
Definitions
Law – a summary of observed behaviors.
Hypothesis – a possible explanation of an observation or set of observations.
Theory – A set of tested hypothesis that gives an overall explanation of some natural phenomenon or phenomena
The Scientific Method
Information or data is gathered by careful observation of the phenomenon being studied.
On the basis of that information a preliminary generalization or hypothesis is formed.
A series of experiments is devised to test the predictive power of the hypothesis.
The Scientific Method (cont.)
On the basis of the experimental tests, the hypothesis may be
(a) Accepted as scientific theory.
(b) Modified so that all results are adequately explained.
(c) Discarded.
Components of the Scientific Method
Making Observations
Formulating Hypothesis
Extracting Predictions From the Hypothesis
Performing Experiments

The Modern Science Paradigm
Paths of Science
• Deduction - going from the general to the particular. An intermediate step,
simulation, is often taken. The "easy" way.
• Induction - going from the particular to the general. The "hard" way.
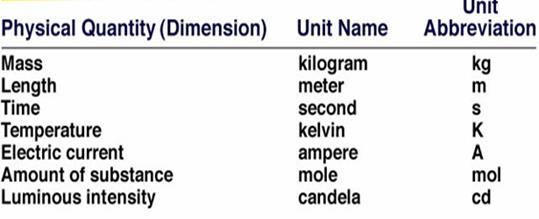
SI system of units Derived SI Units

Glossary
acid - a compound that, when dissolved in water, gives a pH of less than 7.0 or a compound that donates a hydrogen ion
anion - negatively charge ions
atom - a chemical element in its smallest form, and is made up of neutrons and protons within the nucleus and electrons circling the nucleus
atomic number - the number representing an element which corresponds with the number of protons within the nucleus
atomic orbital - the region where the electron of the atom may be found
base - a substance that accepts a proton and has a high pH; a common example is sodium hydroxide (NaOH)
boiling - the phase transition of liquid vaporizing
bond - the attraction and repulsion between atoms and molecules that is a cornerstone of chemistry
burette (also buret) - glassware used to dispense specific amounts of liquid when precision is necessary (e.g. titration and resource dependent reactions)
catalyst - a chemical compound used to change the rate (either to speed up or slow down) of a reaction, but is regenerated at the end of the reaction.
cation - positively charged ion
centrifuge - equipment used to separate substances based on density by rotating the tubes around a centred axis
cell potential - the force in a galvanic cell that pulls electron through reducing agent to oxidizing agent
chemical Law - certain rules that pertain to the laws of nature and chemistry – examples
chemical reaction - the change of one or more substances into another or multiple substances
colloid - mixture of evenly dispersed substances, such as many milks
compound - a substance that is made up of two or more chemically bonded elements
condensation - the phase change from gas to liquid
conductor - material that allows electric flow more freely
covalent bond - chemical bond that involves sharing electrons
crystal - a solid that is packed with ions, molecules or atoms in an orderly fashion
cuvette - glassware used in spectroscopic experiments. It is usually made of plastic, glass or quartz and should be as clean and clear as possible
dissolution or solvation - the spread of ions in a solvent
double bond - sharing of two pairs of electrons
earth metal - see alkaline earth metal
electrolyte - a solution that conducts a certain amount of current and can be split
electrochemical cell - using a chemical reaction's current, electromotive force is made
electron - a subatomic particle with a net charge that is negative
electron shells - an orbital around the atom's nucleus that has a fixed number electric charge - a measured property (coulombs) that determine electromagnetic interaction
element - an atom that is defined by its atomic number
energy - A system's ability to do work
enthalpy - measure of the total energy of a thermodynamic system (usually symbolized as H)
entropy - the amount of energy not available for work in a closed thermodynamic system (usually symbolized as S)
freezing - phase transition from liquid to solid
Faraday constant - a unit of electrical charge widely used in electrochemistry and equal to ~ 96,500 coulombs. It represents 1 mol of electrons, or the Avogadro number of electrons: 6.022 × 1023 electrons.
