Serological markers of HIV were detected in 239 people, which was 11.02% (β = 0.95; (9.74%; 12.42%)) of the total sample. Note that 69.45% (β = 0.95; (63.19%; 75.23%)) of patients with identified HIV markers were young people aged 20 to 39 years. HIV RNA was detected in 58 people, which accounted for 24.27% (β = 0.95 (18.97% ; 30.21%)of patients in the seropositive group (2.68% of the total group).
HIV Diversity and Drug Resistance
The HIV pol-gene of all patients with detectable VL was sequenced and submit in GenBank (MT874291-MT874321, MT874310-MT874321, MT919401-MT919427). The analysis made it possible to identify the following ratio of HIV-1 subtypes. The circulating recombinant form (CRF) 02_AG (56.90 % (β = 0.95; (43.23%; 69.84%))) prevails in the study group compared to HIV A3 (13.79% (β = 0.95; (6.15%; 25.38%))); G identified in one case (8.62 % (β = 0.95; (2.86%; 18.98%))); URF between A1 and G (1.72 %; (β = 0.95; (0.04%; 9.24%))); A1 (12.07 %; (β = 0.95; (4.99%; 23.30%))); A6 (1.72 %; (β = 0.95; (0.04%; 9.24%))); CRF_06cpx (5.17 %; (β = 0.95; (1,08%; 14,38%))) (fig 2). Можно тоже график сделать
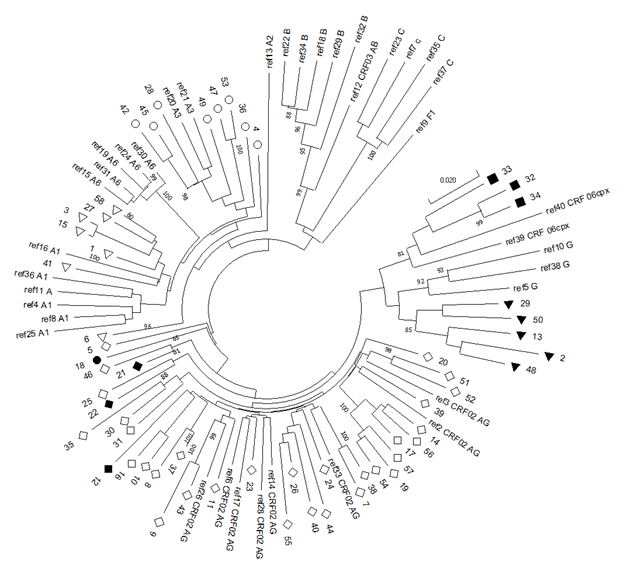
Fig 2. Phylogenetic inference of HIV-1 protease and partial reverse transcriptase sequences from antiretroviral-naïve patients. 1 - 58 is samples; ref 1 - 40 is references sequences from GenBank (Table 2). ◊ - CRF 02AG; ▼ – G; ○ – A3; ■ – CRF 06cpx; ♦ - Recombinant G/A1; ▽ – A1.
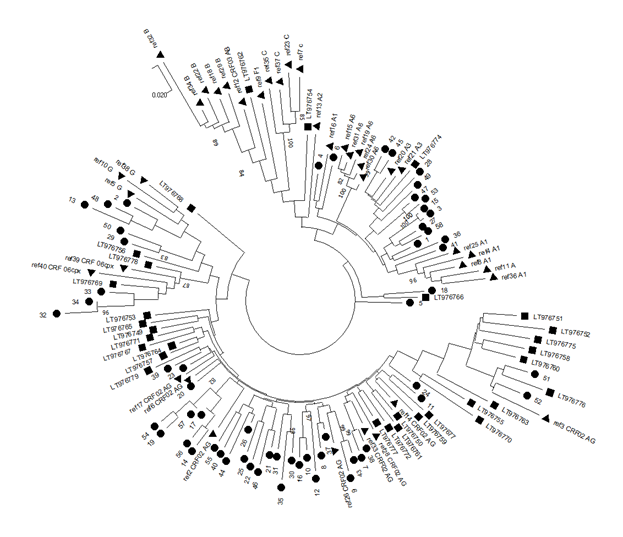
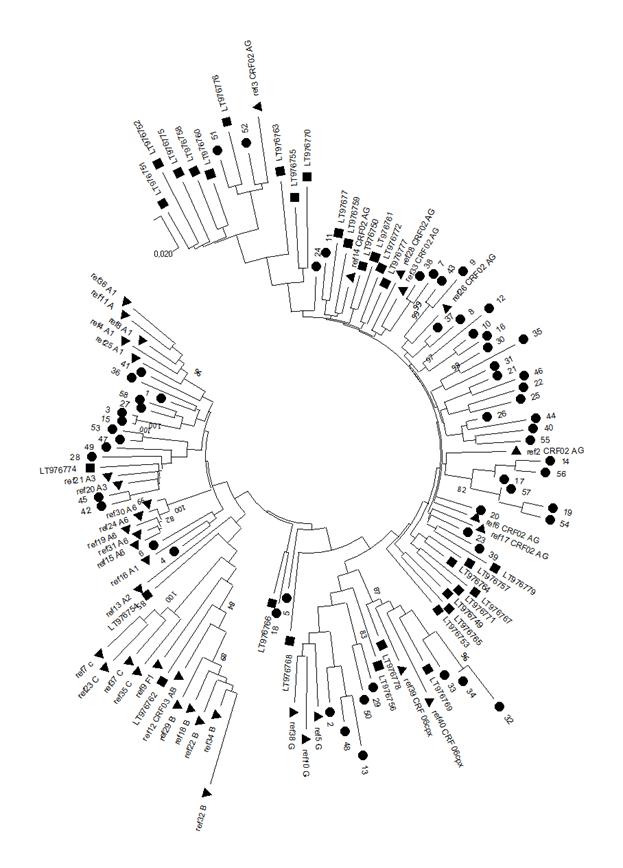
Рисунки с нашими и не нашими образцами. Нужно выбрать какой-то один. Во втором варианте 5 образец более удачно разместился и не выглядит отщепенцем, но на первом в целом субтипы друг относительно друга более удачно расположены.
