3 sodium carbonate
D. AlPO4 aluminium fluoride E. CaCl2 calcium oxide
34. The name for the ion, S 2 – is:
A. sulfide B. sulfate C. Sulfite D. Sulfur E. Carbon
35. Calculate the HO+ ion concentration (in M) in a solution with a pH = 7
A. 1·10–7 M B. 2.0·10–7 M C. 8.0·10–7 M D. 5.0·10–7 M E. 6.0·10–7 M
36. Calculate the pH of a solution whose [H+ ] = 10-12.
A. 2 B. 10 C. 12 D. 8 E. 6
37. Calculate the pH of a solution whose [H+ ] = 10-5.
A. 2 B. 10 C. 5 D. 8 E. 6
38. A pH buffer is best described as a solution containing:
A. A weak acid B. A strong acid
C. A mixture of a weak acid and the salt of a weak acid
D. A strong acid E. A strong base
39. When NaCl dissolves in water, it is present as:
A. NaCl molecules B. Na atoms and Cl atoms C. Na cations and Cl anions
D. Na E. Cl2
40. Insoluble salt is an example of...
A. weak electrolyte B. strong electrolyte C. Cathode D. Anode E. They are all right
41. Soluble salt is an example of...
A. weak electrolyte B. strong electrolyte C. Anode D. Cathode E. They are all right
42. pH equation
A.  -log[Ka] B.
-log[Ka] B.  -log[OH-] C.
-log[OH-] C.  -log[H+] D.
-log[H+] D.  -log[C1/C2] E.
-log[C1/C2] E.  -log[Kb]
-log[Kb]
43. pOH equation
A.  -log[Ka] B.
-log[Ka] B.  -log[OH-] C.
-log[OH-] C.  -log[H+] D.
-log[H+] D.  -log[C1/C2] E.
-log[C1/C2] E.  -log[Kb]
-log[Kb]
44. Which is a characteristic of a strong acid?
A. It has a pH greater than 7. B. It completely ionizes in solution.
C. It contains many hydroxide ions. D. It reacts only with a strong base.
E. It has a pH less than 7.
45. Calculate the ionic strengths of the solution 0.30 M NaCl.
 A. 0.30 B. 0.90 C. 0.80 D. 3.3 E. 6.5
A. 0.30 B. 0.90 C. 0.80 D. 3.3 E. 6.5
46. Calculate the ionic strengths of the solution 0.30 M Na2SO4.
 A. 0.50 B. 0.90 C. 0.20 D. 3.5 E. 6.5
A. 0.50 B. 0.90 C. 0.20 D. 3.5 E. 6.5
47. Calculate the ionic strengths of the solution 0.30 M NaCl and 0.20 M K2SO4.
 A. 0.50 B. 0.90 C. 0.20 D. 3.5 E. 6.50
A. 0.50 B. 0.90 C. 0.20 D. 3.5 E. 6.50
49 Calculate the ionic strengths of the solution 0.20 M Al2(SO4)3 and 0.010 M Na2SO4.
 A. 0.50 B. 0.90 C. 0.20 D. 3.30 E. 6.80
A. 0.50 B. 0.90 C. 0.20 D. 3.30 E. 6.80
48. Calculate the ionic strengths of the solution 0.5 M AlCl3 and 0.010 M Na2SO4.
A. 0.50 B. 0.90 C. 0.20 D. 3.30 E. 5.50
50. Qualitative analysis
А. what chemicals are present В. how much of a chemical is present
С. occurs only with the substance of interest (rare) D. atomic structure
E. matter and energy
51. quantitative analysis
А. what chemicals are present В. how much of a chemical is present
С. occurs only with the substance of interest (rare) D. atomic structure
E. matter and energy
52. gross sample
A. consists of several portions of the material to be tested
B. small portion of the gross sample
C. small portion of the laboratory sample that is analyzed
53. analysis sample
A. consists of several portions of the material to be tested
B. small portion of the gross sample
C. small portion of the laboratory sample that is analyzed
54. Selective separation of the analyte by precipitation followed by measurement of a physical property
A. gravimetric analysis B. volumetric/titrimetric analysis
C. instrumental analysis
D. spectral analysis E. spectrometers methods
55. Analyte reacts with a measured volume of reagent of known concentration. a change in some property signals the completion of the reaction
