

Наброски и зарисовки растений, плодов, цветов: Освоить конструктивное построение структуры дерева через зарисовки отдельных деревьев, группы деревьев...

Индивидуальные и групповые автопоилки: для животных. Схемы и конструкции...

Наброски и зарисовки растений, плодов, цветов: Освоить конструктивное построение структуры дерева через зарисовки отдельных деревьев, группы деревьев...

Индивидуальные и групповые автопоилки: для животных. Схемы и конструкции...
Топ:
Процедура выполнения команд. Рабочий цикл процессора: Функционирование процессора в основном состоит из повторяющихся рабочих циклов, каждый из которых соответствует...
Устройство и оснащение процедурного кабинета: Решающая роль в обеспечении правильного лечения пациентов отводится процедурной медсестре...
Интересное:
Что нужно делать при лейкемии: Прежде всего, необходимо выяснить, не страдаете ли вы каким-либо душевным недугом...
Как мы говорим и как мы слушаем: общение можно сравнить с огромным зонтиком, под которым скрыто все...
Принципы управления денежными потоками: одним из методов контроля за состоянием денежной наличности является...
Дисциплины:
|
из
5.00
|
Заказать работу |
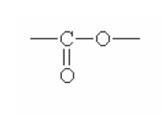
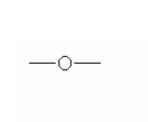
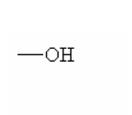
Here are some of the functional groups. Write their names in English.
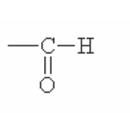
| 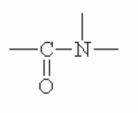
| 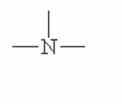
|
| _______________ | _______________ | _______________ |
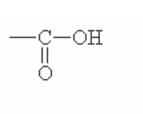
| 
| 
|
| _______________ | _______________ | _______________ |
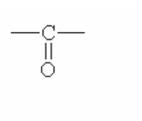
| 
| |
| _______________ | _______________ |
Read and translate the following names of hydrocarbons.
| Alkanes | Alkenes | Alkynes |
| methane | ----- | ----- |
| ethane | ethene | ethyne |
| propane | propene | propyne |
| butane | butene | butyne |
| pentane | pentene | pentyne |
| hexane | hexene | hexyne |
Some of these carbohydrates also have trivial names. Match them.
ethylene, propylene, acetylene, methylacetylene, butylenes
11. Match the systematic and trivial names of the following carboxylic acids:
| 1) methanoic acid | a) propionic acid |
| 2) ethanoic acid | b) formic acid |
| 3) propanoic acid | c) butyric acid |
| 4) butanoic acid | d) acetic acid |
| 5) pentanoic acid | e) valeric acid |
| 6) dodecanoic acid | f) stearic acid |
| 7) hexadecanoic acid | g) lauric acid |
| 8) octadecanoic acid | h) palmitic acid |
Speaking.
Organic chemists at all levels are generally employed by pharmaceutical, biotech, chemical, consumer product, and petroleum industries. Chemists in industry mainly work in development, while chemists in academia are involved in more basic research. The federal and local governments also hire organic chemists (e.g., Federal Service for Supervision of Healthcare, Federal Medical-Biological Agency or Federal Service for Veterinary and Phytosanitary Supervision). Work in groups of 3 or 4 and discuss which industry you would like to work at. Consider advantages and drawbacks of working at each industry and choose the one that fits you best.
UNIT VII. PLASTICS.
1. Discuss the following questions:
1. Have a look at the desk you are sitting at. What plastic things can you name?
2. What is the basic chemical element in plastics formula?
2. You are going to read Text A about polymers. Study new vocabulary from the text:
| 1. branch | разветвленный |
| 2. cellulose | 1) клетчатка; 2) целлюлоза |
| 3. chain | цепь |
| 4. chemicals | хим. вещества |
| 5. coil | 1) сердечник; 2) спираль |
| 6. fibre | волокно, нить |
| 7. flexible | гибкий |
| 8. insulator | 1) непроводник; 2) изоляционный материал |
| 9. resin | смола |
| 10. rubber | резина, каучук |
| 11. thermosetting plastics | термореактивные пластмассы |
| 12. to decompose | разлагаться |
| 13. to harden | делать твердым |
| 14. to prevent | предотвращать |
| 15. to soften | смягчать |
| 16. to subject | подвергать |
| 17. transparent | прозрачный |
3. Look through Text A and fill in the word-web:

Text A. Plastics.
Plastics are non-metallic, synthetic, carbon-based materials. They can be moulded, shaped, or extruded into flexible sheets, films, or fibres. Plastics are synthetic polymers. Polymers consist of long-chain molecules made of large numbers of identical small molecules (monomers). The chemical nature of a plastic is defined by the monomer (repeating unit) that makes up the chain of the polymer. Polyethene is a polyolefin; its monomer unit is ethene (formerly called ethylene). Other categories are acrylics (such as polymethylmethacrylate), styrenes (such as polystyrene), vinys (such as polyvinyl chloride (PVC)), polyesters, polyurethanes, polyamides (such as nylons), polyethers, acetals, phenolics, cellulosics, and amino resins. The molecules can be either natural — like cellulose, wax, and natural rubber — or synthetic — in polyethene and nylon. In co-polymers, more than one monomer is used.
The giant molecules of which polymers consist may be linear, branched, or cross-linked, depending on the plastic. Linear and branched molecules are thermoplastic (soften when heated), whereas cross-linked molecules are thermosetting (harden when heated).
Most plastics are synthesized from organic chemicals or from natural gas or coal. Plastics are light-weight compared to metals and are good electrical insulators. The best insulators now are epoxy resins and teflon. Teflon or polytetrafluoroethene (PTFE) was first made in 1938 and was produced commercially in 1950.
Plastics can be classified into several broad types.
1. Thermoplastics soften on heating, then harden again when cooled. Thermoplastic molecules are also coiled and because of this they are flexible and easily stretched.
Typical example of thermoplastics is polystyrene. Polystyrene resins are characterized by high resistance to chemical and mechanical stresses at low temperatures and by very low absorption of water. These properties make the polystyrenes especially suitable for radio-frequency insulation and for parts used at low temperatures in refrigerators and in airplanes. PET (polyethene terephthalate) is a transparent thermoplastic used for soft-drinks bottles. Thermoplastics are also viscoelastic, that is, they flow (creep) under stress. Examples are polythene, polystyrene and PVC.
2. Thermosetting plastics (thermosets) do not soften when heated, and with strong heating they decompose. In most thermosets final cross-linking, which fixes the molecules, takes place after the plastic has already been formed.
Thermosetting plastics have a higher density than thermoplastics. They are less flexible, more difficult to stretch, and are less subjected to creep. Examples of thermosetting plastics include urea-formaldehyde or polyurethane and epoxy resins, most polyesters, and phenolic polymers such as phenol-formaldehyde resin.
3. Elastomers are similar to thermoplastics but have sufficient cross-linking between molecules to prevent stretching and creep.
4. Read and translate the following words from English into Russian:
To compose – composed – composing - composition; to decompose – decomposed – decomposing – decomposite - decomposition; to harden – hardener; to prevent – preventer – prevention - preventative; to soften - softening; to absorb – absorber – absorbing – absorbent – absorption – absorptive - absorptivity
5. Find English equivalents in the text:
Cинтетические полимеры, молекулы с длинными цепями, характерные свойства полимера, синтезируются из органических химических веществ, хороший электрический изолятор, размягчаться при нагревании, затвердевать при охлаждении, гибкий и легко растяжимый, течь под нагрузкой, более высокая плотность, менее подвержены ползучести, достаточная взаимосвязь между молекулами
6. Comprehension check. Read Text A and answer the following questions:
1. What is the definition of plastics?
2. What do polymers consist of?
3. What are long-chain molecules made of?
4. What are the main types of polymers?
5. Give examples of plastics belonging to these types.
6. What plastics are the best electrical insulators?
7. Describe the difference between thermoplastics and thermosets.
8. What are the main types of structures of polymers?
9. What are the most important properties of plastics?
10. Give the examples of various uses of plastics because of their characteristic properties.
7. Fill in the correct word:
Composition, decomposes, absorbent, prevented, decomposed, absorb, preventative, absorption.
1. If bodies radiate more energy than they ____ from surrounding bodies they will cool. 2. Sodium hydroxide solution is the best _____ for carbon dioxide. 3. The process of absorbing is called ______. 4. Zinc carbonate when heated ______ into zinc oxide and carbon dioxide. 5. Unless we get more funding we’ll be ______ from finishing our experimental programme. 6. This scientist took all possible ______ measures in his laboratory. 7. Water can be ______ into hydrogen and oxygen. 8. A chemical composition of this new polymer is unique.
8. Translate into English using the target vocabulary:
1. Длинные цепи молекул полимеров состоят из одинаковых небольших молекул мономеров. 2. Сополимеры состоят из двух и более мономеров. 3. Пластмассы можно получать в виде листов, тонких пленок, волокон или гранул. 4. Молекулы полимеров могут быть линейными, ветвящимися или с поперечными связями. 5. Малый вес пластмасс и хорошие электроизоляционные свойства позволяют использовать их в радиоэлектронике и электроприборах, а также вместо металлов. 6. Молекулы термопластов имеют извитую форму и, поэтому, они гибкие и легко растяжимы. 7. Эластомеры имеют большое число поперечных связей между молекулами.
