Checking of skin color
Cyanotic skin is a common sign of heart disease. In patients with circulatory disorders, cyanosis is more pronounced in parts of the body that are farther remoted from the heart, i.e. the fingers and toes, the tip of the nose, the lips, and the ear lobes. This phenomenon is known as acrocyanosis. It depends on the increased content of reduced hemoglobin in the venous blood because of excessive oxygen absorption by tissues in slow blood circulation. In other cases, cyanosis becomes central in conditions of oxygen hunger of blood due to its insufficient arterialization in the pulmonary bed. The degree of cyanosis varies from a slightly detectable blue tinge to a dark blue color. Cyanosis is especially pronounced in patients with congenital heart diseases and arteriovenous shunting. It should be remembered that cyanosis can arise in poisoning by chemicals or drugs that form methemoglobin and sulphmethemoglobin.
The color of the skin is important for the diagnosis of some heart diseases. Mitral stenosis can be diagnosed by the violet-red color of the patient's cheeks, mildly cyanotic color of the lips, nose, and extremities ("facies mitralis"). The skin and visible mucosa of patients with aortal heart diseases are usually pale. Cyanosis in combination with paleness (pallid cyanosis) is characteristic of stenosis of the orifice of the pulmonary trunk or thrombosis of the pulmonary artery. The icteric color of the sclera and skin is characteristic of grave circulatory insufficiency. The skin of patients with persisting septic endocarditis has a peculiar color resembling that of coffee with milk (color " coffee with milk ").

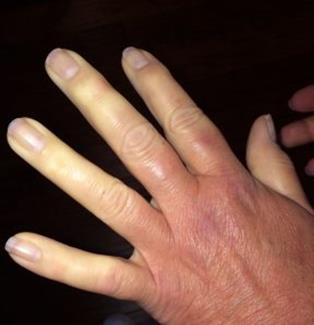
Picture 1. Examples of skin discoloration. Acrocyanosis (left), whitening of fingers (right)
The shape of the nails and distal phalanges of the fingers is informative. Drum-stick (Hippocratic) fingers are characteristic of subacute septic endocarditis and some congenital heart diseases.
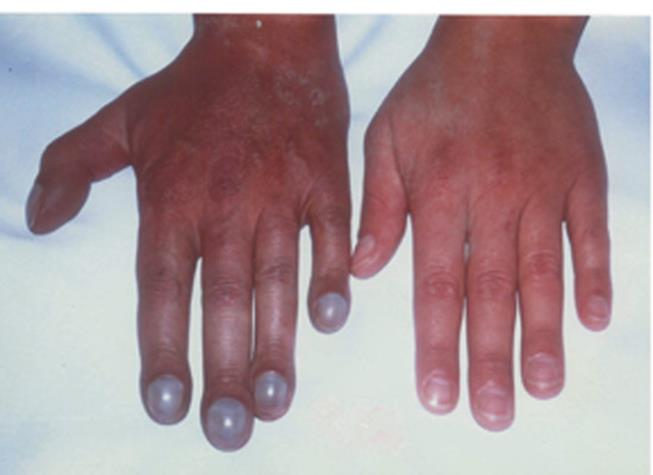
Picture 2. Drum-stick (Hippocratic) fingers
Palpation of arterial pulse
Palpation of arterial pulse Palpation of the arterial pulse is the main method of examination of pulse. As a rule, the pulse is studied first on the radial artery, since it is superficial and runs immediately under the skin and can thus be readily felt between the styloid process of the radial bone and the tendon of the internal radial muscle.
Palpation of the arterial wall allows define the following properties of pulse:
-similarity (uniformity) of pulse on both arms;
- rhythm of pulse, frequency (pulse rate),
- condition of the vascular wall,
- filling (volume) of pulse,
- strain (pressure) of pulse,
- size of pulse,
- deficiency of pulse.