According to the results of the analysis, 25% of patients had at least one significant mutation leading directly to drug resistance of HIV for their virus subtype. The mutations encountered cause resistance to nucleoside and non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors. In one case, several mutations were encountered simultaneously, causing resistance to drugs of both classes. Among them is the K65R mutation, which causes resistance to most NRTIs, together with the S68G mutation, which partially restores the replication defect associated with K65R [9]. No major mutations of resistance to protease inhibitors were found.
Table 1. The incidence of mutations associated with drug resistance HIV in the study group
| Mutation
| Number of patients
| Percentage in the group
| Confidence interval
(Clopper-Pirson)
|
| K20I
| 39
| 67.24 %
| 53,66% - 78,99%
|
| L10I/V
| 17
| 29.31 %
| 18,09% - 42,73%
|
| V179I
| 11
| 18.96 %
| 9,87% - 31,41%
|
| S68G
| 6
| 10.34 %
| 3,89% - 21,17%
|
| V106I
| 3
| 5.17 %
| 1,08% - 14,38%
|
| K20V
| 2
| 3.45 %
| 0,42% - 11,91%
|
| N88NH
| 2
| 3.45 %
| 0,42% - 11,91%
|
| M41ML
| 2
| 3.45 %
| 0,42% - 11,91%
|
| K103N
| 2
| 3.45 %
| 0,42% - 11,91%
|
| E138EQ
| 2
| 3.45 %
| 0,42% - 11,91%
|
| K238R
| 2
| 3.45 %
| 0,42% - 11,91%
|
| L10LF
| 1
| 1.72 %
| 0,04% - 9,24%
|
| K20R
| 1
| 1.72 %
| 0,04% - 9,24%
|
| M46M_M
| 1
| 1.72 %
| 0,04% - 9,24%
|
| A62AV
| 1
| 1.72 %
| 0,04% - 9,24%
|
| K65R(S68G)
| 1
| 1.72 %
| 0,04% - 9,24%
|
| K103E/Q
| 1
| 1.72 %
| 0,04% - 9,24%
|
| V108I
| 1
| 1.72 %
| 0,04% - 9,24%
|
| E138A
| 1
| 1.72 %
| 0,04% - 9,24%
|
| V179T
| 1
| 1.72 %
| 0,04% - 9,24%
|
| Y181Deletion
| 1
| 1.72 %
| 0,04% - 9,24%
|
| T74S
| 1
| 1.72 %
| 0,04% - 9,24%
|
| K238E
| 1
| 1.72 %
| 0,04% - 9,24%
|
| K238T
| 1
| 1.72 %
| 0,04% - 9,24%
|
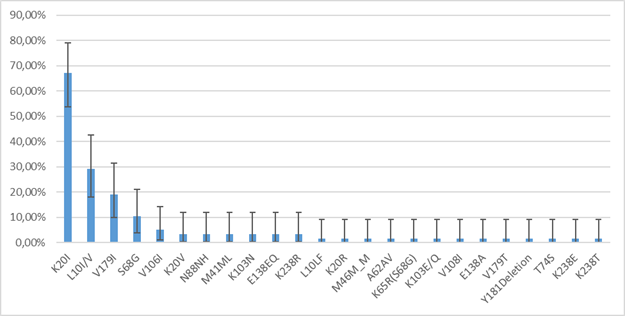
Fig. 4 The incidence of mutations associated with drug resistance HIV in the study group
Discussion
There is a significant discrepancy between the number of HIV-positive people identified using ELISA and those who are found to have viral RNA. Moreover, the percentage of people in whom the virus was detected by the PCR method correlates with the literature data on the prevalence of HIV infection in the Republic of Guinea. However, the significant percentage of apparently healthy people who are HIV seropositive suggests that the incidence of HIV may be higher than the literature suggests. However, to confirm this, additional screening studies with a confirmatory test are necessary.