A. gravimetric analysis B. volumetric/titrimetric analysis
C. instrumental analysis
D. spectral analysis E. spectrometers methods
56. More slective. may be less precise. based on the measurement of a physical property of a sample.
A. gravimetric analysis B. volumetric/titrimetric analysis
C. instrumental analysis
D. spectral analysis E. Chromatography
57. Is the process by which ions are retained on the surface of a solid
A. Adsorption B. Digestion C. Agglomeration D. Dissolution
E. Corrosion
58. mixtures from which particles settle out upon standing
A. Suspensions B.Colloids C. Emulsions D. Complexes E. Solutions
59. geterogeneous mixtures containing particles that are intermediate in size
A. Suspensions B. Colloids C. Emulsions D. Complexes E. Solutions
60 Colloidal dispersion of liquids in liquids
A. Suspensions B. Colloids C. Emulsions D. Complexes E. Solutions
61 Solid particles dispersed in a gas (solid aerosol), example:
A. dust in air B. slime, paste C. whipped cream D. whipped cream
E. Shaving cream
62 Solid particles dispersed in a liquid (sol); example:
A. cloud B. slime, paste C. foam rubber D. mayonnaise
E. hand cream
63. Liquid dispersed in a solid (gel); example:
A. some glasses B. jelly C. whipped cream D. milk
E. hand cream
64. What is the equilibrium constant for the general equation aA 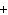 bB «cC
bB «cC 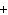 dD?
dD?
A. 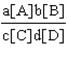 B.
B. 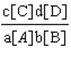 C.
C.  D.
D. 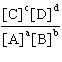
65. The rate of for the general equation aA 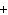 bB
bB  cC
cC 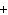 dD?
dD?
A. V=k[A]a[B]b B. V=k[C]a[D]b C. V=k[A][B] D.V=k[A]c[B]d
E. V=k[C]c[D]d
66. Consider the following mechanism for a reaction:
Step 1: HBr + O2 ® HOOBr
Step 2: HBr + HOOBr ® 2HOBr
Step 3: 2HOBr + 2HBr ® 2Br2 + 2H2O
67. Which of the following statements is correct?
A. Br2 is a reactant. B. HBr is a catalyst. C. HOBr is a catalyst.
D. HOOBr is a reaction intermediate. E. H2O is a catalyst.
68. Consider the following reaction mechanism:
Step 1: ClO- +H2O ® HClO + OH- Step 2: I- + HClO ® HIO + Cl-
Step 3: HIO + OH- ® IO- + H2O
The catalyst is
A. IO- B. H2O C. ClO- D. HClO E. OH-
69. Adding or taking away one species in an equilibrium causes the relative rates of reaction to shift to compensate for the change
A. Nernst Equation B. Le Chatelier's Principle
C. Bronsted-Lowry Theory
D. Mendeleev’s law E. Beer-Lambert law
70. Which of the following can be used to represent the rate of a reaction?
A.g / L B. g / mol C. (g · min) / mol D. M / min
71. What is the coordination number of cobalt in the complex ion [Co(en)Cl4]-? (en = ethylenediamine)
A. 1 B. 2 C. 3 D. 5 E. 8
72. In the compound K[Co(C2O4)2(H2O)2] (where C2O42- = oxalate) the oxidation number and coordination number of cobalt are, respectively:
A. -1 and 4 B. -1 and 6 C. 3 and 4 D. 1 and 5 E. 2 and 3
73. Choose the correct name for the formula, [Cr(NH3)4(OH)2]Br
A) chromium(II) tetraamminebis(hydroxo) bromide
B) chromium(III) tetraamminebis(hydroxo) bromide
C) tetraamminedihydroxochromium(III) bromide
74. Choose the correct name for the formula, [Co(en)3][Cr(ox)3]. en = ethylenediamine and ox = C2O42-, oxalate
A. tris(ethylenediamine)cobalt(III) tris(oxalato)chromium(III)
B. tris(ethylenediamine)cobaltate(III) tris(oxalato)chromate(III)
C. tris(ethylenediamine)cobalt(III) tris(oxalato)chromate(II)
D. tris(ethylenediamine)cobalt(III) chromate(II) E. cobalt(III) tris(oxalato)chromate(II)
75. What is the coordinate number for the central atom in [Co(en)(NH3)3Cl]SO4?
A. 2 B. 3 C. 5 D. 7 E. 10
76. In which one of the following pairs is the oxidation number of chromium the same?
A. Cr2O3 and CrCl2 B. CrO3 and CrCl3 C. CrO42- and Cr2O72-
D. Cr2+ and CrO2- E. Cr+2 and Cr2O72-
77. A reducing agent in the cell
A. Electron Donor B. Electron Acceptor C. Cation D.Anion E. Electrolyte
78. An oxidizing agent in the cell
A. Electron Donor B. Electron Acceptor C. Cation D.Anion E. Electrolyte
79. What is the oxidation number of copper in Cu+2?
A. 0 B. +2 C. -3 D. +3 E. -2
80. What is the oxidation number of Br in the BrO3- ion?
A. +2 B. -2 C. +5 D. -5 E. -1
81. What kind of reaction is Cl2 «Cl- + ClO2 (aside from unbalanced)?
A. An oxidation B. A reduction C. A disproportionation D. Redox E. Dissolution
82. In the reaction HNO2 + I- «NO + I3-, what atoms are being oxidized and reduced, respectively?
A. O, I B. I, N C. N, I D. I, O E. H, I
83. Which one of the following reactions is not a redox reaction?
А. Ag+(aq) + Cl-(aq) ® AgCl(s) В. 2Na(s) + Cl2(g) ® 2NaCl(s)
С. Mg(s) + 2HCl(aq) ® MgCl2(aq) + H2(g)
D. Cu2+(aq) + Zn(s) ® Cu(s) + Zn2+(aq)
E. 2Zn (s) + O2 (g) ® 2ZnO (s)
84. The oxidation numbers of nitrogen in NH3, HNO3, and NO2 are, respectively
A. -3, -5, +4 B. +3, +5, +4 C. -3, +5, -4 D. -3, +5, +4
E. +3, +4, -5
85. What is the oxidation number for Cl in the chlorate ion, ClO3-?
A. -1 B. +3 C. +5 D.+7 E. -5
86. What is the oxidation number of Cl in KClO3?
A. -1 B. +2 C. +5 D. -5 E. +7
87. Which equations represent oxidaton-reduction reactions?
I. CaO(s) + CO2(g) ® CaCO3(s)
II. Zn(s) + H2SO4(aq) ® H2(g) + ZnSO4(aq)
A.I only II only B. Both I and II C. Neither I nor II
88. What is the next step in balancing the half reaction
Cr2O7-2 «2 Cr+3?
A. Add 7 H2O to the right B.Add 7 H2O to the left C. Add 3.5 O2 to the left
D. Add 7 O2 to the left E. Add 3.5 O2 to the right
89. What is the next step in balancing the reaction
SO3-2+H2O«SO4-2+2H+?
A. Add 3 H2O to the left B. Add 2 electrons to the left C. Nothing - it is balanced
D. Add 3 H2O to the right E. Add 3 O2 to the right
90. What is the next step in balancing the REDOX reaction having the two half reactions:
Cr(OH)4- → CrO4-2 +4 H+ + 3 e- and ClO- + 2 H+ + 2 e- → Cl- + H2O?
A. Add the two half reactions B. Multiply both by 3
C. Multiply the oxidation by 2 and the reduction by 3
D. Multiply the oxidation by 2 and the reduction by 3
E. Multiply both by 2
91. What is wrong with the REDOX reaction
Cl2 + 2 Br - → 2Cl- + Br2?
