We study Anatomy
1. Translate the words and learn them by heart:
| Head
Hair
Face
Ears
Eyes
Eyelashes
Eyebrows
Forehead
Nose
Mouth
Lips
Tongue
Tooth-teeth
Chin
Cheeks
Neck
| Trunk
Arm
Shoulder
Elbow
Forearm
Wrist
Hand
Finger
Leg
Hip
Thigh
Knee
Shin
Ankle
Calf
Foot-feet
Toe
|
2. Complete the sentences:
1. I can eat with my ….
2. I can smell with my….
3. I can hear with my ….
4. I can run with my ….
5. I can hug with my ….
6. I can speak with my ….
7. I have one …, …, …, …, …, ….
8. I have two …, …, …, …, ….
9. I have ten …, ….
10. I have thirty-two ….
3. Read and translate the text:
We study Anatomy
The study of anatomy is important for all health professionals to understand how the human body is structured.
The principle parts of the human body are the head, the trunk and the limbs (extremities). We speak of the upper extremities (arms) and the lower extremities (legs). The head consists of two parts: the skull which contains the brain, and the face which consists of the forehead, the eyes, the nose, the mouth, the cheeks, the ears and the chin. In the mouth there are gums with teeth, the tongue and the palate.
The head is connected with the trunk by the neck. The upper part of the trunk is the chest (thoracic cavity) and the lower one is the abdomen. The principle organs in the chest are the lungs, the heart and the esophagus. We breathe with the lungs. The heart contracts and makes 60-80 beats per minute. The esophagus passes food and liquids to the stomach.
The principle organs in the abdominal cavity are the stomach, the liver, the spleen, the intestine, the kidneys, the gall-bladder, the pancreas and the urinary bladder.
The skeletal system supports and protects the soft tissues of the body and helps the body to move. It consists of bones, which are bound together by ligaments and cartilages. The skeletal system attaches to muscles. The bones also help in blood formation.
The bones are covered with muscles. The muscular system works with the skeletal system in helping the body to move.
The upper extremity is connected with the chest by the shoulder. Each arm consists of the shoulder, forearm, elbow, wrist and hand. We have five fingers on each hand. The lower extremity (the leg) consists of the hip, the thigh, the knee, the calf, the ankle, the foot and five toes.
4. Translate from Russian into English:
- защищает мягкие ткани;
- верхняя часть туловища;
- верхние конечности – руки;
- нижние конечности – ноги;
- легкие, сердце, пищевод – основные органы в грудной клетки;
- печень, селезенка, желудок, почки, желчный пузырь, поджелудочная железа, кишечник, мочевой пузырь – основные органы в брюшной полости;
- голова состоит из двух частей – черепа, лица;
- головной мозг;
- лицо состоит изо лба, глаз, щек, ушей, носа, рта, подбородка;
- десны, зубы, язык, нёбо находятся во рту;
- сердце совершает 60-80 уд;
- помогает телу двигаться;
-помогает в формировании крови
- передает пищу и жидкости.
Use English equivalents
1.A man has four (конечности).
2. (Глаза) are under the (лоб).
3. (Язык) is the organ for speech.
4. The heart is in the (грудная клетка).
5. We breathe with the (легкие).
6. The skull contains (головной мозг).
7. (Шея) connects the head with the (туловище).
8. The spleen is in the (брюшная полость).
9. (Плечо) connects the upper extremity with the chest.
10. The leg consists of the hip, thigh, knee, (голень), ankle and the foot.
6. Answer the questions:
1. What is studied at anatomy classes?
2. What are the principal parts of the human body?
3. What is the organ of thinking called?
4. What is there in the mouth?
5. What is the head connected with the trunk by?
6. How many beats per minute does the heart make?
7. Which organs are located in the abdominal cavity?
8. What is the function of the skeleton?
9. What does the arm consist of?
10. What does the lower extremity consist of?
The Human Skeleton
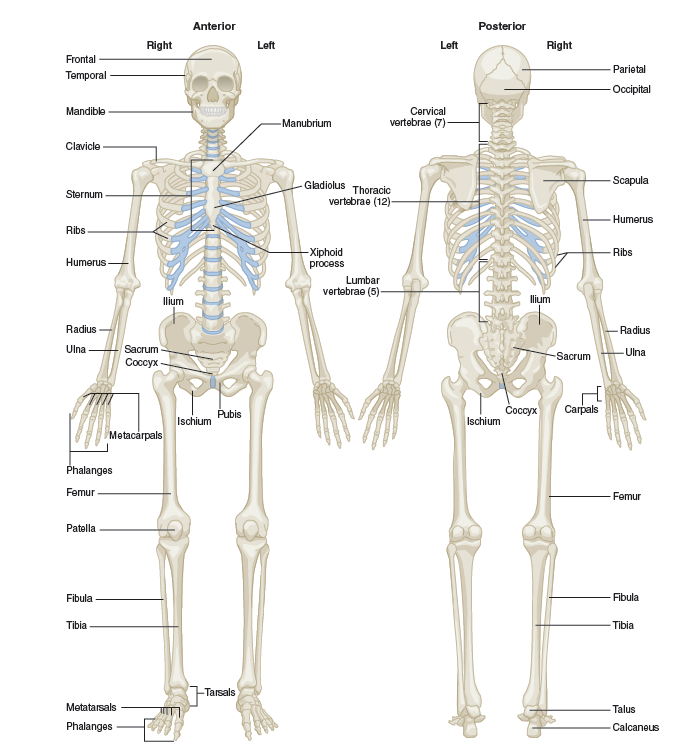
Figure 1.The human skeleton

Figure 2. Anatomy of long bones
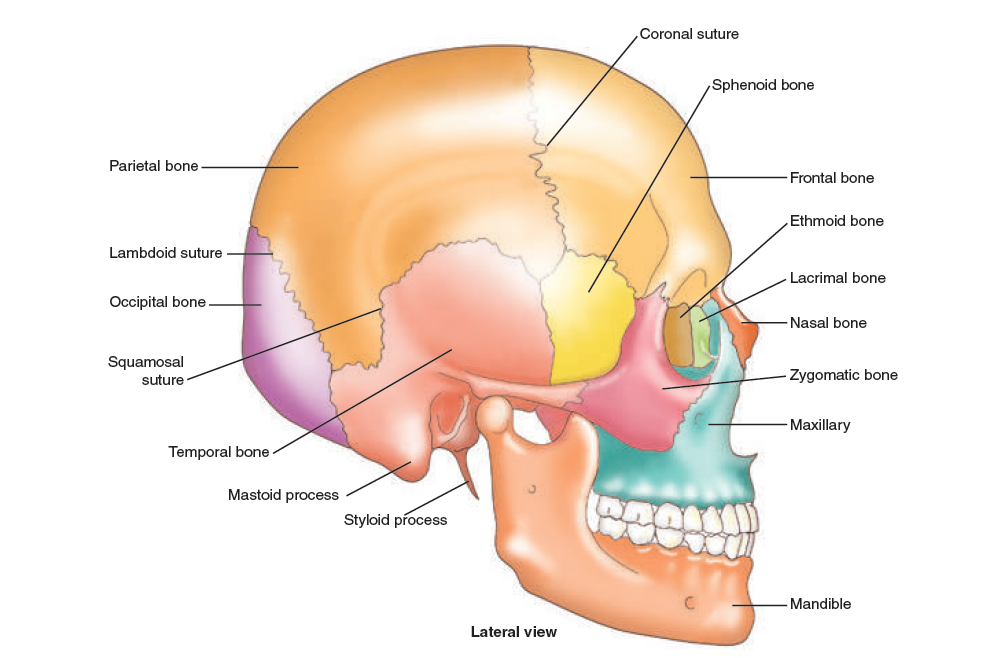
Figure 3. The skull
1. Learn the words:
Framework – основа
To sustain – удерживать
Backbone (spine,) – позвоночник
To serve – служить
To support – поддерживать
Vertebra(e) – позвонок (и)
Hole – отверстие
To correspond – совпадать
Pipe – труба
To contain – содержать
Marrow - костный мозг
Fibro-cartilage – волокнисто хрящевой
To lend – придавать
Flexibility – гибкость
Vertebral column – позвоночный столб
Rib – ребро
To protect – защищать
Triangular – треугольный
Shoulder-blade (scapula) – лопатка
Collar-bone (clavicle) – ключица
Breastbone (sternum) – грудина
Shoulder girdle – пояс верхних конечностей
Humerus – плечевая кость
Radius – лучевая кость
Ulna – локтевая кость