Выявленное генетическое разнообразие соотносится с литературными сведениями о субсубтипах ВИЧ, циркулирующих в Западной Африке и высоким генетическим разнообразием ВИЧ в Африке в целом. В подавляющем большинстве случаев встречается циркулирующая рекомбинантная форма 02_AG. При этом особое внимание необходимо уделить изолятам, генотипирование которых показывает не столь однозначные результаты. Для создания более полной картины мы дополнительно провели филогенетический анализ совместно с изолятами, полученными в исследовании 2016 года. На обоих филогенетических древах выделился образец 18, субтипированный в REGA 3.0 как рекомбинант генотипов A1 и G, но не принадлежащий к CRF02_AG. Интересно отметить, что он образует кластер с изолятом, депонированным под номером LT976766, который в работе 2016 года отнесен к CRF02_AG, что можно объяснить нехваткой информации о последовательности гена протеазы у данного образца. Важно отметить, что образцы 44 и 46, определенных в REGA 3.0 как неизвестные рекомбинантные формы, в обоих филогенетических древах наиболее близко кластеризуются с CRF02_AG. Следует отметить, что образцы 44, 46 и 13, согласно результатам анализа в REGA HIV-1, также являются рекомбинантами между известным CRF_02AG и подтипом A1 (рис. 4).
Исходя из результатов проведенного анализа, мы предполагаем значительный вклад различных рекомбинантных форм ВИЧ в генетическое разнообразие вируса в исследуемом регионе. В связи с этим крайне важным является изучение полных геномов ВИЧ в Гвинейской республике для выявления всех имеющихся в данном регионе рекомбинантных форм и наиболее встречающихся точек рекомбинации.
Genetic diversity of HIV in the surveyed group correlates with what is usually observed in West African countries - in the vast majority of cases, CRF_02AG is found. However, other recombinant forms circulate simultaneously with it. Samples 18, 44, and 46 deserve special attention; they separated from the main branch CRF_02AG on the phylogenetic tree. Analysis of their nucleotide sequence using the REGA HIV-1 subtyping tool showed that these samples are recombinants of genotypes A1 and G, but do not belong to CRF02_AG (Fig 3). Interestingly, sample 13 is also a recombinant of genotypes A1 and G but does not belong to CRF02_AG, although it is located on the CRF02_AG branch. It should be noted that samples 44, 46, and 13, according to the results of the analysis in REGA HIV-1, are also recombinants between the known CRF_02AG and subtype A1 (fig 4).
For some samples, subtyping is difficult. Since in the framework of this study only the region of the pol gene was studied, it is impossible to explore the points of recombination outside the studied fragment. However, the discrepancy between the results of genotyping using the REGA 3.0 tool and our own phylogenetic analysis raises suspicions of a greater part of recombinant forms of the virus to the genetic diversity of HIV in the Republic of Guinea.
Since accurate genotyping is critical to screening a sample for resistant HIV variants, more research is needed to assess the contribution of recombinant forms to the genetic diversity of the virus in the region. Insufficient attention to the high diversity of HIV recombinants and the lack of complete data on common points of recombination can lead to an erroneous determination of the presence or absence of the virus DR.
The incidence of mutations associated with HIV resistance to ARVs was relatively high. Given the increasing number of patients who start taking ART, the high incidence of primary drug resistance can lead to frequent cases of therapy failure and, as a result, change of treatment regimens. To prescribe effective treatment regimens, it is necessary to introduce studies on the presence of primary resistance in newly diagnosed patients.
A similar high incidence of drug resistance mutations in untreated infected individuals has been shown in Sierra Leone, which is associated with disruptions to HIV services during the Ebola epidemic in 2014-2016 since the study was conducted in a close geographic region (Liberia) before the epidemic showed a significantly lower incidence of such cases [10].
Выявленные у наивных пациентов 24 мутации на более обширной выборке, скорее всего, имели бы приблизительно равные частоты встречаемости, что ожидаемо, так как в исследуемой группе отсутствует давление на вирус антиретровирусными препаратами, и мутации спонтанно возникают и исчезают в поколениях вируса.
