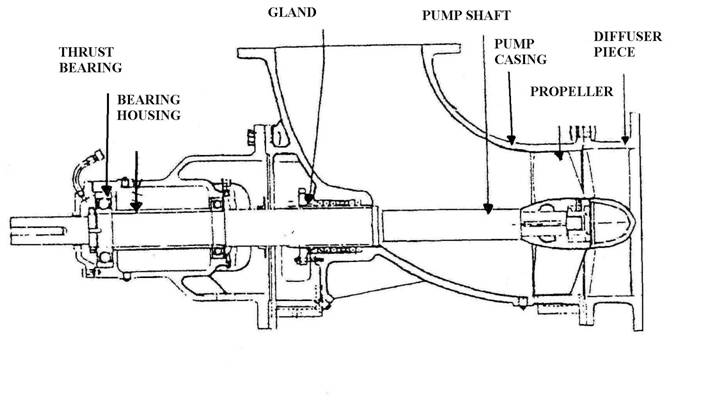
An axial flow pump usually consists of an impeller with a few number of vanes, typically only three or four vanes. The vanes are oriented in such a way that the pumped fluid exits axially (i.e., in the same direction as the shaft), rather than radially (90 degrees from the shaft). The impeller is normally driven by an electric motor. The axial orientation of the impeller vanes produces very low head as the liquid is pumped.
An axial flow pump may generate only 10 to 20 feet of head, much lower than most other types of centrifugal pumps. Axial flow pumps are sometimes called propeller pumps, because the axial flow impeller looks similar to a boat propeller. Some types of axial flow pumps can have their flow and head adjusted by altering the pitch of the impeller vanes.
What is a gear pump?
Gear pumps are considered rotary positive displacement pumps. Gear pump are most common type of positive displacement pump. Like all positive displacement pumps, gear pumps are fixed displacement pumps, meaning that an unchanging volume of liquid moves through at a constant rate provided the pump speed is constant.
How do gear pumps work?
A gear pump uses a rotating set of gears. The moving gears create suction at the inlet port of the pump that draws the fluid into the gears. The rotating gears then move the liquid between the teeth of the gears and the walls of the casing and direct the fluid flow to the discharge port, where the pressure continues to build as the volume of the casing gets smaller near the outlet of the pump. There are two main types of gear pumps. Both consist of a drive gear (the gear that pushes) and an idler (the gear that is pushed).
What is a Piston Pump?
A piston pump is a type of reciprocating pump, which is one of the two major types of positive displacement pump. The piston pump moves and pressurizes fluid using one or more reciprocating pistons, which are normally driven by an electric motor through a crankshaft and connecting rod.
How do Piston Pumps work?
Like most types of positive displacement pumps, piston pumps use the force of the pumping mechanism to expand and contract an internal movable volume of liquid. The power to drive the piston is supplied by an electric motor, internal-combustion engine, or other power source - although more primitive piston pumps may be driven by hand, wind, or flowing water.
The motion behind the piston is usually rotational. Piston pumps can be single acting or double acting. Double acting piston pumps have pumped fluid on both sides of the piston, and two sets of check valves, one on each side of the piston. While the piston is in-taking on one side, it is exhausting on the other. Thus, each time the piston moves in one direction from one end to the other, a full pumping cycle (intake and discharge) has been completed. For single acting piston pumps, the piston must move in both directions to complete a full pumping cycle.
What is a screw pump?
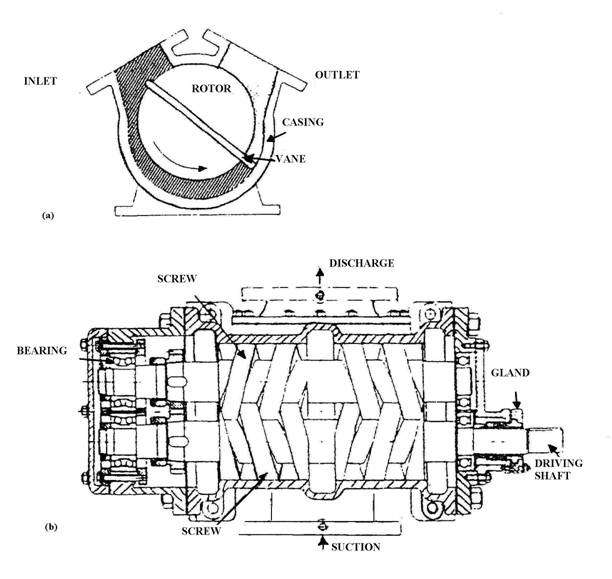
A screw pump is a positive displacement pump that uses two or more intermeshing screws to pressurize fluids in order to pump them in a system. Screw pumps are a type of rotary pump, meaning that they use rotary motion to create a vacuum that draws fluid into the pumping chamber. The meshing screws then push the liquid out the other side with increased pressure.
How do screw pumps work?
There are two major types of screw pumps: two-screw or double screw pumps, and triple screw pumps. Double screw pumps have two intermeshing screws. However, with a double screw pump, one screw cannot drive the other one. So the double screw pump is normally equipped with a set of timing gears, located outside the pumping chamber, and lubricated with clean oil, to ensure that the two screws are rotating correctly relative to each other. With this arrangement, the two screws are not required to be in direct contact with each other. Triple screw pumps have one driving screw intermeshed with two driven screws. This pump type has the screws making contact with each other, so this pump type is limited to cleaner liquids.