Carpal – пястный
Metacarpal – запястный
Pelvic girdle – пояс нижних конечностей
Femur – бедренная кость
Patella – коленная чашечка
Tibia – большая берцовая кость
Fibula – малая берцовая кость
Tarsal – предплюсна
Metatarsal – плюсна
Skull (cranium) - череп
Frontal – лобный
Occipital – затылочный
Temporal – височный
Parietal – теменной
Sphenoid – клиновидный
Ethmoid – решётчатый
Read and translate the text
Use English equivalents
- позвоночник состоит из 33 или 34 позвонков;
- отверстия совпадают друг с другом;
- канал, который содержит спинной мозг;
- на верхней части спины имеются две треугольные кости;
- лопатки и ключицы образуют пояс верхних конечностей;
- плечевая кость, лучевая кость, локтевая кость;
- пястье, запястье и фаланги;
-бедренная кость, коленная чашечка, большая берцовая кость, малая берцовая кость;
- череп состоит из восьми костей;
- корень носа.
5. Answer the questions:
1. What does the skeleton consist of?
2. What is the function of the spine?
3. Does the vertebral column consist of a single elongated bone or a number of independent bones?
4. How many vertebrae are there in man?
5. What is the hole in every vertebra for?
6. What is located in the spinal canal?
7. How many pairs of ribs are there in the human skeleton?
8. What internal organs do the ribs afford protection to?
9. What bones form the shoulder girdle?
10. What are the bones of the upper limbs?
11. What girdle are the lower extremities attached to?
12. What are the bones of lower limbs?
13. What is the skeleton of the head termed?
14. Name the the bones composing the skull.
Review questions
1. Which of the following is a bone of the forearm?
A. Radius B. Femur C. Fibula D. Humerus
2. Which of the following bones is triangular in shape?
A. Sternum B. Scapula C. Clavicle D. Rib
3. The bones that form the wrist are the
A. metacarpals. B. metatarsals. C. tarsals. D. carpals.
4. Which of the following is the longest bone in the body?
A. Tibia B. Femur C. Fibula D. Humerus
5.There are … thoracic vertebrae?
A. 5 B. 7 C. 12 D. 26
Muscles
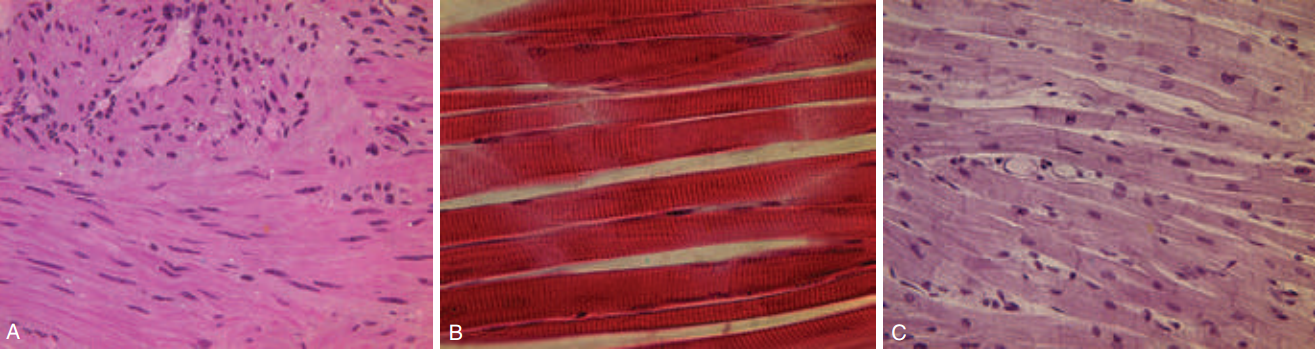
Figure 4. The three types of muscle fibers: (A) skeletal, (B) smooth, (C) cardiac
1. Learn the new words:
Muscle – мышца
Muscular – мышечный
Striated – поперечно-полосатая
Smooth – гладкая
Visceral – висцеральная (внутренних органов)
Cardiac – сердечная
Voluntary – произвольно сокращающаяся
Involuntary – непроизвольно сокращающаяся
Weight – вес
Cell – клетка
Fiber – волокно
Internal – внутренний
Bundle – пучок, связка
Skin – кожа
To contract – сокращаться
Tissue – ткань
To respond – отвечать, реагировать
Vessel – сосуд
Blood – кровь
2. Read and translate into Russian:
the contraction of muscles, the blood vessel wall, the body weight, connective tissue cells, to determine the blood group, a rapid change, to contract slowly, the direction of muscular fibers, to find out the universal method, to introduce into practice, direct connection, to respond to stimuli, wide bundles, excitability, contractility, extensibility, and elasticity.
3. Read and translate the text, find English equivalents of these word combinations:
Согласно одной теории, происходит от латинского слова, греческое выражение, двигательный аппарат, произвольные и непроизвольные, контролируются сознанием, устойчивое сокращение, действие температуры, поворот головы, изменения окружающей среды, характерная черта, не имеет ни начала, ни конца, огромная сеть.
The word “muscle”, according to one theory, comes from a Latin word that means “little mouse”: when a man’s muscles are contracting they look as if a little mouse runs about under the skin. According to another theory the word “muscle” comes from a Greek expression that means “to enclose”, that is layers of muscles enclose the body. We know that the muscles constitute about 50 per cent of the total body weight.
Muscles are needed for many body activities, including breathing, talking, walking, and even sneezing. Muscles are the active part of the motor apparatus.
Functionally all muscles are divided into two groups: voluntary and involuntary muscles.
Skeletal muscle attaches to bones and is the only type of muscle that is consciously controlled. It is, therefore, referred to as voluntary muscle. Skeletal muscle can, however, also be activated by reflexes. Smooth muscle tissue is similar, but not identical, to skeletal muscle. It is not under voluntary control and has slow, sustained contractions. Cardiac muscle tissue is found only in the heart. It is under involuntary control.
There are three main types of muscular tissue that we identify and classify on the basis of its structure:
1. smooth or visceral muscle;
2. striated or skeletal muscle;
3. cardiac muscle.
