

Археология об основании Рима: Новые раскопки проясняют и такой острый дискуссионный вопрос, как дата самого возникновения Рима...

Общие условия выбора системы дренажа: Система дренажа выбирается в зависимости от характера защищаемого...

Археология об основании Рима: Новые раскопки проясняют и такой острый дискуссионный вопрос, как дата самого возникновения Рима...

Общие условия выбора системы дренажа: Система дренажа выбирается в зависимости от характера защищаемого...
Топ:
Выпускная квалификационная работа: Основная часть ВКР, как правило, состоит из двух-трех глав, каждая из которых, в свою очередь...
Характеристика АТП и сварочно-жестяницкого участка: Транспорт в настоящее время является одной из важнейших отраслей народного...
Интересное:
Наиболее распространенные виды рака: Раковая опухоль — это самостоятельное новообразование, которое может возникнуть и от повышенного давления...
Принципы управления денежными потоками: одним из методов контроля за состоянием денежной наличности является...
Финансовый рынок и его значение в управлении денежными потоками на современном этапе: любому предприятию для расширения производства и увеличения прибыли нужны...
Дисциплины:
|
из
5.00
|
Заказать работу |
|
|
|
|


| A. Ariane 5 is a European expendable launch system designed to deliver payloads into geostationary transfer orbit or low Earth orbit. It is manufactured under the authority of the European Space Agency (ESA) and the Centre National d'Etudes Spatiales (CNES), with Astrium Space Transportation as prime contractor, leading a consortium of sub-contractors. The rocket is operated and marketed by Arianespace as part of the Ariane program. Astrium Space Transportation builds the rockets in Europe and Arianespace launches them from the Guiana Space Centre (For more details: Text 1A [1]). It succeeded Ariane 4, but does not derive from it directly. Its development took 10 years and cost?7 billion. Ariane 5 ECA (For more details: Text 1A [2]) is aimed to launch the manned mini shuttle Hermes, and thus intended it to be "human rated" from the beginning. After ESA cancelled Hermes, the rocket became a purely robotic launcher. Two satellites can be mounted using a SYLDA (For more details: Text 1A[3]) carrier. Three main satellites are possible depending on size. Up to eight secondary payloads, usually small experiment packages or minisatellites, can be carried with an ASAP platform (Ariane Structure for Auxiliary Payloads). Ariane 5’s cryogenic main stage is called the EPC "Etage Principal Cryotechnique" (Cryotechnic Main Stage). It consists of a large tank 30.5 metres high with two compartments, one for 130 tonnes of liquid oxygen and one for 25 tonnes of liquid hydrogen, and a Vulcain engine (For more details: Text 1A [4]) at the base with thrust of 115 tonnes-force (1.13 meganewtons). This part of the first stage weighs about 15 tonnes when empty. Attached to the sides are two solid propellant boosters, each weighing about 277 tonnes full. Each delivers thrust of about 630 tonnes-force (6.2 MN). These boosters can be recovered with parachutes, like the Space Shuttle Solid Rocket Boosters. They may have been retrieved for examination on early missions, but are not reused. |
| The second stage is on top of the main stage and below the payload. The Ariane 5G used the Storable Propellant Stage, which is fueled by monomethylhydrazine (MMH) and nitrogen tetroxide, where as the Ariane 5 ECA uses the ESC (Etage Superieur Cryotechnique/Cryogenic Upper Stage), which is fueled by liquid hydrogen and liquid oxygen. The payload and all upper stages are covered at launch by the fairing (For more details: Text 1A [5]), which splits off once sufficient altitude has been reached. (2142 charcaters) Translate using a dictionary B. The Ariane 5 Launch vehicle provides standard interfaces that fit all spacecraft buses and allow an easy switch between the launch vehicles of the European Transportation Fleet. The spacecraft is mated to the L\V through a dedicated structure called an adaptor that provides mechanical interface, electrical harnesses routing and systems to ensure the spacecraft separation. The electrical interface provides communication with the launch vehicle and the ground support equipment during all phases of spacecraft preparation, launch and flight. For a spacecraft in single launch, one of the available fairing designs protects the spacecraft mounted on top of an adaptor which can be a standard Ariane or Customer’s design. For dual launch two configurations are available with the two carrying structures SPELTRA and SYLDA 5. The difference lies in the fact that SYLDA is totally protected by the fairing while the SPELTRA is an external carrying structure. (813 characters) |  SPELTRA
SPELTRA
 SYLDA 5
SYLDA 5
|
Word-combinations
|
|
| 1. To deliver a thrust | развивать тягу |
| 2. Standard interfaces | стандартные поверхности контактов |
