What does the Maxwell–Boltzmann distribution law state?
What is called the Arrhenius equation?
Which factors may determine the rate of phase change?
Do any difficulties occur with the process of nucleation and growth transformation?
8. Read text B and choose the best title for it:
Nucleation in solids.
The strain energy and surface energy.
3. The energy of a semi-coherent interface.
Make sure that you know the following words and word combinations:
Dimensional changes - мерные изменения
The rigidity of the surrounding matrix - жесткость окружающей матрицы
Elastic strains - эластичные деформации
High-angle grain boundary - высокоугловая граница зерен
Text B
When the transformation takes place in the solid state, i.e. between two solid phases, a second factor giving rise to hysteresis operates. The new phase usually has a different parameter and crystal structure from the old so that the transformation is accompanied by dimensional changes. However, the changes in volume and shape cannot occur freely because of the rigidity of the surrounding matrix, and elastic strains are induced. The strain energy and surface energy created by the nuclei of the new phase are positive contributions to the free energy and so tend to oppose the transition.
The total free energy change is 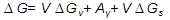 (3.17) where A is the area of interface between the two phases and
(3.17) where A is the area of interface between the two phases and 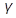 the interfacial energy per unit area, and
the interfacial energy per unit area, and 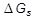 is the misfit strain energy per unit volume of new phase.
is the misfit strain energy per unit volume of new phase.
For a spherical nucleus of the second phase 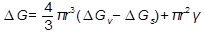 (3.18) and the misfit strain energy reduces the effective driving force for the transformation. Differentiation of equation (3.18) gives
(3.18) and the misfit strain energy reduces the effective driving force for the transformation. Differentiation of equation (3.18) gives 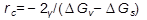 , and
, and 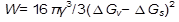 . The value of γ can vary widely from a few mJ/
. The value of γ can vary widely from a few mJ/  to several hundred mJ/
to several hundred mJ/  depending on the coherency of the interface. A coherent interface is formed when the two crystals have a good ‘match’ and the two lattices are continuous across the interface. This happens when the interfacial plane has the same atomic configuration in both phases, e.g.
depending on the coherency of the interface. A coherent interface is formed when the two crystals have a good ‘match’ and the two lattices are continuous across the interface. This happens when the interfacial plane has the same atomic configuration in both phases, e.g. 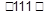 in fcc and
in fcc and 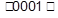 in cph. When the ‘match’ at the interface is not perfect it is still possible to maintain coherency by straining one or both lattices.
in cph. When the ‘match’ at the interface is not perfect it is still possible to maintain coherency by straining one or both lattices.
These coherency strains increase the energy and for large misfits it becomes energetically more favourable to form a semi-coherent interface in which the mismatch is periodically taken up by misfit dislocations. The coherency strains can then be relieved by a cross grid of dislocations in the interface plane, the spacing of which depends on the Burgers vector b of the dislocation and the misfit ε, i.e. b/ε. The interfacial energy for semi-coherent interfaces arises from the change in composition across the interface or chemical contribution as for fully-coherent interfaces, plus the energy of the dislocations. The energy of a semi-coherent interface is 200–500 mJ/ 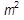 and increases with decreasing dislocation spacing until the dislocation strain fields overlap. When this occurs, the discrete nature of the dislocations is lost and the interface becomes incoherent. The incoherent interface is somewhat similar to a high-angle grain boundary with its energy of 0.5 to 1 J/
and increases with decreasing dislocation spacing until the dislocation strain fields overlap. When this occurs, the discrete nature of the dislocations is lost and the interface becomes incoherent. The incoherent interface is somewhat similar to a high-angle grain boundary with its energy of 0.5 to 1 J/ 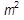 relatively independent of the orientation.
relatively independent of the orientation.
SECTION III
SECTION IV



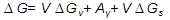 (3.17) where A is the area of interface between the two phases and
(3.17) where A is the area of interface between the two phases and 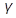 the interfacial energy per unit area, and
the interfacial energy per unit area, and 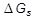 is the misfit strain energy per unit volume of new phase.
is the misfit strain energy per unit volume of new phase.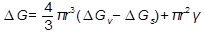 (3.18) and the misfit strain energy reduces the effective driving force for the transformation. Differentiation of equation (3.18) gives
(3.18) and the misfit strain energy reduces the effective driving force for the transformation. Differentiation of equation (3.18) gives 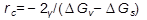 , and
, and 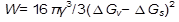 . The value of γ can vary widely from a few mJ/
. The value of γ can vary widely from a few mJ/ 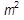 to several hundred mJ/
to several hundred mJ/  in fcc and
in fcc and 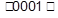 in cph. When the ‘match’ at the interface is not perfect it is still possible to maintain coherency by straining one or both lattices.
in cph. When the ‘match’ at the interface is not perfect it is still possible to maintain coherency by straining one or both lattices.