Muscle tissue has four unique characteristics, which include excitability, contractility, extensibility, and elasticity.
Smooth muscles can contract slowly. They make up the walls of the internal organs. Since we identify the internal organs as viscera, we sometimes call smooth muscles visceral muscles. The walls of the blood vessels are contracting when they respond to some chemicals in the blood or to the effect of temperature. For this reason we may call them involuntary muscles. Smooth muscle tissue consists of long cells. Smooth muscle fibers are bound into bundles by connective tissue which contains blood vessels and nerves.
Striated muscle tissue consists of large fibers in the form of bundles. These muscles are necessary for manipulation of the bones of the skeleton for walking, running, turning the head and so on. That’s why we sometimes call them skeletal muscles. This type of muscular tissue includes the large muscle masses of the body, the muscles of the arms, legs, back, etc. It includes all the muscles which must respond quickly to changes in the environment. For this reason we call striated muscles voluntary muscles. There are more than 400 skeletal muscles in the human body.
Cardiac muscle is made up of striated tissue. A characteristic feature of cardiac muscle is that fibers have neither a beginning nor an end. In other words the heart is a huge net of muscles in which all elements are continuous with each other. Cardiac muscles have the strength of contraction of the skeletal muscles.
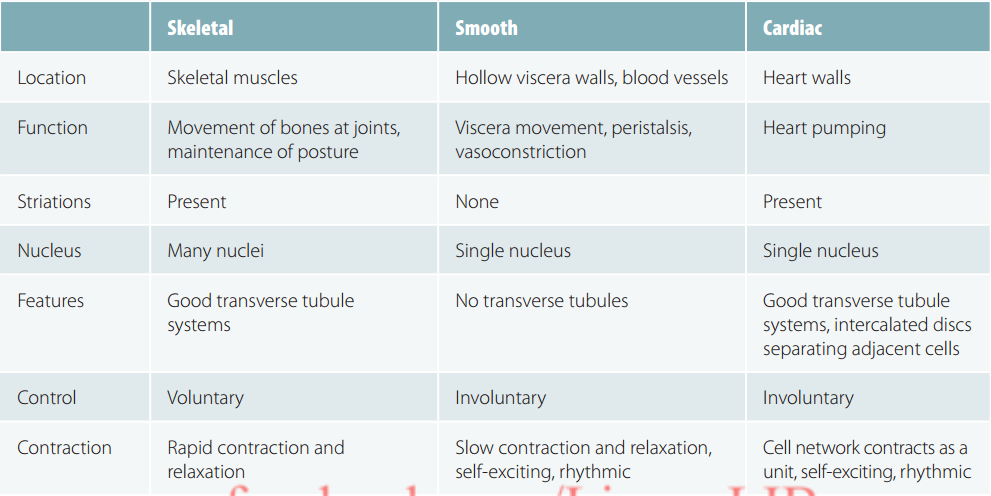
Figure 5. Skeletal, Smooth and Cardiac Muscle
4. Complete the following sentences:
1. Functionally all muscles can be divided into …
A. three groups
B. two groups
C. numerous groups
2. Smooth muscles make up …
A. free parts of the extremities
B. the walls of the internal organs
C. the main parts of the trunk
3. Striated muscles are necessary for …
A. motion and contraction
B. formation of fibrous bundles
C. manipulation of the bones of the skeleton
4. Cardiac muscle is …
A. under involuntary control
B. under voluntary control
C.
5. Express your agreement or disagreement with the following statements:
1. The word muscle is an English word.
2. Muscles constitute about 50 per cent of the total body weight.
3. Muscles are the active part of the nervous system.
4. There are five main types of muscular tissue on the basis of its structure and functions.
5. Smooth muscles make up the walls of the internal organs.
6. Striated muscles are called involuntary or visceral muscles.
7. Cardiac muscle tissue is found in the heart and in the stomach.
6. Answer the questions:
1. What is the origin of the word muscle?
2. What groups of muscles do you know?
3. What are the other names for smooth muscles?
4. Why can we call smooth muscles visceral muscles?
5. Why can we call them involuntary muscles?
6. What are the other names for striated muscles?
7. Why can we call them voluntary muscles?
7. Translate the sentences into English:
1. Мышцы необходимы для многих видов деятельности человека.
2. В теле человека примерно 400 скелетных мышц.
3. По функциям мышцы можно разделить на две основные группы.
4. Гладкие мышечные волокна связаны в пучки соединительной тканью, которая содержит кровеносные сосуды и нервы.
5. Поперечно-полосатые мышцы иначе можно назвать скелетными мышцами.
6. Волокна сердечной мышцы непрерывны.
7. Сердце – это огромная сеть мышц.
Skin and its functions
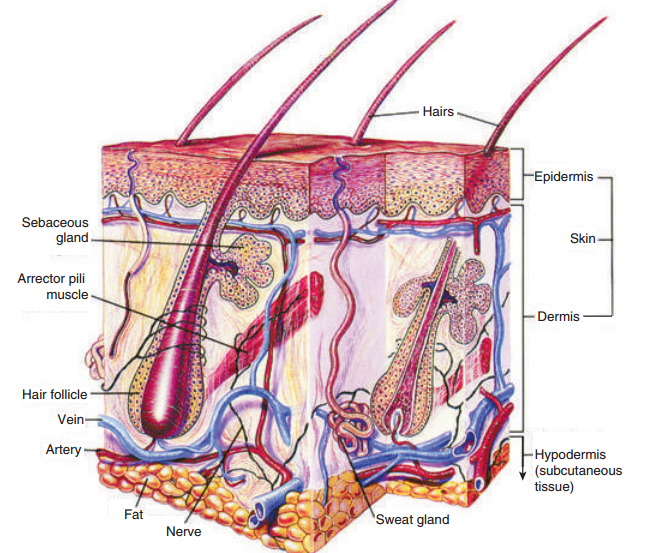
Figure 6. Anatomy of the skin
The skin
The skin is the largest organ of the body. It is composed of two main layers: the dermis with a rich network of blood vessels and nerves and epidermis, a protective outer layer without blood vessels. The cells of the surface layer are non-living and require no supply of blood for nourishment. The cells at the base of the epidermis are alive and are constantly growing. The epidermis is thinner than the dermis and is made up of several layers of different kinds of cells. The number of cells varies in different parts of the body; the greatest number is in the palms of the hands and soles of the feet, where the skin is the thickest. An adult’s skin weighs about 6.6 pounds.
Skin colour is caused by the presence of melanin, a pigment that is produced by special cells in the epidermis. The amount of melanin determines the differences in skin colours among the different races. Melanin makes an Indian brownish-red, a Chinese yellow, and an African black. The skin of the white race contains the least melanin pigment.
Albinism is a genetic disorder in which there is a lack of melanin. Albinism affects the hair, skin, and eyes. The hair is usually white, the skin extremely pale, and the eyes may range in color from blue to reddish, violet, hazel, or brown. Patients must avoid skin damage from the sun.