F = 96 485.339 9(24) C/mol
Faraday's law of electrolysis - a two part law that Michael Faraday published about electrolysis
galvanic cell - battery made up of electrochemical with two different metals connected by salt brid ge
gas - particles that fill their container though have no definite shape or volume
Gibbs energy - value that indicates the spontaneity of a reaction (usually symbolized as G)
halogens - Group 17 on the Periodic Table and are all non-metals
heat - energy transferred from one system to another by thermal interaction
jodium – Latin name of the halogen element iodine
indicator - a special compound added to solution that changes color depending on the acidity of th e solution; different indicators have different colors and effective pH ranges
inorganic compound - compounds that do not contain carbon, though there are exceptions (see main article)
inorganic chemistry - a part of chemistry concerned with inorganic compounds
ion - a molecule that has gained or lost one or more electrons
ionic bond - electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions
Kinetics - A sub-field of chemistry specializing in reaction rates
Kinetic energy - The energy of an object due to its motion.
lanthanides - Elements 57 through 71
lattice - Unique arrangement of atoms or molecules in a crystalline liquid or solid.
liquid - A state of matter which takes the shape of its container
Metal - Chemical element that is a good conductor of both electricity and heat and forms cations and ionic bonds with non-metals.
melting - The phase change from a solid to a liquid
metalloid - A substance possessing both the properties of metals and non-metals
microcentrifuge - a small plastic container that is used to store small amounts of liquid
mole - abbreviated mol - a measurement of an amount of substance; a single mole contains approximately 6.022×1023 units or entities
molecule - a chemically bonded number of atoms that are electrically neutral
molecular orbital - region where an electron can be found in a molecule (as opposed to an atom)
neutron - a neutral unit or subatomic particle that has no net charge
nucleus - the centre of an atom made up of neutrons and protons, with a net positive charge
noble gases - group 18 elements, those whose outer electron shell is filled
non-metal - an element which is not metallic
number density – a measure of concentration of countable objects (atoms, molecules, etc.) in space; number per volume
orbital - may refer to either an atomic orbital or a molecular orbital
organic compound - compounds that contain carbon
organic chemistry - a part of chemistry concerned with organic compounds
pH - the measure of acidity (or basicity) of a solution
poor metal - Metallic elements in the p-block, characterized by lower melting and boiling points than other metals
proton - a positive unit or subatomic particle that has a positive charge
protonation - the addition of a proton (H+) to an atom, molecule, or ion
s-block elements - Group 1 and 2 elements (alkali and alkaline metals), which includes Hydrogen and Helium
salts - ionic compounds composed of anions and cations
salt bridge - devices used to connection reduction with oxidation half-cells in an electrochemical cell
saline solution - general term for NaCl in water
single bond - sharing of one pair of electrons
solid - one of the states of matter, where the molecules are packed close together, there is a resistance of movement/deformation and volume change; see Young's modulus
solution - homogeneous mixture made up of multiple substances. It is made up of solutes and solvents.
solvent - the part of the solution that dissolves the solute (H2O in saline water)
spectroscopy - study of radiation and matter, such as X-ray absorption and emission spectroscopy
speed of light - the speed of anything that has zero rest mass (Energyrest = mc² where m is the mass and c is the speed of light)
Standard condit ions for temperature and pressure or SATP - a standardisation used in order compare experimental results (25 °C and 100.000 kPa)
state of matter - matter having a homogeneous, macroscopic phase; gas, plasma, liquid, and solid are the most well known (in increasing concentration)
subatomic particles - particles that are smaller than an atom; examples are protons, neutrons and electrons
substance - material with definite chemical composition
temperature - the average energy of microscopic motions of particles
theory - a model describing the nature of a phenomenon
thermochemistry - the study of absorption/release of heat within a chemical reaction
thermodynamics - the study of the effects of changing temperature, volume or pressure (or work, heat, and energy) on a macroscopic scale
thermodynamic stability - when a system is in its lowest energy state with its environment (equilibrium)
titration - the process of titrating one solution with another, also called volumetric analysis
Tyndall effect - the effect of light scattering by colloidal (mixture where one substance is dispersed evenly through another) or suspended particles
unit cell - the smallest repeating unit of a lattice
universal or ideal gas constant - proportionality constant in the ideal gas law (0.08206 L·atm/(K·mol))
valence electron - the outermost electrons of an atom, which are located in electron shells
Valence bond theory - a theory explaining the chemical bonding within molecules by discussing valencies, the number of chemical bonds formed by an atom
van der Waals force - one of the forces (attraction/repulsion) between molecules
vapor - when a substance is below the critical temperature while in the gas phase
vapour pressure - pressure of vapour over a liquid at equilibrium
water - H2O - a chemical substance, a major part of cells and Earth, and covalently bonded
work - the amount of force over distance and is in terms of joules (energy)
X-ray - form of ionizing, electromagnetic radiation, between gamma and UV rays
X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy - a spectroscopic technique to measure composition of a material
zone melting - a way to remove impurities from an element by melting it and slowly travel down an ingot (cast)
absolute zero - Absolute zero is 0K. It is the lowest possible temperature. Theoretically, at absolute zero, atoms stop moving.