A. Nothing is being reduced B. Chloride can not be oxidized
C. Bromide can not be oxidized D. Chloride can not be reduced
E. Bromide can not be reduced
92. When the balanced reaction
2 MnO4- + SO3-2 + H2O → 2 MnO4-2 + SO4-2 + 2 H+ is changed to be balanced in basic solution, the result is:
A. 2 MnO4- + SO3-2 ® 2MnO4-2 + SO4-2 + H2O
B. 2 MnO4- + SO3-2 + 2OH- ® 2MnO4-2 + SO4-2 + H2O
C. 2 MnO4- + SO3-2 ® 2MnO4-2 + SO4-2 + H2O + 2 OH-
D. 3MnO4- + SO3-2 ® 3MnO4-2 + SO4-2 + H2O + 3OH-
E. 2MnO4- + SO3-2 ® 4MnO4-2 + SO4-2 + H2O
93. What are the oxidation numbers of the V, O and Cl atoms in VOCl3?
A. -5, -2, -1 B. -5, +2, -1 C. +5, -2, -1 D. -5, -1, +1 E. -2, +5, +1
94. The molar mass of MgSO4
A.120.00 g/mol B.193.03 g/mol C.165.02 g/mol D. 170.85 g/mol E. 130.85 g/mol
95. Calculate the molar mass of (NH4)3AsO4
A. 417.80 g/mol B. 193.03 g/mol C. 165.02 g/mol D. 250.02 g/mol
E. 365.52 g/mol
96. Calculate the molar mass of (NH4)2Ca
A. 76.00 g/mol B. 193.03 g/mol C. 165.02 g/mol D. 250.02 g/mol
E. 365.52 g/mol
97. Calculate the molar mass of K3PO4
A. 417.80 g/mol B. 212.00 g/mol C. 165.02 g/mol D. 250.02 g/mol
E. 365.52 g/mol
98. Calculate the molar mass of Ag3AsO4
A. 417.80 g/mol B. 463.03 g/mol C. 545.02 g/mol D. 250.02 g/mol
E. 365.52 g/mol
99. The empirical formula of a compound is CH2. If the molecular weight of the compound is 56, how many carbon atoms does a molecule contain?
A. 4 B. 1 C. 3 D. 5 E. 6
100. One mole of KClO3 decomposes to yield:
A. 1 mole of oxygen atoms B. 1.5 moles of O2 C. 2 moles of KCl
D. 2 moles of O2 E. 1 moles of KCl
101. A given liquid occupies 445 mL and weighs 540 g. The density of this liquid is (units missing):
A. 0.73 B. 0.85 C. 0.82 D. 0.65 E. 0.96
102. To what volume must you dilute 200 mL of a 6.00 M solution of NaCl to obtain a 0.3 M solution of NaCl?
A. 1.0 L B. 2.0 L C. 4.0 L D. 5.0 L E. 6.0 L
103. A compound is subjected to chemical analysis and you receive the following report from the analysis laboratory. Determine the simplest formula for the compound
% P = 31.6% O = 65.4% H=3.06.
A. PH3O4 B. P2H6O8 C. P2H O2 D. P3H6O8 E. P2 H3O8
104. How much iron can be made from 495 g of aluminum by the following process:
Fe2 O3 + 2 Al «Al2 O3 + 3 Fe
A. 495 g B. 1644 g C. 149 g D. 153 g E. 253 g
105. How many grams of water will be formed when a mixture containing 1.93 g C2 H4 and 5.92 g O2 is ignited in a closed vessel?
A. 2.22 g B. 5.89 g C. 10.21 g D. 15.3 g
E. 25.3 g
106. This balanced equation represents a chemical reaction: 2KClO3 (s) ® 2KCl(s) + 3O2 (g) How many moles of KCl are produced when 4.25 moles of KClO3 decompose?