Figure 7. Albinism
| Skin layer
| Contains blood vessels and nerves
| Contains melanin
| Comparison in thickness
|
|
| -
| +
| thinner
|
|
| +
| -
| thicker
|
Answer the questions:
1. Which layer of the skin contains blood vessels?
2. Which layer is thicker?
3. What kinds of cells – living or non-living – are in the epidermis?
4. What amount of melanin – the least or the most – does the skin of the white race contain?
5. What is albinism?
Make up sentences
| Подлежащее (термин)
| Глагол- связка
| Именная часть сказуемого
(с сопутствующими словами)
|
| 1. The epidermis
|
is/are
| the organs that filter the blood.
|
| 2. A bone
| the part of the body which has eyes, mouth, and brain in it.
|
| 3. A cell
| the bony box that encloses the brain.
|
| 4. The eyes
| the tiny unit of the living tissue.
|
| 5. The heart
| the muscular organ that pumps the blood.
|
| 6. The kidneys
| the organs of sight.
|
| 7. The skull
| the outer layer of the skin.
|
| 8. The head
| a piece of the skeleton.
|
Make up sentences
|
The function of
| the skin
|
is
| to protect the brain.
|
| the skull
| to pump blood through the body.
|
| the bones
| to provide anchorage for the muscles.
|
| the heart
| to maintain the temperature of the body.
|
| the blood
| to transport oxygen and nutrients to the organs.
|
Blood Components

Figure 8. The composition of whole blood.
1. Read and translate the text:
Blood Components
Normally, 7-8% of human body weight is from blood. In adults, this amounts to 4.5-6 quarts of blood. This essential fluid carries out the functions of transporting oxygen and nutrients to our cells and getting rid of carbon dioxide, ammonia, and other waste products. In addition, it plays a vital role in our immune system and in maintaining a relatively constant body temperature. Blood is a highly specialized tissue composed of more than 4,000 different kinds of components. Four of the most important ones are red cells, white cells, platelets and plasma.
Red Cells
Red cells, or erythrocytes, are relatively large microscopic cells without nucleus. Red cells normally make up 40-50% of the total blood volume. They transport oxygen from the lungs to all of the living tissues of the body and carry away carbon dioxide. The red cells are produced continuously in our bone marrow. Hemoglobin is the gas transporting protein molecule that makes up 95% of a red cell. Each red cell has about 270,000,000 iron-rich hemoglobin molecules.
White Cells
White Cells protect the body against bacteria, viruses, parasites, cancer cells, and toxins. Leukocytes exist in variable numbers and make up a very small part of blood's volume – normally only about 1% in healthy people. Leukocytes are not limited to blood. They occur elsewhere in the body as well, most notably in the spleen, liver, and lymph glands. Most are produced in our red bone marrow.
Platelets
Platelets, or thrombocytes, are small cell fragments without nucleus. They live for about 10 days. Approximately one third of the body’s platelets are held in the spleen and other vascular organs instead of in the bloodstream. The function of platelets is primarily to block injuries to damaged blood vessels and to start forming blood clots. They accomplish this by sticking to the damaged site and forming a temporary plug to seal the broken area. Recent research has shown that platelets also help fight infections by releasing proteins that kill invading bacteria and some other microorganisms. In addition, platelets stimulate the immune system. Like the red and white blood cells, platelets are produced in bone marrow from stem cells.
Plasma
Plasma is the relatively clear, yellow liquid made up of 90% water. It also contains amino acids, carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, hormones, electrolytes, vitamins, and waste materials. As the heart pumps blood to cells throughout the body, plasma brings nourishment to them and removes the waste products of metabolism.
Use English equivalents
Необходимая жидкость, транспортировка кислорода и питательных веществ, выведение углекислого газа, играть жизненно важную роль, постоянная температура тела, различные виды компонентов, объем крови, костный мозг, газотранспортная белковая молекула, богатая железом, защищает тело, непостоянное количество, здоровый человек, лимфатические железы, находятся в селезенке, кровоток, блокировать повреждения, сгустки крови, стенки сосудов, прикрепляться к поврежденному месту, временная закупорка, бороться с инфекциями, убивать вторгающиеся бактерии, стимулировать иммунную систему, прозрачная желтая жидкость, удаляет продукты метаболизма.
3. Replace with synonyms the underlined words 1. The function of erythrocytes is
to carry oxygen and carbon dioxide.2. Thrombocytes are
tiny particles of the blood.3. Leuccocytes
differ in size and shape.4. White cells
are situated not only in the bloodstream.5. Plasma
includes different components.6. The function of platelets is
first of all to block injuries to damaged blood vessels.
4. Answer the questions:
Organ Systems
Answer the questions
1. What are the major organ systems of the body?
2. Name the organs of each system.
3. What are the functions of the organ systems?
4. Which system controls breathing?
5. Which organ system is not vital?6. Which system connects the brain to the rest of the body?7. What system includes the liver and the pancreas?8. What organ system differs women from men?
The Cardiovascular System
Learn the new words
cardiovascular system – сердечнососудистая система
blood circulation – кровообращение
artery – артерия
vein – вена
capillary – капилляр
blood vessel – кровеносный сосуд
to pump blood – выталкивать кровь
oxygen-poor blood – кровь, бедная кислородом
oxygen-rich blood – кровь, обогащённая кислородом
chamber of the heart – камера сердца
atrium (atria) – предсердие
ventricle – желудочек
valve – клапан
cardiac cycle – сердечный цикл
vascular system – сосудистая система
pulmonary system – лёгочная система
to separate – разделять
portal system – портальная система
The Cardiovascular System
The cardiovascular system is the system of blood circulation. It includes the heart, the arteries, the veins and the capillaries.
The centre of the circulatory system is the heart. The heart is the size of about clenched (сжатый) fist. The average adult heart is about 14 cm long by 9 cm wide and weighs approximately 300 g. The normal weight of the heart is about half of one per cent of the total body weight. The human heart contracts from the first moment of life to the last one.
The contractions of the heart pump blood through the arteries to all parts of the body. Blood flows through your body using your blood vessels such as capillaries, veins and arteries. When the oxygen-poor blood goes to your lungs, the blood will be oxygen-rich and will give oxygen to your whole body and does this over and over again.
There are four chambers in the heart. There are two chambers on the top and two chambers on the bottom. The top two chambers are called the atria. There's a left atrium and a right atrium. They receive blood returning to the heart from the body and lungs. The bottom two chambers are the ventricles. There is also a right ventricle and a left ventricle. The ventricles give the blood to the body and lungs. The valves separate the atria from the ventricles. The valves are located at the entrance and exit of each ventricle.
Each beat of the heart is followed by a period of rest for the cardiac muscle. Each wave of contraction and period of rest of the heart compose a cardiac cycle.
The vascular system consists of three groups of vessels – arteries, veins and capillaries. The vessels carrying blood to and from the tissues of the body compose the general system. They are called the systemic vessels. The pulmonary system is formed by the vessels carrying blood to and from the lungs. The portal system is formed by the veins passing to the liver.
