|
| Annealing involves heating a material
| a
| and before the appearance of new strain-free grains.
|
|
| In the cases of copper, steel, silver, and brass, this process
| b
| such as shaping, stamping, or forming.
|
|
| In steel, there is a decarburation mechanism that can be described
| c
| and eradicating the dislocations in metals and (to a lesser extent) in ceramics.
|
|
| The metal is softened and prepared for further work
| d
| is performed by heating the material for a while and then slowly letting it cool to room temperature in still air.
|
|
| The movement of atoms has the effect of redistributing and
| e
| that proceed as the temperature of the material is increased are: recovery, recrystallization, and grain growth.
|
|
| The three stages of the annealing process
| f
| to above its recrystallization temperature, maintaining a suitable temperature, and then cooling.
|
|
| Recovery occurs at the lower temperature stage of all annealing processes
| g
| as three distinct events: the reaction at the steel surface, the interstitial diffusion of carbon atoms and the dissolution of carbides within the steel.
|
6. Read text C. Answer the questions:
1) What is annealing?
2) What stages does the process of annealing include?
3) How is the process of annealing performed in the cases of copper, silver and brass?
4) Is the relief of internal stress a thermodynamically spontaneous process?
5) How many stages are there in a decarburation mechanism? What are they?
6) What is recovery? When does it occur?
7) What stage does the grain growth take place at?
8) What atmosphere is the annealing carried out in?
7. What do you know about:
1) Gibbs free energy;
2) the Arrhenius equation;
3) Fick’s laws of diffusion.
Can you explain these laws?
8. Fill in the correct word from the list: martensite, shape, coarse grains, annealing, composition, quenching, properties of metals.
Heat treatment such as 1) ____, tempering, or 2) ___ controls the nature of the grains and their size in the metal. Small amounts of other metals (less than 1 per cent) are often added to a pure metal. This is called alloying (легирование) and it changes the grain structure and 3) ____.Tempering reduces the hardness in the 4) ____ by transforming it into various forms of tempered martensite. The properties of the metals depend on the size, 5) ____, orientation, and 6) ___ of these grains. In general, a metal with small grains will be harder and stronger than one with 7) ____.
9. a) Open the brackets. Pay attention to the use of the Present Simple Tense (Active and Passive Voices).
b) Translate the text in writing. Use a dictionary if necessary.
Typically, large oven (to use) for the annealing process. The inside of the oven (to be) large enough to place the workpiece in a position to receive maximum exposure to the circulating heated air. For high volume process annealing, gas fired conveyor furnaces (to use). For large workpieces or high quantity parts, car-bottom furnaces are used so workers can easily move the parts in and out.
Once the annealing process successfully (to complete), workpieces sometimes (to leave) in the oven so the parts cool in a controllable way. While some workpieces are left in the oven to cool in a controlled fashion, other materials and alloys (to remove) from the oven. Once removed from the oven, the workpieces often quickly (to cool) off in a process known as quench hardening.
Typical methods of quench hardening materials (to involve) media such as air, water, oil, or salt. Salt (to use) as a medium for quenching usually in the form of brine (salt water). Brine (to provide) faster cooling rates than water. This is because when an object (to quench) in water air bubbles form on the surface of the object reducing the surface area the water is in contact with. The salt in the brine (to reduce) the formation of air bubbles on the object's surface, meaning there is a larger surface area of the object in contact with the water, providing faster cooling rates. Quench hardening (to be) generally applicable to some ferrous alloys, but not copper alloys.
Part IV
Learn the words.