What is a vane pump?
A vane pump is a type of positive displacement pump that uses the back and forth movement of rectangle shaped vanes inside slots to move fluids.
How do vane pumps work?
A vane pump includes a cylindrically-shaped rotor turning about its centerline inside of an asymmetrically- shaped casing. The cylindrical rotor has a number of rectangle shaped slots running linearly along the outside of the cylinder. As the cylindrical rotor turns, centrifugal force causes the vanes to move outward, such that the outer edge of the vane stays in touch with the inside surface of the asymmetrically-shaped casing. Like many rotary pumps, the direction of flow can be reversed by reversing the direction of rotation of the pump.
Figures of:
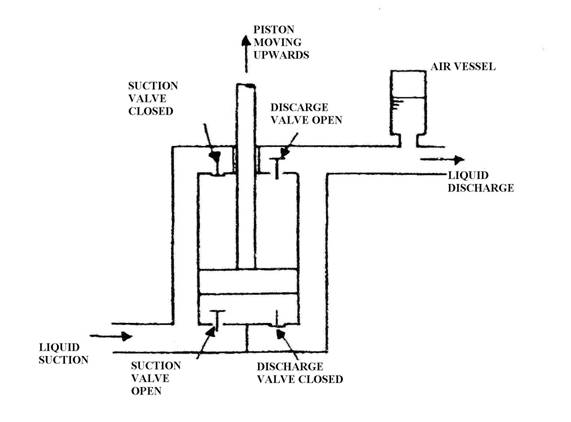
Diagrammatic reciprocating displacement pump
Rotary displacement pumps: (a) rotary vane displacement pump, (b) screw displacement pump.
Axial-flow pump
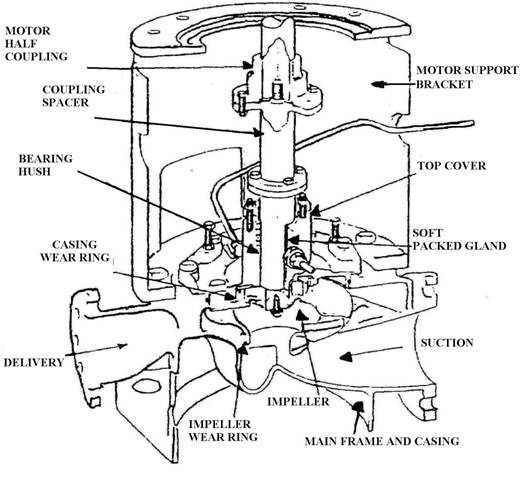
Centrifugal pump operation
Single-entry centrifugal pump

Double-entry centrifugal pump
UNIT ONE. AUXILIARIES
WORDS AND EXPRESSIONS
| auxiliaries
heat exchanger
distillation equipment
bilge water
sewage treatment plant
incinerator
to range
multi-stage
crank
second stage piston assembly
first stage cooler tubes
first stage drain
second stage drain
steady reading
moisture
to clear
reciprocating machinery
troublesome
rapid
to reface
incorrect
dirt
to stick
to pit
to strip
to lap
reassembly
seal
| вспомогательные двигатели
теплообменник
опреснительное оборудование
льяльные воды, сточные воды
установка для обработки сточно-фекальных
вод
инсинератор
колебаться (от)
многоступенчатый
кривошип
поршневой блок второй ступени
охладитель первой ступени
клапан продувания первой ступени
клапан продувания второй ступени
устойчивое показание (прибора)
влага
очищать
поршневые механизмы
причиняющий беспокойство
быстрый
зд: восстанавливать поверхность (притиранием)
неправильный зд: нерекомендованный
грязь
зд: заклинивать
подвергаться язвенной коррозии
разбирать
шлифовать
повторная сборка
герметичность
|
TEXT
Machinery other than the main propulsion unit is usually called auxiliary. These include the following: air compressors, heat exch angers, distillation equipment, oil / bilge water separators, sewage treatment plants and incinerators.
AIR COMPRESSOR
Compressed air has many uses on board ship ranging from diesel engine starting to the cleaning of machinery during maintenance. The air pressures of 25 bar or more are usually provided in multi-stage machines. Here the air is compressed in the first stage, cooled and compressed to a higher pressure in the next stage and so on. The most common is two-stage crank machine.

(Figure 4.1 Two-stage compressor, p.)
STARTING
The compressor motor is started. The lube oil pressure should reach the correct value. The first stage drains and then the second stage drains are closed and the machine will begin to operate. The pressure gauge cocks should be adjusted to give a steady reading. Where manual drains are fitted they should be slightly opened to discharge any moisture which may collect in the coolers. The cooling water supply should be checked as well as operating temperatures.
STOPPING
To stop the compressor the first and second-stage cooler drain valves should be opened and the machine run unloaded for 2 or 3 minutes which will clear the coolers of condensate. The compressor can now be stopped and the drains should be left open.