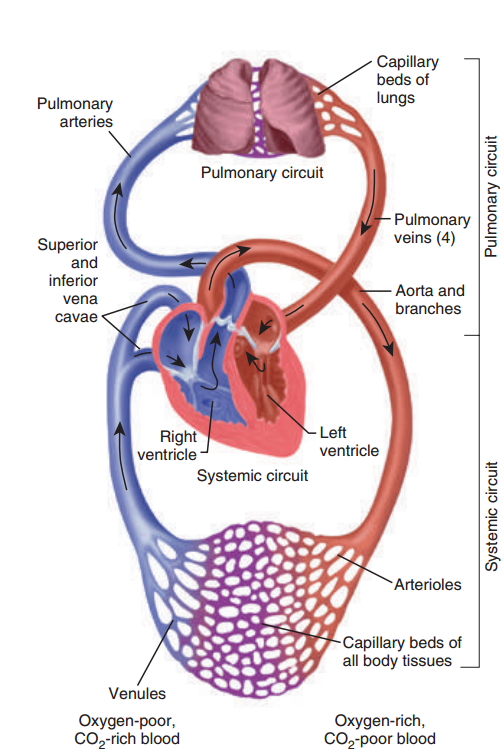
Figure 9. The blood pathway includes two circuits: systemic and pulmonary
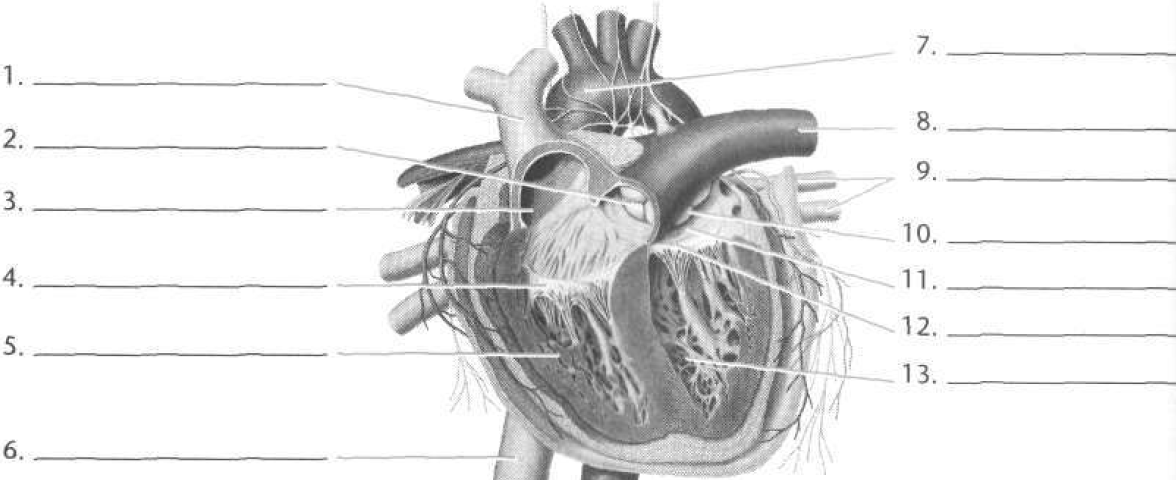
Match the terms
Aorta, aortic semilunar valve, bicuspid valve, inferior vena cava, left ventricle, left atrium, pulmonary artery, pulmonary semilunar valve, pulmonary veins, right atrium, right ventricle, superior vena cava, tricuspid valve.
Heart diseases
Find the matches
| heartache
| немедленно
|
| headache
| состояние
|
| immediately
| боль в сердце
|
| calm the patient
| давление крови
|
| condition
| головная боль
|
| prescribe drugs
| успокоить пациента
|
| the pressure of blood
| выписать лекарство
|
| complain of
| жаловаться на
|
Use English equivalents
Врожденный, приобретенный, пороки сердца, структурные дефекты, врожденные пороки сердца, посиневшие губы, пальцы на руках и ногах закругленные, похожие на барабанные палочки, отверстие, легочная артерия, обнаруживать, плановый осмотр, одышка, отеки, хирургический путь.

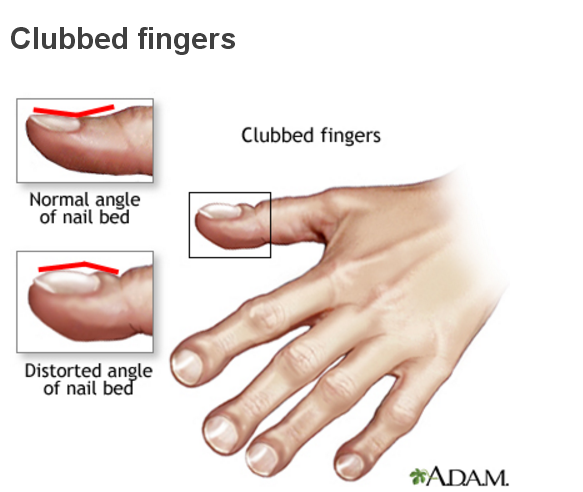
Figure 11. Cyanosis Figure 12. Club-like fingers
Hypertension
Read out
hypertension
hypertensive crisis
primary hypertension
essential hypertention
secondary hypertension
blood
blood pressure
measure blood pressure
high blood pressure
persistent high blood pressure
low blood pressure
to treat – treatment
to prevent – prevention
to measure – measurement
to cause – cause
to complain of – complaint
to elevate – elevation
to reduce – reduction
Warm-up discussion
What is hypertension?
Why do you think so many people in developed countries suffer from this disease?
What can we do to solve the problem?
Hypertension
Hypertension is a persistent elevation of the systolic blood pressure above 140 mm Hg and the diastolic blood pressure above 80 mm Hg. It can be classified as primary (or essential) and secondary. Primary hypertension indicates that no specific medical cause can be found. Secondary hypertension indicates that the high blood pressure is the result of another condition, such as kidney disease or certain tumors.
High blood pressure is the major risk factor for coronary, cerebral, renal, and peripheral vascular disease. The disease is initially asymptomatic. But later the patient may complain of headache, visual disturbances, dizziness, chest pain, tinnitus, etc.
One of the serious complications of hypertension is hypertensive crisis. It refers to any clinical condition requiring immediate reduction in blood pressure. It is acute and life-threatening. The accelerated hypertension requires emergency treatment, since target organ damage (brain, heart, kidneys, retina of the eye) can occur quickly. Death can be caused by stroke, renal failure, or cardiac disease.
Diagnosis of hypertension is generally made on the basis of a persistent high blood pressure. It usually requires three separate measurements at least one week apart. If an elevation is extreme, or end- organ damage is present, the diagnosis may be applied immediately.
The treatment includes reduction of blood pressure and prevention or lessening of the extent of organ damage. Non pharmacological methods, such as lifestyle changes, may be initially prescribed. The patient may require pharmacological treatment: such medications as beta-blockers, ACE-inhibitors, diuretics and others.
It is evident that our health mostly depends on us. If you want to be healthy, people should keep to a diet, be active, even-tempered, and never smoke or use any substances, such as drugs or alcohol.