After the definition of similarity (uniformity) of pulse on both hands, a physician determines the rhythmicity of pulse. For definition of rhythmicity of pulse 2, 3, 4 fingers (Pict. 3) of a palpating arm are positioned on a radial artery and the big finger on a forward surface of a forearm from the backside. If pulsations follow one after another through identical intervals pulse is rhythmical (pulsus regularis, s. rhythmicus). When the cardiac rhythm is upset, pulse waves follow at irregular intervals (pulsus irregularis, s. arrhythmicus).
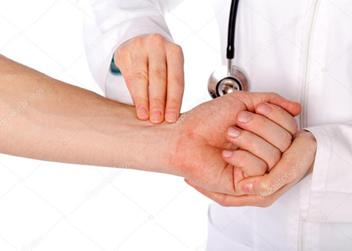
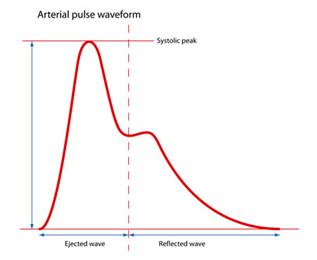
Picture 3. Pulse determination technique (left) and pulse wave formation diagram (right)
Some pulse waves may be missing or they may appear prematurely, which is characteristic of extrasystole and also complete arrhythmia (fibrillation), in which pulse waves follow one another at irregular intervals. In normal conditions, the pulse is rhythmic and the pulse wave uniform. Such a pulse is called uniform (pulsus equalis). In cardiac rhythm disorders, when the heart contracts at irregular intervals, the pulse wave becomes nonuniform, and this pulse is called unequal (pulsus inequalis).
For definition of pulse rate a physician puts three fingers of a palpating arm (2-, 3-d, 4-th) on radial arteria and counts the number of pulse strokes for 15 s or 30 s and received number multiply accordingly on 4 or 2 (at rhythmical pulse). At arrhythmic pulse rate is counted inventory within 1 minute. A normal frequency of pulse rate is 60-90 in 1 minute. A pulse rate of more than 90 for a 1-minute pulse refers to a frequent pulse (pulsus frequens). Decrease of a pulse rate less than 60 for 1 minute refers to infrequent pulse (pulsus rarus).
The condition of the vascular wall should be assessed simultaneously. A normal artery is a thin elastic tube. In norm, an arterial wall is mild, elastic, smooth, and flat. In some diseases, for example, in atherosclerosis, the arteries change, their walls become firm, and the course more tortuous. If calcification is considerable, the artery walls are rough, tortuous tubes, sometimes with bead-like thickenings.
For definition filling (volume) of pulse three fingers of a palpating arm (the 2-, 3-d, 4-th) are placed on a. radialis. In the beginning, the 2-nd finger squeezes a. radialis up to the arrest of a reversed current of blood from vessels of a hand, and then the 4-th finger squeezes out blood from the vessel and squeezes it up to the arrest of transit of pulse wave. The 3-rd finger freely lies on an empty arteria. The 4-th finger is raised with a pulse wave. Pulse wave passing under the 3-rd finger raises it and hits about the 2-nd finger. The filling of a pulse is estimated on a degree of arising of the 3-rd finger.
A normal pulse is of satisfactory filling. It is a distinguished pulse of the good filling - complete pulse (рulsus plenus), and bad filling - empty pulse (рulsus vacuus). Complete pulse may be in sportsmen during sports meets, at exercise stresses. Pulse volume shows the artery filling with blood, which in turn depends on the amount of blood that is ejected during systole into the arterial system and which produces variations in the artery volume. Pulse volume depends on the stroke volume, on the total amount of circulating blood, and its distribution in the body. If the stroke volume is normal and the artery is sufficiently filled with blood, the pulse is said to be full (pulsus plenus). In abnormal circulation and blood loss, the pulse volume decreases (pulsus vacuus).