It is interesting to note that in more than half of the cases (72 %) there were substitutions in the twentieth position. Можно заметить, что из этих мутаций наиболее выделяется K20I - is a polymorphic variant for subtypes CRF_02AG and G, but reduces sensitivity to nelfinavir in subtypes B and C. However, there is evidence that this mutation may enhance viral replication in non-B subtypes [11]. Данная мутация имеет встречаемость значительно более высокую, чем все остальные (67.24 % (β = 0.95, (53,66%; 78,99%)) несмотря на отсутствие факторов отбора в виде АРВТ, что может быть следствием преимущества, получаемого носителями данной мутации.
A non-polymorphic variant of K20V has also been identified, which is rare, and its effect on HIV susceptibility to ARVs is poorly understood. Also, two mutations in the tenth position were identified, one of which, detected in one case, L10LF, is a minor mutation of resistance to PI, and the other, found in 29.03% of cases, L10I, increases the replication of viruses with other resistance mutations to SP [12]. Two rare mutations were identified: M46M_M and N88NH, in the positions of which resistance mutations to protease inhibitors are found, however, these variants have not been described among them.
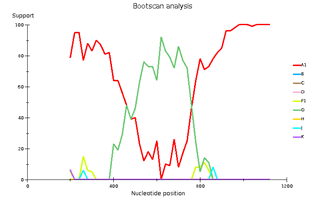
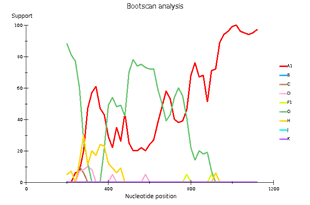
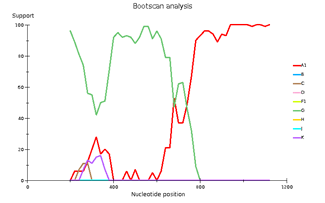
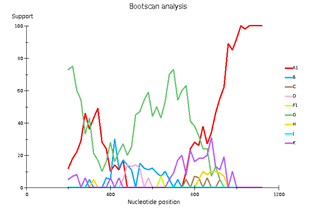
Fig 3. Subtype recombination analysis with REGA HIV-1 Subtyping Tool 3.0. Bootscan analysis performed with window size 400 and step size 20.
A – sample 18; B – sample 44; C – sample 46; D – sample 13.
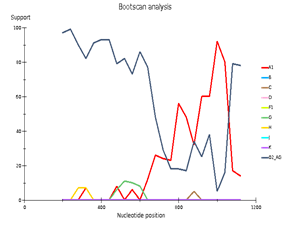
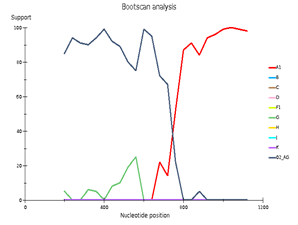
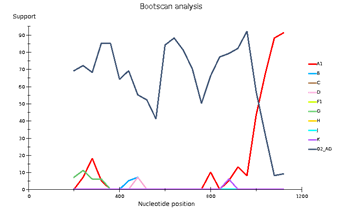
Fig 4. CRF/Subtype Recombination Analysis with REGA HIV-1 Subtyping Tool 3.0. Bootscan analysis performed with window size 400 and step size 40.
A – sample 44; B – sample 46; C – sample 13
Among the mutations associated with HIV resistance to non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors, a relatively rare non-polymorphic V179T mutation has been shown, which is sometimes selected in patients receiving NNRTIs. This is due to the minimal decrease in the sensitivity of etravirine and rilpivirine [13, 14]. Several substitutions were also encountered in position 238: K238T, which reduces the susceptibility to nevirapine and efavirenz by about 5 times; K238R, which is a common polymorphism that does not reduce susceptibility to NNRTIs [15]; K238E is a rare mutation in this position, the effect of which is not well described in the literature.
Выявленные мутации, ассоциированные с лекарственной устойчивостью, как возникающие спонтанно, так и вследствие передачи от пациентов с вирусологической неэффективностью, могут активно распространяться среди новых пациентов, вследствие низкой информированности населения о ВИЧ-инфекции, труднодоступности медицинской помощи и средств контрацепции. Следствием низкой информированности о гемоконтактных инфекциях может быть повышен травматический риск передачи вируса, возможность которого показана в различных исследованиях (ссылка на нас и еще-кого-нибудь желательно)
В заключение необходимо отметить, что даже совместный анализ данных, полученных в ходе данного исследования и в работе 2016 года, недостаточен для того, чтобы в полной мере изучить генетическое разнообразие ВИЧ в Гвинейской республике. Необходимы более подробные исследования на больших выборках для того, чтобы сделать заключение о генетической структуре вируса на территории со столь сложной эпидемиологической ситуацией.
Table 2. Complete name of samples and reference sequences in phylogenetic tree (fig. 2)

