4. Answer the questions:
1. What is the systolic blood pressures in hypertension?
2. What is the diastolic blood pressure in hypertension?
3. List the risk factors for this disease.
4. What does the patient with hypertension complain of?
5. How can we make a diagnosis of hypertension?
6. What are the ways of treatment of hypertension?
7. What does non pharmacological method of treatment include?
8. What organs can be damaged in hypertensive crisis?
The Respiratory System
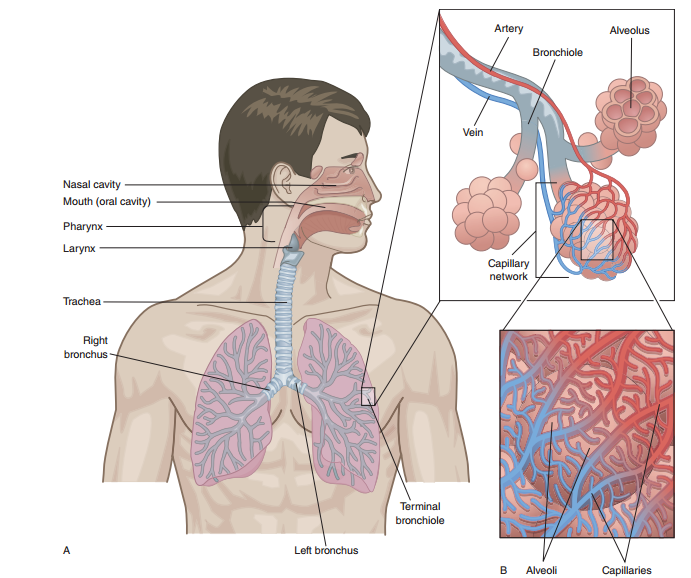
Figure 13. The structure of Respiratory System
1. Learn the following new words:
Airway – дыхательные пути
Alveolus – альвеола
Bronchus – бронх
Bronchiole – бронхиола
Breathe – дышать
Сarbon dioxide – углекислый газ
Diaphragm – диафрагма
Division – граница
Exhalation – выдох
Inhalation – вдох
Larynx – гортань
Lung – легкое
Muscles of respiration – дыхательные мышцы
Muscular tunnel – мышечная трубка
Pharynx – глотка
Pleura – плевра
Oxygen – кислород
Trachea – трахея
2. Read and translate the text:
The Digestive System
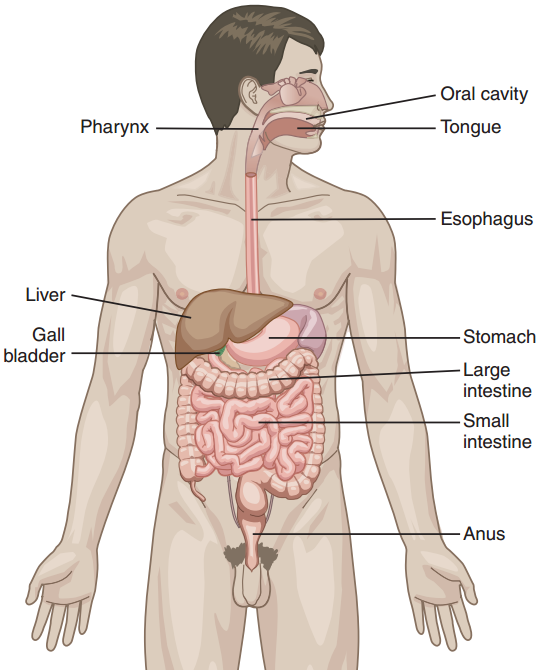
Figure 14. The digestive system
1. Learn the following new words:
Abdomen – брюшная полость
Alimentary tract – пищеварительный тракт
Anus – анальное отверстие
Caecum – слепая кишка
Colon – ободочная кишка
Digestive system – пищеварительная система
Duodenum – двенадцатиперстная кишка
Esophagus – пищевод
Ileum – подвздошная кишка
Jejunum – тощая кишка
Gallbladder – желчный пузырь
Gland – железа
Large intestine – толстый кишечник
Length – длина
Liver – печень
Musculomembraneous – мышечно - мембранный
Oral cavity – ротовая полость
Pancreas – поджелудочная железа
Palate – нёбо
Rectum – прямая кишка
Salivary glands – слюнные железы
Small intestine – тонкий кишечник
Stomach – желудок
Tube – трубка
2. Translate the following word combinations from English into Russian:
To extend from the oral cavity to the anus, the first division, to pass through the pharynx to the esophagus, the upper part of the abdomen, to be composed of, a thin-walled muscular tube, to absorb water, the largest gland in the human body, a major role in metabolism, a number of functions in the body, a hollow sac, a long thin gland.
3. Put words in the appropriate column:
| Parts of the cardiovascular system
| Parts of the digestive system
|
Ileum, heart, vessel, anus, jejunum, artery, duodenum, tongue, vein, pharynx, stomach, capillary, esophagus, intestine, aorta, atria, rectum, oral cavity, salivary glands, mouth, chamber, caecum, colon, teeth, ventricle.
4. Read and translate the text:
Text 1
Read and translate the text:
Text 2
Read and translate the text:
The Brain
The brain (cerebrum) is the enlarged and highly developed mass of nervous tissue that forms the upper end of the central nervous system. The average adult human brain weighs about 1400 g and is continuous below with the spinal cord. The spinal cord is the portion of the central nervous system enclosed in the vertebral column, consisting of nerve cells and bundles of nerves connecting all parts of the body with the brain. It contains a core of grey matter and is enveloped in three layers of membrane (the meninges) and extends from the medulla oblongata in the skull to the level of the second lumbar vertebra.
The brain is a complicated organ which consists of grey matter or nerve cells on the surface, and white matter or nerve fibers in the center. It contains many important nerve centers which make it not only the largest but the most important part of the brain.
The functions of the brain. The role of nervous system in our body is often compared to that of a centralized computer which controls the functioning of an entire system. The nervous system plays an important role in the smooth functioning of the different parts of our body. It is basically a complex network of cells with specialized functions. These cells communicate with each other by means of electrochemical waves. The neurons are the important components of the nervous system.
Central nervous system is the seat of all sensation due to the bringing in of the stimuli from the tissues by afferent fibers to the sensory centers of the brain. These stimuli pass through three or more afferent neurons before they reach the sensory centers of the cerebrum. Central nervous system controls all movements of voluntary muscles – muscles of the head, limbs and trunk. Movement is due to nerve stimulus. Movement is classified as voluntary and reflex one. The brain is the special seat of all the special senses – sight, hearing, smell, touch, and taste. The brain is the seat of all the higher mental powers – reasoning, will power, consciousness, memory, emotions, etc. The brain also controls the vital functions of the respiration and circulation, the controlling centers being located in the medulla.
1. Answer the questions:
1. What is the brain?
2. What is the average weight of the human brain?
3. What is the spinal cord like?
4. Where does the spine extend?
5. What parts does the brain comprise?
6. What is the most important part of the brain?
7. What is the role of nervous system in the body?
8. What processes does CNS control?
9. What is movement due to?
2. Match terms with their definitions:
| 1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
| consciousness
spinal cord
sensitivity
stimulus
brain
memory
medulla
| a) It is the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate animals. It is located in the head, usually close to the primary sensory organs for such senses as vision, hearing, balance, taste, and smell;
b) It is the ability to remember past experiences, and the power or process of recalling to mind previously learned facts, experiences, impressions, skills and habits;
c) In physiology it is a detectable change in the internal or external environment;
d) The ability of an organism or organ to respond to external stimuli;
e) It is the quality or state of being aware of an external object or something within oneself;
f) It is the part of the brainstem that is situated between the pons and the spinal cord;
g) It is a long, thin, tubular bundle of nervous tissue and support cells that extends from the medulla oblongata in the brainstem to the lumbar region of the vertebral column.
|
Text 3
Read and translate the text:
The Urinary System
The urinary system is a group of organs in the body concerned with filtering out excess of fluid and wastes from the bloodstream. Wastes in the blood come from the normal breakdown of active tissues and from food. The body uses food for energy and self-repairs. After the body has taken what it needs from food, wastes are sent to the blood.