| 3. Spacecraft buses | платформы космических аппаратов |
| 4. Electrical harnesses routing | маршрутизация бортовой кабельной системы |
| 5. The ground support equipment | наземная служба сопровождения |
| 6. The launch facilities | стартовое оборудование |
| 7. Solid strap-on boosters | боковые отделяемые ускорители |
| 8. Dual launch systems | двухплатформенная выводящая система |
| 9. An increased payload carrying capacity | увеличенная грузоподъемность |
| 10. To perform a wide range of missions | выполнять широкий спектр запусков |
| 11. The cryogenic core stage | центральная ступень с низкокипящим топливом |
Exercise 6. Complete the sentences and make a review of Ariane 5 program:
| 1. Ariane 5 was designed … | a. a decade and cost 7 billion |
| 2. The rocket is operated and marketed … | b. the Guiana Space Centre |
| 3. It is launched from … | c. a SYLDA carrier |
| 4. Its development took … | d. EPC (Cryotechnic Main Stage) |
| 5. From the beginning it was planned to launch … | e. can be recovered with parachutes |
| 6. Two satellites can be mounted using … | f. liquid oxygen and hydrogen |
| 7. The main stage is called … | g. Arianespace |
| 8. A large tank accommodates … | h. thrust of 1.13 meganewtons |
| 9. A Vulcan engine delivers … | i. to deliver payload into GTO |
| 10. Two solid propellant boosters … | j. the mini shuttle Hermes |
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
Exercise 7. Give complete answers to the following questions (text 3A).
| 1. What is the Ariane 5 designed for? | a. by the fairing |
| 2. What authority is the Ariane 5 manufactured under? | b. two large satellites or eight minisatellites |
| 3. What Agency is the rocket operated and marketed? | c. after mini Shuttle Hermes program was cancelled. |
| 4. What pad is the Ariane 5 launched from? | d. to deliver payloads into GTO |
| 5. Does the Ariane 5 resemble much the Ariane 4? | e. the European Space Agency and the Centre National d’Etudes Spatiales |
| 6. When did the Ariane 5 become a purely robotic launcher? | f. like the Space Shuttle Solid Rocket Boosters |
| 7. What payloads can be carried with an ASAP platform (Ariane Structure for Auxiliary Payloads)? | g. monomethylhydrazine (MMH) and nitrogen tetroxide |
| 8. What does the Cryotechnic Main stage consist of? | h. the Guiana Space Centre, Cape Kourou |
| 9. What is the second stage fueled by | i. a large tank with two compartments (liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen) and engine |
| 10. What are the payload and upper stages protected by at launch? | j. is not derived from it directly |
| k. its development took a decade | |
| l. the Arianespace |
|
|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
Exercise 8. Match the right and left items.
| 1. To deliver a thrust | a. маршрутизация бортовой кабельной системы |
| 2. Standard interfaces | b. центральная ступень с низкокипящим топливом |
| 3. Spacecraft buses | c. выполнять широкий спектр запусков |
| 4. Electrical harnesses routing | d. наземная служба сопровождения |
| 5. The ground support equipment | e. стандартные поверхности контактов |
| 6. Solid strap-on boosters | f. увеличенная грузоподъемность |
| 7. Dual launch systems | g. двухплатформенная выводящая система |
| 8. An increased payload carrying capacity | h. развивать тягу |
| 9. To perform a wide range of missions | i. боковые отделяемые ускорители |
| 10. The cryogenic core stage | e. платформы космических аппаратов |
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
Supplementary Texts
Text 1A[1]. European Spaceport and CSG Facilities
The launch preparation and launch are carried out from the Guiana Space Centre (GSC) — European spaceport operational since 1968 in French Guiana. The spaceport accommodates Ariane 5, Soyuz and Vega separated launch facilities.
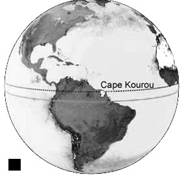 The GSC provides state-of — the-art Payload Preparation Facilities. The facilities are capable to process several satellites of different customers in the same time. The satellite/launch vehicle integration and launch are carried out from launch sites dedicated for Ariane, Soyuz or Vega.
The GSC provides state-of — the-art Payload Preparation Facilities. The facilities are capable to process several satellites of different customers in the same time. The satellite/launch vehicle integration and launch are carried out from launch sites dedicated for Ariane, Soyuz or Vega.
The Ariane 5 Launch Site is located approximately 15 km to the North-West of the CSG Technical Center (near Kourou). The moderate climate, the regular air and sea connection, accessible local transportation, and excellent accommodation facilities as for business and for recreation — all that devoted to Customer’s team and invest to the success of the launch mission.