accuracy - Accuracy is a measure of how close a measured value is to its true value. For example, if an object is exactly a meter long and you measure it as 1.1 meters long, that is more accurate than if you measured it at 1.5 meters long.
acid - There are several ways to define an acid, but they include any chemical that gives off protons or H+ in water. Acids have a pH less than 7. They turn the pH indicator phenophthalein colorless and turn litmus paper red.
acid anhydride - An acid anhydride is an oxide that forms an acid when it is reacted with water. For example, when SO3- is added to water, it becomes sulfuric acid, H2SO4.
actual yield - The actual yield is the amount of product you actually obtain from a chemical reaction, as in the amount you can measure or weigh as opposed to a calculated value.
addition reaction - An addition reaction is a chemical reaction in which atoms add to a carbon-carbon multiple bond.
alcohol - An alcohol is any organic molecule that has an -OH group.
aldehyde - An aldehyde is any organic molecule that has a -COH group.
alkali metal - An alkali metal is a metal in Group I of the periodic table. Examples of alkali metals include lithium, sodium, and potassium.
alkaline earth metal - An alkaline earth metal is an element belonging to Group II of the periodic table. Examples of alkaline earth metals are magnesium and calcium.
alkane - An alkane is an organic molecule that only contains single carbon-carbon bonds.
alkene - An alkene is an organic molecule that contains at least one C=C or carbon-carbon double bond.
alkyne - An alkyne is an organic molecule that contains at least one carbon-carbon triple bond.
allotrope - Allotropes are different forms of a phase of an element. For example, diamond and graphite are allotropes of carbon.
alpha particle - An alpha particle is another name for a helium nucleus, which contains two protons and two neutrons. It's called an alpha particle in reference to radioactive (alpha) decay.
amine - An amine is an organic molecule in which one or more of the hydrogen atoms in ammonia have been replaced by an organic group. An example of an amine is methylamine.
base - A base is a compound that produces OH- ions or electrons in water or that accepts protons. An example of a common base is sodium hydroxide, NaOH.
beta particle - A beta particle is an electron, although the term is used when the electron is emitted in radioactive decay.
binary compound - A binary compound is one made up of two elements.
binding energy - Binding energy is the energy that holds protons and neutrons together in the atomic nucleus.
bond energy - Bond energy is the amount of energy required to break one mole of chemical bonds.
bond length - Bond length is the average distance between the nuclei of two atoms that share a bond.
buffer - A liquid that resists change in pH when an acid or base is added. A buffer consists of a weak acid and its conjugate base. An example of a buffer is acetic acid and sodium acetate.
calorimetry - Calorimetry is the study of heat flow. Calorimetry may be used to find the heat of reaction of two compounds or the heat of combustion of a compound, for example.
carboxylic acid - A carboxylic acid is an organic molecule containing a -COOH group. An example of a carboxylic acid is acetic acid.
catalyst - A catalyst is a substance that lowers the activation energy of a reaction or speeds it up without being consumed by the reaction. Enzymes are proteins that act as catalysts for biochemical reactions.
cathode - A cathode is the electrode which gains electrons or is reduced. In other words, it is where reduction occurs in an electrochemical cell.
chemical equation - A chemical equation is a description of a chemical reaction, including what reacts, what is produced, and which direction(s) the reaction proceeds.