The urinary system keeps the chemicals and water in your body balanced. A type of waste called urea is removed from the blood by the urinary system. Urea is produced when foods containing protein, such as meat, are broken down in the body. Urea is carried in the bloodstream to the kidneys.
The urinary system consists of two kidneys, which secrete the urine, the ureters, or ducts, which convey urine to the urinary bladder, where it is stored for some time; and the urethra, through which it is discharged from the body.
The kidneys are paired bean-shaped organs with two surfaces, two borders, and an upper and lower extremity. There are three major regions of the kidney: the renal cortex, the renal medulla and the renal pelvis. The kidneys are situated in the posterior part of the abdomen, behind the peritoneum. They are covered by the renal capsule. The left kidney is longer and narrower, than the right one.
There are more than 1000000 nephrons in each kidney. The nephron carries out nearly all of the kidney's functions. Its chief function is to regulate the concentration of water and soluble substances like sodium salts by filtering the blood, reabsorbing what is needed and excreting the rest as urine. The nephron eliminates waste substances from the body, regulates blood volume and blood pressure, controls levels of electrolytes and metabolites, and regulates blood pH. The inflammation of nephrons in the kidneys is called nephritis.
The ureters are two tubes which measure from 25 to 30 cm in length. They convey the urine from the kidneys to the urinary bladder. Muscles in the ureter walls continually tighten and relax forcing urine away from the kidneys. If urine backs up or stands still, a kidney infection can develop.
The urinary bladder is a triangle-shaped, hollow musculomembranous organ. It is located in the lower part of the abdomen and is held in place by ligaments that are attached to other organs and the pelvic bones. The urinary bladder is a temporary storage for the urine. The bladder's walls relax and expand to store urine, and contract to empty it. Nerves in the bladder alert a person when it is time to urinate.
The urethra is a tube that connects the urinary bladder with the outside of the body. Male and female urethra differs in shape and length. Male urethra length varies from 17.5 to 20 cm; and it is divided into three portions, the prostatic, membranous, and cavernous. The female urethra is a narrow membranous canal, about 4 cm. long. The brain signals the bladder muscles to tighten, which squeezes urine out of the bladder. At the same time, the brain signals the sphincter muscles to relax to let urine exit the bladder through the urethra. When all the signals occur in the correct order, normal urination occurs. Normal urine is sterile fluid. It contains fluids, salts and waste products, but it is free of bacteria, viruses and fungi.
1. Answer the questions:
1. What does the urinary system consist of?
2. What is urine?
3. Where are the kidneys situated?
4. What is the function of nephrons?
5. What is the function of the ureters?
6. Where is the urine stored before it is discharged from the body?
7. What is urethra?
8. What is the function of the urethra?
9. What conveys urine from the kidneys?
10. What is the function of the urinary bladder?
2. Fill in the gaps with words from the box:
| nephrons
| urine
| bladder
| kidneys
| wastes
| urea
| ureters
| nerves
|
1. … in the blood come from the normal breakdown of active tissues.
2. Normal … contains fluids, salts and waste products.
3. … usually holds 300-350 ml of urine.
4. … carry urine from the kidneys to the bladder.
5. All the blood in our bodies passes through … several times a day.
6. Urine is formed by … together with water and other waste substances.
7. A person gets an alarm from the … in the bladder when it is time to urinate.
8. In humans, a normal kidney contains 800,000 to 1.5 million ….
3. Agree or disagree with the following statements:
1. Urine is stored in the urethra before discharging from the body.
2. A nephron regulates the concentration of water and soluble substances.
3. The urinary bladder is a hollow bean-shaped organ, which discharges urine from the body.
4. The ureters convey the urine from the kidneys to the urinary bladder.
5. Kidney is a muscular sac which stores the urine before eliminating it from the body.
6. The urine is discharged from the body through the ureters.
7. Urethra is a tube that connects the kidney and the urinary bladder.
8. The main function of the ureters is to regulate the concentration of water and soluble substances.
Text 4
Read and translate the text:
Text 5
Read and translate the text:
The Endocrine Glands
All glands in the human body can be divided into glands with ducts and ductless. Ductless glands have no duct but they make a secretion which they pour into the blood stream. These secretions are called internal secretions or hormones, and glands which produce them are also called endocrine glands.
The chief ductless glands are: the thyroid gland, the adrenal glands and the pituitary gland.
There are also other important glands which produce internal secretions as well as other substances, e.g. the pancreas, the liver and the reproductive glands.
The thyroid gland lies in the front of the neck. It consists of two lobes lying on either side, joined by a narrow band which crosses the trachea immediately below the larynx. The gland is well supplied with blood vessels and consists essentially of secreting cells. The cells secrete thyroxin, which passes into the circulation. Thyroxin controls the general metabolism or activity of the body tissues.
The adrenal glands are two small triangular glands lying one over each kidney. They consist of two parts, cortex and medulla. The outer part produces a secretion which affects sex. Oversecretion produces masculinity in the female and in the male it produces too early development of the male reproductive organs.
The medulla produces a very important secretion called adrenalin, It secreted amount increases in excitement and strong emotions such as fear or anger. The adrenals are therefore sometimes called the glands of “flight and fight”.
The pituitary gland (hypophysis) is a small gland about the size of a pea and yet is of great importance. It lies in the pituitary fossa in the base of the skull. It consists of an anterior and a posterior lobe.
The anterior lobe is the larger and produces a number of important hormones affecting growth and sexual development and the functioning of the ductless glands, particularly the thyroid and the adrenal glands. Undersecretion of this lobe in childhood causes dwarfing. Oversecretion causes overgrowth or gigantism. In the adult this oversecretion causes overgrowth of the head, hands, and feet, particularly affecting the lower jaw. This condition is known as acromegaly.
The posterior lobe produces the secretion known as pituitrin. This stimulates involuntary muscle and therefore contracts the blood vessels and raises blood pressure, stimulates peristalsis, contracts the uterus; it affects the use of water by the body.
1. Answer the questions:
1. How are glands in the human body classified?
2. What is hormone?
3. What are the main ductless glands?
4. What is the structure of the thyroid gland?
5. What does thyroxin control?
6. What is the structure of the adrenal glands?
7. When is adrenalin secreted?
8. What is the structure of the pituitary gland?
9. What does the pituitary gland affect?
2. Open the brackets using the correct form of the verb. Translate the sentences:
1. Thyroxin (to control) the general metabolism or activity of the body tissues.
2. The anterior lobe of the hypothesis (to produce) a number of important hormones.
3. The thyroid gland (to supply) well with blood vessels.
4. The hormones (to deliver) to various organs.
5. The chemical composition of some hormones (to be) well-known.
6. Each gland (to consist) of glandular epithelial tissue.
7. The outer part of the adrenal glands (to produce) a secretion which affects sex.
8. The hormones (to affect) the functions of the different parts of the nervous system.
We study Anatomy
1. Translate the words and learn them by heart:
| Head
Hair
Face
Ears
Eyes
Eyelashes
Eyebrows
Forehead
Nose
Mouth
Lips
Tongue
Tooth-teeth
Chin
Cheeks
Neck
| Trunk
Arm
Shoulder
Elbow
Forearm
Wrist
Hand
Finger
Leg
Hip
Thigh
Knee
Shin
Ankle
Calf
Foot-feet
Toe
|
2. Complete the sentences:
1. I can eat with my ….
2. I can smell with my….
3. I can hear with my ….
4. I can run with my ….
5. I can hug with my ….
6. I can speak with my ….
7. I have one …, …, …, …, …, ….
8. I have two …, …, …, …, ….
9. I have ten …, ….
10. I have thirty-two ….
3. Read and translate the text:
We study Anatomy
The study of anatomy is important for all health professionals to understand how the human body is structured.