A. 1.06 moles B. 2.57 moles C. 4.25 moles D. 8.50 moles E. 8.95 moles
107. Considering this balanced chemical equation, how many grams of HgO will be produced when 44 g of Hg react with excess O2? 2Hg (l) + O2 (g) → 2HgO (s)
A. 28 g B. 44 g C. 47 g D. 96 g E. 55 g
108. What is the molarity of 28.9 g of CaCl2 dissolved in water to make 0.78 L of solution?
A. 0.33 M B. 0.69 M C. 1.5 M D. 3.0 M E. 0.82 M
109. What is the molarity of 60 g of MgCl2 dissolved in water to make 2 L of solution?
A. 0.31 M B. 0.69 M C. 1.5 M D. 3.0 M E. 0.56 M
110. What is the molarity of a solution containing 9.478 grams of RuCl3 in enough water to make 1.00 L of solution?
А. 0.045 M В. 0.25 М С. 0.036 М D. 0.56 М E. 0.085 М
111. What is the molarity of a solution containing 5.035 grams of FeCl3 in enough water to make 500 mL of solution?
А. 0.036 М В. 0.062 M С. 0.085 М D. 0.027 М E. 0.046 М
112. What is the molarity of a solution containing 72.9 grams of HCl in enough water to make 500 mL of solution?
А. 5.0 М В. 6.0 М С. 4.0 M D. 3.0 M E. 2.0 M
113. What is the molarity of a solution containing 11.522 grams of KOH in enough water to make 350 mL of solution?
А. 0.362 М В. 0.586 M С. 0.256 М D. 0.158 М E. 0.615 М
114. What is the molarity of a solution containing 72.06 grams of BaCl2 in enough water to make 800 mL of solution?
А. 0.433 M В. 0.255 М С. 0,852 М D. 0,358 М e. 0,758 М
115. How many grams of NaCl are required to prepare 100 mL of a solution of 1 M NaCl?
A. 5.844 grams of NaCl B. 6.024 grams of NaCl C. 5.044 grams of NaCl
D. 2.585 grams of NaCl E. 3.086 grams of NaCl
116. How many grams of KMnO4 are required to prepare 1.0 L of a solution of 1.5 M KMnO4?
A. 237 grams of KMnO4 B. 452 grams of KMnO4 C. 156 grams of KMnO4
D. 325 grams of KMnO4 E. 758 grams of KMnO4
117. How many grams of HNO3 are required to prepare 500 mL of a 0.601 M HNO3 solution?
A. 12.92 grams of HNO3 B. 15.92 grams of HNO3 C. 18.92 grams of HNO3
D. 25.34 grams of HNO3 E. 16.58 grams of HNO3
118. What is the volume of a 0.1 M HCl solution containing 1.46 grams of HCl?
A. 0.200 L or 200 mL B. 0.400 L or 400 mL C. 0.600 L or 600 mL
D. 0.500 L or 500 mL E. 0.300 L or 300 mL
119. What is the volume of a 0.2 M AgNO3 solution containing 8.5 grams of AgNO3?
A. 0.15 L or 150 mL B. 0.35 L or 350 mL C. 0.25 L or 250 mL
D. 0.45 L or 150 mL E. 0.55 L or 350 mL
120. The correct relationship for the solubility of a gas in a liquid is:
A. solubility increases with increasing pressure and increasing temperature.
B. solubility increases with increasing pressure and decreasing temperature.
C. solubility increases with decreasing pressure and increasing temperature
D. solubility increases with decreasing pressure and decreasing temperature
B. solubility increases with decreasing volume and decreasing temperature
121. Bond in which one or more electrons from one atom are removed and attached to another atom, resulting in positive and negative ions which attract each other.
A. Covalent bond B. Ionic bond C. Metallic Bond D. Hydrogen Bond
E. Oxygen Bond
122. Bond in which one or more pairs of electrons are shared by two atoms.
A. Covalent bond B. Ionic bond C. Metallic Bond D. Hydrogen Bond
E. Oxygen Bond
123. When electrons are shared by two metallic atoms may be formed…
A. Covalent bond B. Ionic bond C. Metallic Bond D. Hydrogen Bond
E. Oxygen Bond
124. can exchange both matter and energy with an outside system
A. Open systems B.Closed systems
C. Isolated systems D. Standard system
E. Dynamic system
125. exchange energy but not matter with an outside system.