| bainite
| бейнит
|
| casting
| литье, заливка (металла)
|
| cold-rolled steel
| холоднокатаная сталь
|
| cooling rate
| скорость охлаждения; скорость остывания
|
| critical temperature
| критическая температура
|
| dendritic segregation
| дендритная (внутрикристаллитная) ликвация (разделение по крупности)
|
| dimensional
| пространственный, размерный
|
| equilibrium
| равновесие
|
| ferrous alloy
| сплав на железной основе
|
| in-process annealing
| промежуточный отжиг
|
| intermediate annealing
| промежуточный отжиг
|
| machinability
| обрабатываемость (резанием)
|
| normalization
| нормализация
|
| process annealing
| промежуточный отжиг
|
| soaking
| выдержка (при определенной температуре)
|
| subcritical annealing
| отжиг при температуре ниже критической
|
| the temperature range
| температурный интервал; предел изменения температуры
|
| ultimate strength
| предел прочности
|
| upper critical point
| верхний предел критической точки
|
| wire-drawn steel
| сталь для холоднотянутой проволоки
|
2. Translate the following groups of terms (use a dictionary if necessary):
1) grain, austenitic grains, ferritic grains, columnar grains, fine-grained structure, austenite-cementite grain structure;
2) steel, carbon steel, low-carbon steel, normalized steel, pearlitic steel, wire-drawn steel, cold-rolled steel, old-worked steel;
3) temperature, the temperature range, tempering temperature, the lower critical temperature, austenitic temperature;
4) strength, tensile strength, maximum strength, yield strength, ultimate strength
3. Translate the following terms with the suffixes –able (-ible):
controllable properties, obtainable hardness value, hardenable steels,detectable defects, hardenable alloys, considerable improvement, visible cracks.
4. Read text D and answer the question: What annealing processes are mentioned in the text?
Text D.
Annealing
(continued)
Normalization is an annealing process applied to ferrous alloys to give the material a uniform fine-grained structure and make it less brittle. It involves heating the steel to 20-50°C above its upper critical point, soaking it for a short period at that temperature and then allowing it to cool in air. Heating the steel just above its upper critical point creates austenitic grains (much smaller than the previous ferritic grains), which during cooling, form new ferritic grains with a further refined grain size. The process produces a tougher, more ductile material, and eliminates columnar grains and dendritic segregation that sometimes occurs during casting. 1) ___________________________________________.
Process annealing, also called intermediate annealing, subcritical annealing, or in-process annealing, is a heat treatment cycle that restores some of the ductility to a product being cold-worked so it can be cold-worked further without breaking.
The temperature range for process annealing ranges from 260 °C (500 °F) to 760 °C (1400 °F), depending on the alloy in question. 2) __________________________________. The material is heated up to a temperature just below the lower critical temperature of steel. Cold-worked steel normally tends to possess increased hardness and decreased ductility, making it difficult to work. Process annealing tends to improve these characteristics. This is mainly carried out on cold-rolled steel like wire-drawn steel
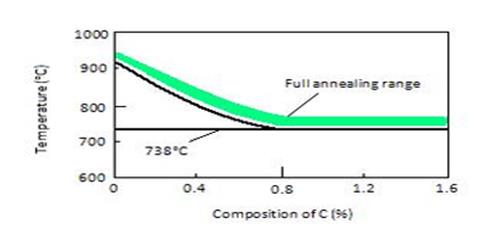
Full annealing temperature ranges
A full anneal typically results in the second most ductile state a metal can assume for metal alloy. Its purpose is to originate a uniform and stable microstructure that most closely resembles the metal's phase diagram equilibrium microstructure, thus letting the metal attain relatively low levels of hardness, yield strength and ultimate strength with high plasticity and toughness. 3) ___________________________________. The material is then allowed to cool very slowly so that the equilibrium microstructure is obtained. In most cases this means the material is allowed to furnace cool (the furnace is turned off and the steel is let cool down inside) but in some cases it's air cooled. The cooling rate of the steel has to be sufficiently slow so as to not let the austenite transform into bainite or martensite, but rather have it completely transform to pearlite and ferrite or cementite. This means that steels that are very hardenable (i.e. tend to form martensite under moderately low cooling rates) have to be furnace cooled. The details of the process depend on the type of metal and the precise alloy involved. 4) _____________________. The process is also called LP annealing for lamellar pearlite in the steel industry as opposed to a process anneal, which does not specify a microstructure and only has the goal of softening the material. Often the material to be machined is annealed, and then subject to further heat treatment to achieve the final desired properties.
5. Look through the text and find English equivalents to the following Russian terms:
предел прочности, аустенитное зерно, ферритное зерно, термическая обработка, предел текучести, низкоуглеродистая сталь, нормализация, обрабатываемость, критическая температура, карбид железа, прочность, степень охлаждения, пластичность, печь (топка), упрочняемый (в процессе обработки).