The strain of pulse, or pulse pressure, is determined by the force that should be applied to the pulsating artery to compress it completely. For definition of the strain of pulse the 2-, 3-d, and 4-th fingers of a palpating arm squeeze an artery up to the arrest in its pulsations. This property of pulse depends on the magnitude of the systolic arterial pressure. If arterial pressure is normal, the artery can be compressed by moderate pressure. A normal pulse is therefore of moderate tension or satisfactory strain. The higher the pressure, the more difficult it is to compress the artery; such a pulse is called pulsus durus (hard or high-tension pulse). If the arterial pressure is small, the artery is easy to compress, and the pulse is soft (pulsus mollis).
Pulse size. The pulse size implies its filling and tension. It depends on the expansion of the artery during systole and its collapse during diastole. These in turn depend on the pulse volume, fluctuation of the arterial pressure during both systole and diastole, and distensibility of the arterial wall. Pulse wave increases with increasing stroke volume, great fluctuations in the arterial pressure, and also with decreasing tone of the arterial wall. This pulse is called high pulse (pulsus altus) or pulsus magnus. Large-volume or high pulse is characteristic of aortic valve incompetence in thyrotoxicosis when the pulse wave increases due to the high difference between systolic and diastolic arterial pressure. Such a pulse may develop in fever in connection with a decreased tone of the arterial wall. Pulse wave decreases with decreasing stroke volume and amplitude of pressure fluctuations during systole and diastole and with an increasing tone of the arterial wall. The pulse becomes a small pulse (pulsus parvus). Pulse is small when the amount of blood discharged into the arterial system is small, and the rate of its discharge is low. This is observed in stenosis of the aortic orifice or of the left venous orifice, and also in tachycardia and acute cardiac failure. The pulse wave may be quite insignificant (barely perceptible) in shock, acute cardiac failure and massive loss of blood. This pulse is called thready pulse (pulsus filiformis). In rare cases (in rhythmic pulse), high and low pulse waves are alternating. This is alternating pulse (pulsus alternans). It is believed that this 62 pulse is due to alternation of heart contractions that vary in force. It usually occurs in severe myocardial affection.
Deficiency of pulse is disharmony between a heart rate and a number of pulse waves on the periphery. Deficiency of pulse is defined by a palpatory auscultative method. For deficiency of pulse, the heart rate does not correspond with the pulse rate on the radial artery. There are two methods for the definition of deficiency of pulse:
1. It is performed by one physician. The doctor simultaneously positions the bell of the stethoscope on the point of an apex beat for counting of heart rate, and other loose arms - on the radial artery for scoring the pulse rate during 1 minute.
2. It is performed by two physicians. In this case, the first physician listens to the heart and counts heart rate within 1 minute, and the second physician counts the pulse rate on the radial artery during the same time. Then among the number of cardiac beats is subtracted the pulse rate and received the deficiency of pulse. The presence of a deficiency of pulse is typical in atrial fibrillation.
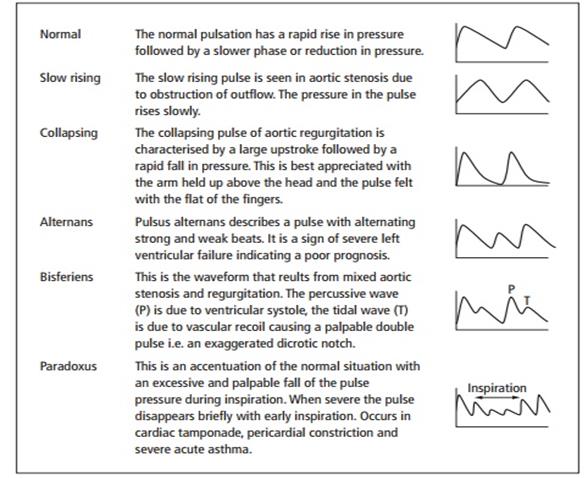
Picture 4. Arterial pulse waveforms