chemical property - A chemical property is a property that can only be observed when achemical change occurs. Flammability is an example of a chemical property, since you can't measure how flammable a substance is without igniting it (making/breaking chemical bonds).
covalent bond - A covalent bond is a chemical bond formed when two atoms share two electrons.
critical mass - Critical mass is the minimum quantity of radioactive material needed to cause a nuclear chain reaction.
critical point - The critical point is the endpoint of the liquid-vapor line in a phase diagram, past which a supercritical liquid forms. At the critical point, the liquid and vapor phases become indistinguishable from one another.
crystal - A crystal is an ordered, repeating three-dimensional pattern of ions, atoms, or molecules. Most crystals are ionic solids, although other forms of crystals exist.
delocalization - Delocalization is when electrons become free to move all over a molecule, such as when double bonds occur on adjacent atoms in a molecule.
denature - There are two common meanings for this in chemistry. First, it can refer to any process used to make ethanol unfit for consumption (denatured alcohol). Second, denaturing can mean breaking down the three-dimensional structure of a molecule, such as a protein is denatured when exposed to heat.
diffusion - Diffusion is the movement of particles from an area of higher concentration to one of lower concentration.
dilution - Dilution is when solvent is added to a solution, making it less concentrated.
dissociation - Dissociation is when a chemical reaction breaks a compound into two or more parts. For example, NaCl dissociates into Na+ and Cl- in water.
double displacement reaction - A double displacement or double replacement reaction is when cations of two compounds switch places.
effusion - Effusion is when a gas moves through an opening into a low pressure container (e.g., is drawn by a vacuum). Effusion occurs more quickly than diffusion because additional molecules aren't in the way.
electrolysis - Electrolysis is using electricity to break the bonds in a compound to break it apart.
electrolyte - An electrolyte is an ionic compound that dissolves in water to produce ions, which can conduct electricity. Strong electrolytes completely dissociate in water, while weak electrolytes only partially dissociate or break apart in water.
enantiomers - Enantiomers are molecules that are nonsuperimposable mirror images of each other.
endothermic - Endothermic describes a process that absorbs heat. Endothermic reactions feel cold.
energy level - An energy level is a possible value of energy that an electron can have in an atom.
enthalpy - Enthalpy is a measure of the amount of energy in a system.
entropy - Entropy is a measure of the disorder or randomness in a system.
Kelvin - Kelvin is a unit of temperature. A Kelvin is equal in size to a degree Celsius, although Kelvin starts from absolute zero. Add 273.15 to a Celsius temperature to get the Kelvin value. Kelvin is not reported with a ° symbol. For example, you would simply write 300K not 300°K.
ketone - A ketone is a molecule that contains a R-CO-R' functional group. An example of a common ketone is acetone (dimethyl ketone).
kinetic energy - Kinetic energy is energy of motion. The more an object moves, the more kinetic energy it has.
lanthanide contraction - The lanthanide contraction refers to the trend in which lanthanideatoms become smaller as you move left to right across the periodic table, even though they increase in atomic number.
lattice energy - Lattice energy is the amount of energy released when one mole of a crystal forms from its gaseous ions.
law of conservation of energy - The law of conservation of energy states the energy of the universe may change form, but its amount remains unchanged.
ligand - A ligand is a molecule or ion stuck to the central atom in a complex. Examples of common ligands include water, carbon monoxide, and ammonia.
mass - Mass is the amount of matter in a substance. It is commonly reported in units of grams.
mole - Avogadro's number (6.02 x 1023) of anything.
node - A node is a location in an orbital with no probability of containing an electron.
nucleon - A nucleon is a particle in the nucleus of an atom (proton or neutron).
oxidation number The oxidation number is the apparent charge on an atom. For example, the oxidation number of an oxygen atom is -2.
period - A period is a row (left to right) of the periodic table.
precision - Precision is how repeatable a measurement is. More precise measurements are reported with more significant figures.
pressure - Pressure is force per area.
product - A product is something made as a result of a chemical reaction.
quantum theory - Quantum theory is the description of energy levels and the predictions about the behavior of atoms at specific energy levels.
radioactivity - Radioactivity occurs when the atomic nucleus is unstable and breaks apart, releasing energy or radiation.