Kourou lies at latitude 5°3', just over 500 km north of the equator. Its nearness to the equator makes it ideally placed for launches into geostationary transfer orbit as few changes have to be made to a satellite’s trajectory.
(986 characters)
Text 1A [2]. Ariane versions
 The Ariane 5 ECA is the latest – and most powerful member – of the Ariane 5 family, with a hefty payload lift capacity of 9,600 kg. to geostationary transfer orbit (GTO).
The Ariane 5 ECA is the latest – and most powerful member – of the Ariane 5 family, with a hefty payload lift capacity of 9,600 kg. to geostationary transfer orbit (GTO).
This performance ensures that Ariane 5 will be able to loft the heaviest telecom satellites and enables Arianespace to match up most spacecraft for highly efficient dual launches.
Ariane 5 ECA is a follow-on to the highly mature Ariane 5 Generic launcher version, which carries 6,700-kg. payloads to GTO and has demonstrated its reliability in 16 successful missions.
With the Ariane 5 ECA, Arianespace is able to offer customers even greater performance, flexibility and competitiveness to meet the satellite telecommunications industry demands.
(604 characters)
Text 1A [3]. Ariane 5 Payloads: Internal Structure for Dual Launches
 The SYLDA 5 structure is housed inside Ariane 5's payload fairing, and allows the vehicle to carry two primary payloads on a single flight. The mission's "lower" satellite is carried inside the SYLDA 5 structure, while the "upper" payload is mounted atop it. SYLDA 5 has a useful interior diameter of 4 meters, and exists in 6 versions to accommodate satellites in the lower position with a maximum height of 2.9 to 4.4 meters.
The SYLDA 5 structure is housed inside Ariane 5's payload fairing, and allows the vehicle to carry two primary payloads on a single flight. The mission's "lower" satellite is carried inside the SYLDA 5 structure, while the "upper" payload is mounted atop it. SYLDA 5 has a useful interior diameter of 4 meters, and exists in 6 versions to accommodate satellites in the lower position with a maximum height of 2.9 to 4.4 meters.
|
|
The upper passenger satellite mounted on top of the SYLDA 5 can be in the 4,500 kg. weight class. During the flight, Ariane 5's upper satellite is deployed first. The Sylda 5 is then cut at its base by a pyrotechnic charge, and the structure is separated by push-off springs. The lower passenger is then ready for its deployment, completing the mission. Sylda 5 is a cylindrical-conical structure manufactured from carbon-honeycomb sandwich panels, assembled by bonded joints, and bonded and riveted aluminum frames.
(788 characters)
Text 1A[4]. The Vulcain Engine
The Vulcain engines are gas-generator cycle cryogenic rocket engines fed with liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen. They feature regenerative cooling through a tube wall design, and the Vulcain 2 introduced a particular film cooling for the lower part of the nozzle, where exhaust gas from the turbine is re-injected in the engine. They power the first stage of the Ariane 5 launcher, the EPC and provide 8% of the total lift-off thrust.
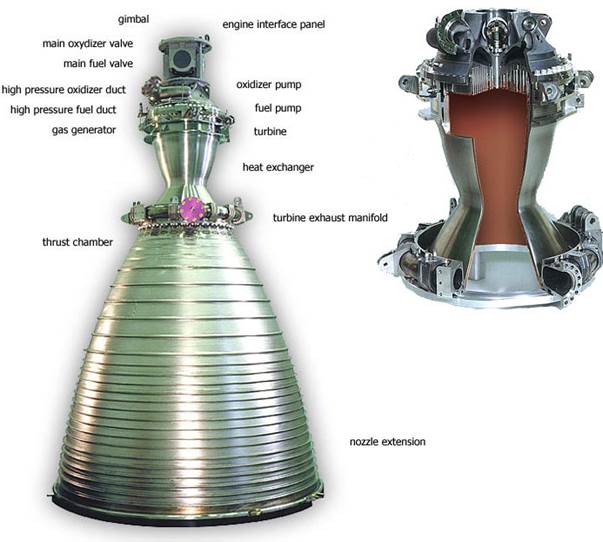
The engine operating time is 600 s in both configurations. 3 m tall and 1.76 m in diameter, the engine weights 1686 kg and provides 137 t of thrust in its latest version. The Italian-built oxygen turbopump rotates at 13600 rpm with a power of 3 MW while the hydrogen turbopump rotates at 34000 rpm with 12 MW of power. The total mass flow rate is 235 kg/s, of which 41.2 kg/s are of hydrogen.
(681 characters)
Text 1A[5]. Ariane 5 Payloads: The Payload Fairings
 The ASAP platform carries mini- or micro-satellites as secondary payloads.
The ASAP platform carries mini- or micro-satellites as secondary payloads.
It can be mounted on top of the upper stage, as well as on the SPELTRA or SYLDA structures. When located under a primary payload, the ASAP platform accommodates up to eight micro-satellites, each weighing under than 120 kg.
On missions when ASAP is mounted inside a dedicated SYLDA structure, it can carry up to four mini-satellites weighing up to 300 kg. each, or two 300-kg mini-satellites and six 120-kg micro-satellites.
(419 characters)
|
|
|

Кормораздатчик мобильный электрифицированный: схема и процесс работы устройства...

Эмиссия газов от очистных сооружений канализации: В последние годы внимание мирового сообщества сосредоточено на экологических проблемах...

Организация стока поверхностных вод: Наибольшее количество влаги на земном шаре испаряется с поверхности морей и океанов (88‰)...

Своеобразие русской архитектуры: Основной материал – дерево – быстрота постройки, но недолговечность и необходимость деления...
© cyberpedia.su 2017-2024 - Не является автором материалов. Исключительное право сохранено за автором текста.
Если вы не хотите, чтобы данный материал был у нас на сайте, перейдите по ссылке: Нарушение авторских прав. Мы поможем в написании вашей работы!