A. Open systems B. Closed systems C. Isolated systems
D. Standard system
E. Dynamic system
126. can exchange neither energy nor matter with an outside system
A. Open systems B. Closed systems C. Isolated systems
D. Standard system
E. Dynamic system
127. Thermodynamic Extensive Properties
A. volume B. Pressure C. Temperature D. Density E. Energy
128. It is not a thermodynamic Extensive Properties
A. volume B. Pressure C. Temperature D. Density E. energy
129. Energy and matter can be neither created nor destroyed; only transformed from one form to another.
A. The first law of thermodynamics. B. The second law of thermodynamics.
C. Hess’s Law D. Mendellev’s law E. Vant Goff’s law
130. If DG<0 (is negative)
A. the reaction is spontaneous B. the reaction is nonspontaneous
C. the reaction is at equilibrium D. Oxidation E. Reduction
131. If DG> 0 (is positive)
A. the reaction is spontaneous B. the reaction is nonspontaneous
C. the reaction is at equilibrium D. Oxidation E. Reduction
132. If DG =0
A. the reaction is spontaneous B. the reaction is nonspontaneous
C. the reaction is at equilibrium D. Oxidation E. Reduction
133. Which number gives the number of energy levels in a Bohr-Rutherford diagram of an atom?
A. Atomic mass number B.Atomic number C. Group number
D. Period number Е. None of the obove
134. What is the number of electrons in 1735 Cl-1?
A. 16 B. 17 C. 18 D. 34 E. 35
135. What are the forces between ionic molecules called?
A. Electrostatic B.Covalent C. Dipole-dipole D.Polar covalent
E. Ionic bond
136. Which atom has the largest electron affinity?
A.In B.Sb D. Rb E. Al
137. Which of the following elements has the smallest radius?
A. Rb B. Ba C. F D. Zn E. Li
138. Elements in the same family tend to be similar in which way?
A. Electron arrangements B. Numbers of electrons C. Atomic mass
D. Similar isotopes E. Both a and c are correct
139. Which of the following is a non-metal?
A. Ti B. Cu C. Sr D. Cl E. Fe
140. The elements in the periodic table are arranged according to?
A. Atomic mass B. Number of neutrons C.Reactivity D. Atomic number
E. Number of electrons
141. Which of the following elements is most reactive?
A. Mg B. Cl C. Br D. Kr E. S
142. Which of the following compounds has the most polar bond?
A. K2O B. SO2 C. CaO D. Li2O E. H2O
143. What is the correct formula of the ionic compound formed when calcium and nitrogen bond?
A. CaN B. Ca2N3 C. Ca3P D. CaP3 E. CaN2
144. What type of bond forms when there is only fluorine present?
A. Ionic B.Non-polar covalent C. Polar Covalent D. Covalent E. Metallic
145. What type of bond forms when barium and bromine react?
A. Ionic B. Non-polar covalent C. Polar Covalent D.Covalent E. Metallic
146. The correct Lewis Diagram for ammonia, NH3 will have _____ non bonding electrons on the central atom?
A. 0 B. 2 C. 4 D. 6 E. None of these
147. Which of the following compound has a cation (positive ion) and anion (negative ion) that is isoelectronic?
A. LiBr B. H2O2 CaO CaCl2 BeO
148 Elevation of boiling point of the solutions
A. PoA - PA/PoA = XB B. ΔTb = kbm C. π = nRT/V; π = CRT
D. pH=-log[H+] E. v=k[A]a[B]b
149. Calculate the mass percent of oxygen in C4H10O.
A. 18.57% B. 20.3% C. 50.3% D. 9.2% E. 15.2%
150. What is the mass percent of potassium in K3Fe(CN)6?
A. 66.62% B. 35.62% C. 26.25% D. 85.62% E. 29.25%





 -log[Ka] B.
-log[Ka] B.  A. 0.30 B. 0.90 C. 0.80 D. 3.3 E. 6.5
A. 0.30 B. 0.90 C. 0.80 D. 3.3 E. 6.5 bB «cC
bB «cC 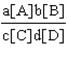 B.
B. 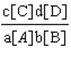 C.
C.  D.
D. 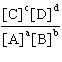
 cC
cC 