The principle parts of the human body are the head, the trunk and the limbs (extremities). We speak of the upper extremities (arms) and the lower extremities (legs). The head consists of two parts: the skull which contains the brain, and the face which consists of the forehead, the eyes, the nose, the mouth, the cheeks, the ears and the chin. In the mouth there are gums with teeth, the tongue and the palate.
The head is connected with the trunk by the neck. The upper part of the trunk is the chest (thoracic cavity) and the lower one is the abdomen. The principle organs in the chest are the lungs, the heart and the esophagus. We breathe with the lungs. The heart contracts and makes 60-80 beats per minute. The esophagus passes food and liquids to the stomach.
The principle organs in the abdominal cavity are the stomach, the liver, the spleen, the intestine, the kidneys, the gall-bladder, the pancreas and the urinary bladder.
The skeletal system supports and protects the soft tissues of the body and helps the body to move. It consists of bones, which are bound together by ligaments and cartilages. The skeletal system attaches to muscles. The bones also help in blood formation.
The bones are covered with muscles. The muscular system works with the skeletal system in helping the body to move.
The upper extremity is connected with the chest by the shoulder. Each arm consists of the shoulder, forearm, elbow, wrist and hand. We have five fingers on each hand. The lower extremity (the leg) consists of the hip, the thigh, the knee, the calf, the ankle, the foot and five toes.
4. Translate from Russian into English:
- защищает мягкие ткани;
- верхняя часть туловища;
- верхние конечности – руки;
- нижние конечности – ноги;
- легкие, сердце, пищевод – основные органы в грудной клетки;
- печень, селезенка, желудок, почки, желчный пузырь, поджелудочная железа, кишечник, мочевой пузырь – основные органы в брюшной полости;
- голова состоит из двух частей – черепа, лица;
- головной мозг;
- лицо состоит изо лба, глаз, щек, ушей, носа, рта, подбородка;
- десны, зубы, язык, нёбо находятся во рту;
- сердце совершает 60-80 уд;
- помогает телу двигаться;
-помогает в формировании крови
- передает пищу и жидкости.
Use English equivalents
1.A man has four (конечности).
2. (Глаза) are under the (лоб).
3. (Язык) is the organ for speech.
4. The heart is in the (грудная клетка).
5. We breathe with the (легкие).
6. The skull contains (головной мозг).
7. (Шея) connects the head with the (туловище).
8. The spleen is in the (брюшная полость).
9. (Плечо) connects the upper extremity with the chest.
10. The leg consists of the hip, thigh, knee, (голень), ankle and the foot.
6. Answer the questions:
1. What is studied at anatomy classes?
2. What are the principal parts of the human body?
3. What is the organ of thinking called?
4. What is there in the mouth?
5. What is the head connected with the trunk by?
6. How many beats per minute does the heart make?
7. Which organs are located in the abdominal cavity?
8. What is the function of the skeleton?
9. What does the arm consist of?
10. What does the lower extremity consist of?
The Human Skeleton

Figure 1.The human skeleton

Figure 2. Anatomy of long bones

Figure 3. The skull
1. Learn the words:
Framework – основа
To sustain – удерживать
Backbone (spine,) – позвоночник
To serve – служить
To support – поддерживать
Vertebra(e) – позвонок (и)
Hole – отверстие
To correspond – совпадать
Pipe – труба
To contain – содержать
Marrow - костный мозг
Fibro-cartilage – волокнисто хрящевой
To lend – придавать
Flexibility – гибкость
Vertebral column – позвоночный столб
Rib – ребро
To protect – защищать
Triangular – треугольный
Shoulder-blade (scapula) – лопатка
Collar-bone (clavicle) – ключица
Breastbone (sternum) – грудина
Shoulder girdle – пояс верхних конечностей
Humerus – плечевая кость
Radius – лучевая кость
Ulna – локтевая кость
Carpal – пястный
Metacarpal – запястный
Pelvic girdle – пояс нижних конечностей
Femur – бедренная кость
Patella – коленная чашечка
Tibia – большая берцовая кость
Fibula – малая берцовая кость
Tarsal – предплюсна
Metatarsal – плюсна
Skull (cranium) - череп
Frontal – лобный
Occipital – затылочный
Temporal – височный
Parietal – теменной
Sphenoid – клиновидный
Ethmoid – решётчатый
Read and translate the text
The structure of the Human Skeleton
The skeleton consists of bones and constitutes the framework, which sustains the softer parts of the human organism. The backbone or the spine serves as the support to the body. It consists of thirty-three or thirty-four vertebrae. There are seven cervical, twelve thoracic, five lumbar, five sacral and three or four coccygeal vertebrae. There is a hole in every vertebra. These holes correspond with each other through all the vertebrae forming a long bony pipe, or canal, which contains the marrow. A fibro-cartilage substance forms the intervertebral discs between the vertebrae uniting them and lending a certain degree of flexibility to the vertebral column.
The chest is composed of the thoracic cage, which includes 12 pairs of ribs connected to the thoracic vertebrae and the sternum. The first seven pairs are true ribs, the last five pairs are false ribs. The thoracic cage protects the heart, lungs and other internal organs.
On the upper part of the back there are two triangular bones, the shoulder-blades or scapulae. Each shoulder-blade is connected with the clavicle or collarbone, which is jointed at the other end to the breastbone or sternum. The shoulder-blades and the clavicles form the shoulder girdle, to which the upper limbs are attached. The arm has the humerus, the radius, the ulna. The hand is the part of the upper limb that consists of the wrist, palm, and fingers. They include carpal bones, metacarpal bones and phalanges (finger bones).
The pelvic girdle attaches the lower limbs to the skeleton. The leg consists of a femur (the longest bone in the body), a patella, a tibia, a fibula, tarsals, metatarsals and phalanges.
The skull, or the cranium, is a bony case that forms the framework of the head and encloses the brain. It consists of eight bones, namely, the frontal and occipital bones, the two temporal and parietal bones; the sphenoid bone of the base of the skull; and the ethmoid bone at the top of the root of the nose.
3. Complete the sentences:
1. The skeleton consists of bones and constitutes (основу) which sustains the (мягкие части) of the human body.
2. (Позвоночник) serves as support to the body.
3. There are seven (шейных) vertebrae, twelve (грудных позвонков), five (поясничных позвонков).
4. There is (отверстие) in every vertebra.
5. On the upper part of the back there are two flat (треугольные кости), the shoulder blade or (лопатки).
6. (Пояс нижних конечностей) attaches the lower limbs to the skeleton.
7. The skull or (череп) is (костный каркас) that forms the framework of the head and (включает) the brain.
8. It consists the (лобная) and (затылочная) bones, the two (височные) and (теменные)



