Raoult's Law - Raoult's Law states that the vapor pressure of a solution is directly proportional to the mole fraction of solvent.
rate determining step - The rate determining step is the slowest step in any chemical reaction.
rate law - A rate law is a mathematical expression relating the speed of a chemical reaction as a function of concentration.
redox reaction - A redox reaction is a chemical reaction that involves oxidation and reduction.
resonance structure - Resonance structures are the set of Lewis structures that can be drawn for a molecule when it has delocalized electrons.
reversible reaction - A reversible reaction is a chemical reaction which can go both ways: reactants make products and products make reactants.
RMS velocity - The RMS or root mean square velocity is the square root of the average of the squares of individual velocities of gas particles, which is a way of describing the average speed of gas particles.
salt - An ionic compound formed from reacting an acid and a base.
solute - The solute is the substance that gets dissolved in a solvent. Usually it refers to a solid that is dissolved in a liquid. If you are mixing two liquids, the solvent is the one that is present in a smaller amount.
solvent - This is the liquid that dissolves a solute in solution. Technically, you can dissolve gases into liquids or into other gases, too. When making a solution where both substances are in the same phase (e.g., liquid-liquid), the solvent is the largest component of the solution.
STP - STP means standard temperature and pressure, which is 273K and 1 atmosphere.
strong acid - A strong acid is an acid that completely dissociates in water. An example of a strong acid is hydrochloric acid, HCl, which dissociates into H+ and Cl- in water.
strong nuclear force - The strong nuclear force is the force that holds the protons and neutrons in an atomic nucleus together.
sublimation - Sublimation is when a solid changes directly into a gas. At atmospheric pressure, dry ice or solid carbon dioxide goes directly into carbon dioxide vapor, never becoming liquid carbon dioxide.
synthesis - Synthesis is making a larger molecule from two or more atoms or smaller molecules.
system - A system includes everything you are evaluating in a situation.
temperature - Temperature is a measure of the average kinetic energy of particles.
theoretical yield - Theoretical yield is the amount of product which would result if a chemical reaction proceeded perfectly, to completion, with no loss.
thermodynamics - Thermodynamics is the study of energy.
titration - Titration is a procedure in which the concentration of an acid or base is determined by measuring how much base or acid is required to neutralize it.
triple point - The triple point is the temperature and pressure at which the solid, liquid, and vapor phases of a substance exist in equilibrium.
unit cell - A unit cell is the simplest repeating structure of a crystal.
unsaturated - There are two common meanings for unsaturated in chemistry. The first refers to a chemical solution that does not contain all of the solute that can be dissolved in it. Unsaturated also refers to an organic compound which contains one or more double or triple carbon-carbon bonds.
unshared electron pair - An unshared electron pair or lone pair refers to two electrons that aren't participating in chemical bonding.
valence electron - The valence electrons are the atom's outermost electrons.
volatile - Volatile refers to a substance that has a high vapor pressure.
VSEPR - VSEPR stands for Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion. This is a theory used that predicts molecular shapes based on the assumption that electrons stay as far as possible from each other.
Chemistry Lab Safety
The chemistry laboratory can be a place of discovery and learning. However, by the very nature of laboratory work, it can be a place of danger if proper common-sense precautions aren't taken. You are expected to learn and adhere to the following general safety guidelines to ensure a safe laboratory environment for both yourself and the people you may be working near. Additional safety precautions will be announced in class prior to experiments where a potential danger exists.
Conduct
· Eating, drinking, and smoking are strictly prohibited in the laboratory.
· No unauthorized experiments are to be performed. If you are curious about trying a procedure not covered in the experimental procedure, consult with your laboratory instructor.
· Never taste anything. Never directly smell the source of any vapor or gas; instead by means of your cupped hand, waft a small sample to your nose. Do not inhale these vapors but take in only enough to detect an odor if one exists.
· Always wash your hands before leaving lab.
· Learn where the safety and first-aid equipment is located. This includes fire extinguishers, fire blankets, and eye-wash stations.
· Notify the instructor immediately in case of an accident.













