1 Match each kind of law to its definition:
| 1. Substantive law
| a) body of law determining how a case is administered by the courts
|
| 2. Procedural law
| b) body of law governing relationships between states or nations
|
| 3. Constitutional law
| c) body of law related to the ownership of real estate, that is land and buildings on it
|
| 4. Public international law
| d) body of law governing the relations between persons engaged in business
|
| 5. Private international law
| e) common law and statute law used by the courts in making decisions
|
| 6. Family law
| f) body of law governing the relationship between employers and employees, including the right to organize in unions
|
| 7. Intellectual property law
| g) body of law dealing with disputes between private persons living in different jurisdictions
|
| 8. Commercial law
| h) body of law related to family relationships especially divorce, child custody and adoption
|
| 9. Land law
| i) body of law including legislation based on the fundamental law of the nation
|
| 10. Employment law
| j) body of law protecting legal rights of inventors, creators and authors
|
FOLLOW-UP I
Join parts of the sentences from the table and write them down.
Example: Judges (1) deal with cases in court (2).
| (1)
| (2)
|
| Judges
| people who break the law
|
| Police
| different legal documents
|
| Lawyers
| human rights
|
| Traffic wardens
| cases in court
|
| Notaries
| illegal parking
|
| Ombudsmen
| research into cases of crime
|
| Criminologists
| different legal problems
|
2. Look through the text and give Russian equivalents to the words in bold. Then look at the picture and answer the questions below:
In court, the defendants must try to prove that they did not commit the crime. In other words, they must try to prove that they are innocent, but not guilty. One can easily discern the chair person, presiding over the court procedure, who is a judge. He/she wears a wig and a black gown which is a traditional form of clothing for court trials. As a rule a judge holds a hammer in his hand. Twelve members of the public, called the jury, listen to the evidence and then make their decision. People who see a crime are witnesses, and they usually give evidence at a trial.
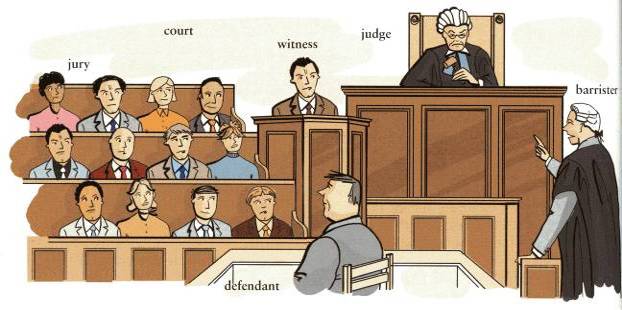
1) What can you see in the picture?
2) What is going on in the picture?
3) How many people are there in the picture?
4) Where are all these people?
5) Who decides if someone is innocent or guilty?
6) What is the number of jury? Count them.
7) Who commits crimes?
8) What is the defendant doing?
9) Who sentences people?
10) What is the judge doing?
11) What is he wearing?
12) What is he holding in his hand?
13) Who defends people and presents evidence?
14) What is the barrister doing?
15) What is he wearing?
16) Who is the barrister addressing to?
FOLLOW-UP II
Below is a list of things you can do to prevent a burglary. Write a story with the following word combinations (12 sentences).
· fit a burglar alarm
· get a safe
· take karate lessons
· put bars on the windows
· tell your neighbours you are going away
· insure your valuables
· buy a big dog
· get a bodyguard
· get a gun
· fit stronger locks
· change your address
· cancel the meeting
You may start in the following way:
Ø I would tell my neighbours that I was going away for some time and ask them to keep an eye on my house and notify the police if they notice anything strange.
Ø I would……
Ø I would never/wouldn’t……
Ø I would prefer……
Ø ……
Ø ……
GRAMMAR FOCUS: CONTINUOUS TENSES
Длительное действие, которое происходит (Present Continuous), происходило (Past Continuous), или будет происходить (Future Continuous) в точно указанный момент в прошлом, настоящем либо будущем. Все времена этой группы выражают действие в процессе его развития и переводятся глаголами несовершенного вида.
Времена группы Continuous.
Affirmative forms
Present
am is are
|
Ving
| |
Past
| was were
|
| Future
| Will
| Be
|
| Examples:
| Present Continuous
| We are sitting at the moment.
|
| Past Continuous
| W e were playing tennis when the rain started. He was doing test while I was reading a book.
|
| Future Continuous
| Tomorrow at six I' ll be writing letters.
|
| | | | |
Времена группы Continuous.
Interrogative forms
Present
am is are
| + S +Ving?
| |
Past
| was were
|
| Future
| Will
| Be
|
| Examples:
| Present Continuous
| What are you doing? Are you revising for your exams?
|
| Past Continuous
| Was he questioning the witness while you were out?
|
| Future Continuous
| Will you be studying the case when I come?
|
| | | | |
Времена группы Continuous.
Negative forms
Present
am not is not (isn’t) are not (aren’t)
| + S +Ving?
| |
Past
| was not (wasn’t) were not (weren’t)
|
| Future
| Will
| be not (won’t be)
|
| Examples:
| Present Continuous
| They are not working at the moment
|
| Past Continuous
| She wasn’t doing any research in the evening yesterday.
|
| Future Continuous
| I won’ be lecturing at this time tomorrow.
|
| | | | |
C временами группы Continuous обычно употребляются следующие указатели времени (ключевые слова):
1. Present Continuous – now, right/just now, at the moment, today, this week/month/season, these days, tonight/this evening.
2. Past Continuous – at that time, all day/night long, at six o’clock, the whole evening/morning/afternoon/night, from three to five.
3. Future Continuous – at this time tomorrow, next week/month/year, at 9 o’clock on Saturday.
Некоторые глаголы не употребляются во временах группы Continuous, так как не могут выражать действие или состояние как процесс. К ним относятся глаголы, выражающие чувства, умственную деятельность, физическое восприятие, глаголы обозначающие начало и окончание действия:
| To be
| быть
|
| To love
| любить
|
| To want
| хотеть
|
| To like/to dislike
| нравиться/не нравиться
|
| To hate
| ненавидеть
|
| To wish
| желать
|
| To desire
| желать
|
| To see
| видеть
|
| To hear
| слышать
|
| To feel
| чувствовать
|
| To understand
| понимать
|
| To know
| знать
|
| To believe
| верить
|
| To notice
| замечать
|
| To belong
| принадлежать
|
| To recognize
| узнавать
|
| To consist
| состоять
|