9. Open the brackets:
The packaging industry 1) (to be) a leading user of plastics. High-density polyethene (HPDE) 2) (to use) for some thicker plastic films, such as those used for plastic waste bags and containers. Other packaging plastics 3) (to include) polypropene, polystyrene, polyvinyl chloride (PVC), and polyvinylidene chloride. Polyvinylidene chloride 4) (to use) primarily for its barrier properties, which can keep gases such as oxygen from passing into or out of a package. Similarly, polypropene 5) (to be) an effective barrier against water vapour and as a fibre for carpeting and rope.
The building industry 6) (to be) a major consumer of plastics, including many of the packaging plastics mentioned above. PVC also 7) (to use) in sheets for building materials and similar items. Many plastics 8) (to use) to insulate cables and wires, and polystyrene in the form of foam serves as insulation for walls, roofs, and other areas.
Many other industries, especially motor manufacturing, also 9) (to depend) on plastics. Tough engineering plastics 10) (to find) in vehicle components like fuel lines, fuel pumps, and electronic devices. Plastics are also used for interior panelling, seats, and trim. Many car bodies 11) (to make) of fibreglass-reinforced plastic.
10. Speaking. Tell your groupmates about:
1) inventor(s) of plastics;
2) about modern scientists working on improving properties of plastics.
11. You are going to read Text B. Study new vocabulary from the text:
| 1. adhesion | a. прилипание |
| 2. adhesive | b. клей |
| 3. bond | c. связь |
| 4. capacitor | d. эл. конденсатор |
| 5. casting | e. литье |
| 6. catalyst | f. катализатор |
| 7.coating | g. слой, покрытие |
| 8. durable | h. прочный |
| 9. envelope | i. зд. обрамление |
| 10. foam | j. пена |
| 11. granule | k. гранула |
| 12. impact | l. удар |
| 13. lattice | m. латекс |
| 14. modifier | n. модификатор |
| 15. paste | o. паста |
| 16. syringe | p. шприц |
| 17. void | q. пустота |
| 18. yield | r. выход |
12. Read the text “Types of plastics” and say what the following abbreviations stand for:
PVC; LDPE; HDPE
Text B. Types of plastics.
1. Epoxy resin.
Epoxy resin is a thermoset plastic containing epoxy groups. Epoxy resin hardens when it is mixed with solidifier and plasticizer. Plasticizers make a polymer more flexible.
Epoxy resins have outstanding adhesion, toughness, and resistance to attack from chemicals. They form strong bonds and have excellent electrical insulation properties. Large, complex, void-free castings can be made from them. They are also used as adhesives, and in composites for boat building and sports equipment.
2. PVC (polyvinyl chloride)
PVC (polyvinyl chloride) is a thermoplastic polymer made from vinyl chloride is a colourless solid with outstanding resistance to water, alcohols, and concentrated acids and alkalis. It is obtainable as granules, solutions, lattices, and pastes. When compounded with plasticizers, it yields a flexible material more durable than rubber. It is widely used for cable and wire insulation, in chemical plants, and in the manufacture of protective garments. Blow moulding of unplasticized PVC produces clear, tough bottles which do not affect the flavour of their contents. PVC is also used for production of tubes or pipes.
3. Polystyrene.
Polystyrene is a thermoplastic produced by the polymerization of styrene. The electrical insulating properties of polystyrene are outstandingly good and it is relatively unaffected by water. Typical applications include light fixtures, toys, bottles, lenses, capacitor dielectrics, medical syringes, and light-duty industrial components. Extruded sheets of polystyrene are widely used for packaging, envelope windows, and photographic film. Its resistance to impact can be improved by the addition of rubber modifiers. Polystyrene can be readily foamed; the resulting foamed polystyrene is used extensively for packaging.
4. Polythene (polyethene, polyethylene)
Polythene (polyethene, polyethylene) is a plastic made from ethane. It is one of the most widely used important thermoplastic polymers. It was first developed by the polymerization of ethane at a pressure of 2,000 bar at 200°C. This produced low-density polythene (LDPE). A relatively high-density form (HDPE) was synthesized in the 1950s using a complex catalyst. Polythene is a white waxy solid with very low density, reasonable strength and toughness, but low stiffness. It is easily moulded and has a wide range of uses in containers, packaging, pipes, coatings, and insulation.

Индивидуальные очистные сооружения: К классу индивидуальных очистных сооружений относят сооружения, пропускная способность которых...

Особенности сооружения опор в сложных условиях: Сооружение ВЛ в районах с суровыми климатическими и тяжелыми геологическими условиями...

Общие условия выбора системы дренажа: Система дренажа выбирается в зависимости от характера защищаемого...

Опора деревянной одностоечной и способы укрепление угловых опор: Опоры ВЛ - конструкции, предназначенные для поддерживания проводов на необходимой высоте над землей, водой...
© cyberpedia.su 2017-2024 - Не является автором материалов. Исключительное право сохранено за автором текста.
Если вы не хотите, чтобы данный материал был у нас на сайте, перейдите по ссылке: Нарушение авторских прав. Мы поможем в написании вашей работы!